|
Conjugate Vaccine
A conjugate vaccine is a type of subunit vaccine which combines a weak antigen with a strong antigen as a carrier so that the immune system has a stronger response to the weak antigen. Vaccines are used to prevent diseases by invoking an immune response to an antigen, part of a bacterium or virus that the immune system recognizes. This is usually accomplished with an attenuated or dead version of a pathogenic bacterium or virus in the vaccine, so that the immune system can recognize the antigen later in life. Most vaccines contain a single antigen that the body will recognize. However, the antigen of some pathogens does not elicit a strong response from the immune system, so a vaccination against this weak antigen would not protect the person later in life. In this case, a conjugate vaccine is used in order to invoke an immune system response against the weak antigen. In a conjugate vaccine, the weak antigen is covalently attached to a strong antigen, thereby eliciting a stronger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
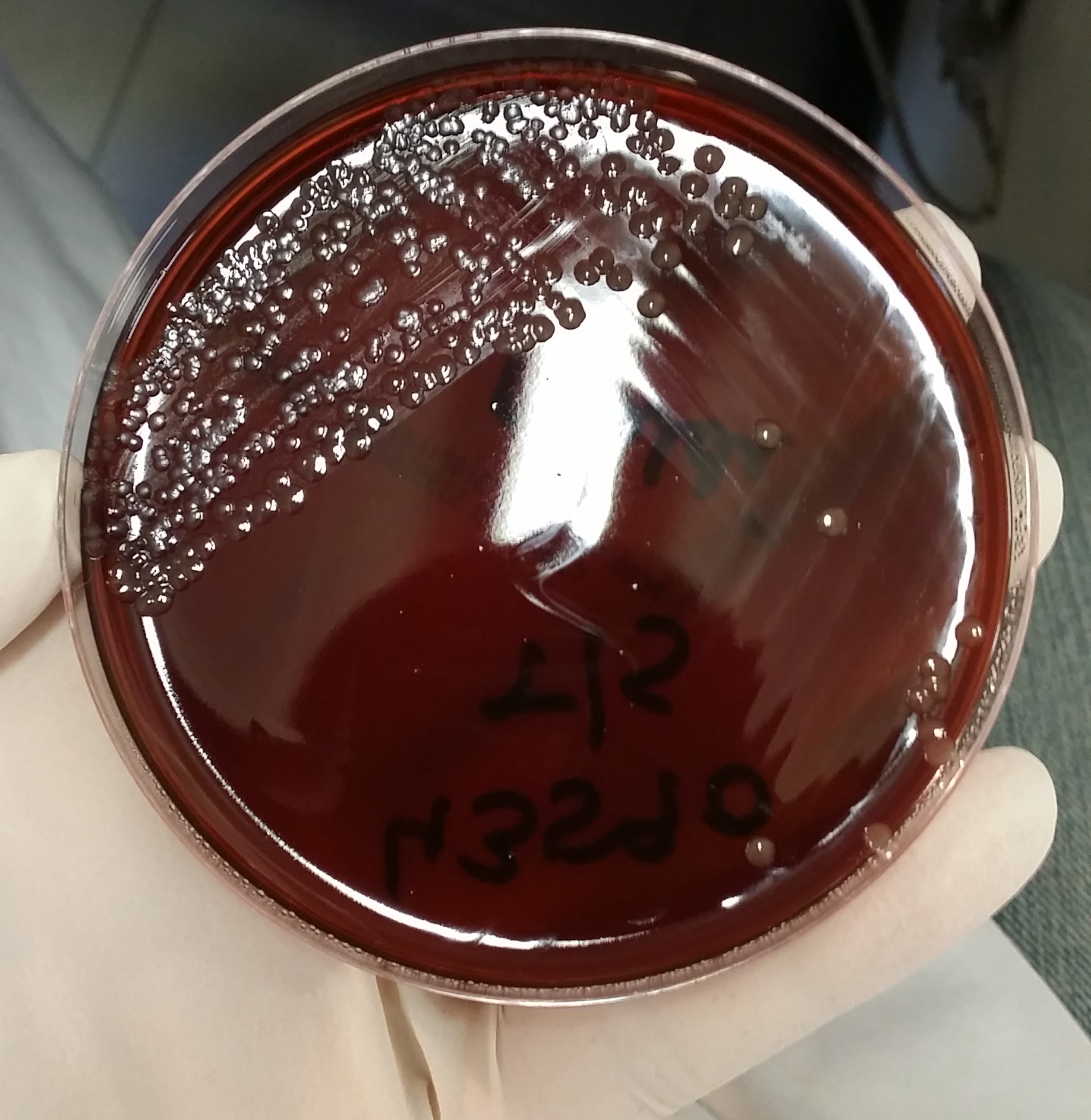
Haemophilus Influenzae 01
''Haemophilus'' is a genus of Gram-negative, pleomorphic, coccobacilli bacteria belonging to the family Pasteurellaceae. While ''Haemophilus'' bacteria are typically small coccobacilli, they are categorized as pleomorphic bacteria because of the wide range of shapes they occasionally assume. These organisms inhabit the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract, mouth, vagina, and intestinal tract. The genus includes commensal organisms along with some significant pathogenic species such as ''H. influenzae''—a cause of sepsis and bacterial meningitis in young children—and '' H. ducreyi'', the causative agent of chancroid. All members are either aerobic or facultatively anaerobic. This genus has been found to be part of the salivary microbiome. Metabolism Members of the genus ''Haemophilus'' will not grow on blood agar plates, as all species require at least one of these blood factors for growth: hemin (X-factor) and/or nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (V-facto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NicVAX
NicVAX is an experimental conjugate vaccine intended to reduce or eliminate physical dependence to nicotine. According to the U.S. National Institute of Drug Abuse, NicVAX can potentially be used to inoculate against nicotine addiction. This proprietary vaccine is being developed by Nabi Biopharmaceuticals of Rockville, MD. with the support from the U.S. National Institute on Drug Abuse. NicVAX consists of the hapten 3'-aminomethylnicotine which has been conjugated (attached) to ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' exotoxin A. Early trials of NicVax were promising; two successive phase III trials showed results no better than placebo,http://phx.corporate-ir.net/phoenix.zhtml?c=100445&p=irol-newsArticle&ID=1586001&highlight=http://phx.corporate-ir.net/phoenix.zhtml?c=100445&p=irol-newsArticle&ID=1626882&highlight= and a more recent study showed that the drug decreased subjects' cravings for cigarettes. Mechanism Nicotine is a small molecule that, after inhalation into the lungs, quickly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keyhole Limpet Hemocyanin
Keyhole limpet hemocyanin (KLH) is a large, multisubunit, oxygen-carrying, metalloprotein that is found in the hemolymph of the giant keyhole limpet, ''Megathura crenulata'', a species of keyhole limpet that lives off the coast of California, from Monterey Bay to Isla Asuncion off Baja California. Protein properties There are two keyhole limpet hemocyanin genes, termed KLH1 and KLH2 which share around 60% identity at the protein level. Both encode large glycosylated proteins consisting of around 3400 amino acids and a molecular weight of around 390,000 Daltons, excluding the glycosylation. The protein oligomerises to form a barrel shaped didecameric complex which is composed of 20 monomers. Each domain of a KLH subunit contains two copper atoms that together bind a single oxygen molecule (O2). When oxygen is bound to hemocyanin, the molecule takes on a distinctive transparent, opalescent blue color, due to the Cu2+ state of the copper. In the absence of oxygen, the bound copp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunocontraception
Immunocontraception is the use of an animal's immune system to prevent it from fertilizing offspring. Contraceptives of this type are not currently approved for human use. Typically immunocontraception involves the administration of a vaccine that induces an adaptive immune response which causes an animal to become temporarily infertile. Contraceptive vaccines have been used in numerous settings for the control of wildlife populations. However, experts in the field believe that major innovations are required before immunocontraception can become a practical form of contraception for human beings. Thus far immunocontraception has focused on mammals exclusively. There are several targets in mammalian sexual reproduction for immune inhibition. They can be organized into three categories. ;Gamete production: Organisms that undergo sexual reproduction must first produce gametes, cells which have half the typical number of chromosomes of the species. Often immunity that prevents gamet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
COVID-19 Vaccine
A COVID19 vaccine is a vaccine intended to provide acquired immunity against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2), the virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID19). Prior to the COVID19 pandemic, an established body of knowledge existed about the structure and function of coronaviruses causing diseases like severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS). This knowledge accelerated the development of various vaccine platforms during early 2020. The initial focus of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines was on preventing symptomatic, often severe illness. In January 2020, the SARS-CoV-2 genetic sequence data was shared through GISAID, and by March 2020, the global pharmaceutical industry announced a major commitment to address COVID19. In 2020, the first COVID19 vaccines were developed and made available to the public through emergency authorizations and conditional approvals. Initially, most COVID19 vaccines were t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soberana 02
Soberana 02 or Soberana 2, technical name FINLAY-FR-2, is a COVID-19 vaccine produced by the Finlay Institute, a Cuban epidemiological research institute. The vaccine is known as PastoCovac ( fa, پاستوکووک) in Iran, where it has been developed in collaboration with the Pasteur Institute of Iran. It is a conjugate vaccine that requires two doses, the second one being administered 28 days after the first shot. A third ( booster) dose of Soberana Plus may also be given on day 56. It has received emergency use authorization in Iran on June 2021, and in Cuba on August 2021, where it has also been approved for children above 2 years old. The name of the vaccine, Soberana, is a Spanish word that means "sovereign". It followed a previous candidate vaccine called SOBERANA-01 (FINLAY-FR-1). Medical uses The vaccine requires two doses, the second one being administered four weeks after the first shot. A third (boost) dose of Soberana Plus may also be given on eight weeks. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typhoid Fever
Typhoid fever, also known as typhoid, is a disease caused by '' Salmonella'' serotype Typhi bacteria. Symptoms vary from mild to severe, and usually begin six to 30 days after exposure. Often there is a gradual onset of a high fever over several days. This is commonly accompanied by weakness, abdominal pain, constipation, headaches, and mild vomiting. Some people develop a skin rash with rose colored spots. In severe cases, people may experience confusion. Without treatment, symptoms may last weeks or months. Diarrhea may be severe, but is uncommon. Other people may carry the bacterium without being affected, but they are still able to spread the disease. Typhoid fever is a type of enteric fever, along with paratyphoid fever. ''S. enterica'' Typhi is believed to infect and replicate only within humans. Typhoid is caused by the bacterium ''Salmonella enterica'' subsp. ''enterica'' serovar Typhi growing in the intestines, peyers patches, mesenteric lymph nodes, spleen, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typhoid Vaccine
Typhoid vaccines are vaccines that prevent typhoid fever. Several types are widely available: typhoid conjugate vaccine (TCV), Ty21a (a live oral vaccine) and Vi capsular polysaccharide vaccine (ViPS) (an injectable subunit vaccine). They are about 30 to 70% effective in the first two years, depending on the specific vaccine in question. The Vi-rEPA vaccine has been shown to be efficacious in children. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends vaccinating all children in areas where the disease is common. Otherwise they recommend vaccinating those at high risk. Vaccination campaigns can also be used to control outbreaks of disease. Depending on the vaccine, additional doses are recommended every three to seven years. In the United States the vaccine is only recommended in those at high risk such as travelers to areas of the world where the disease is common. The vaccines available as of 2018 are very safe. Minor side effects may occur at the site of injection. The injecta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of health". Headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, it has six regional offices and 150 field offices worldwide. The WHO was established on 7 April 1948. The first meeting of the World Health Assembly (WHA), the agency's governing body, took place on 24 July of that year. The WHO incorporated the assets, personnel, and duties of the League of Nations' Health Organization and the , including the International Classification of Diseases (ICD). Its work began in earnest in 1951 after a significant infusion of financial and technical resources. The WHO's mandate seeks and includes: working worldwide to promote health, keeping the world safe, and serve the vulnerable. It advocates that a billion more people should have: universal health care ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meningococcal Vaccine
Meningococcal vaccine refers to any vaccine used to prevent infection by ''Neisseria meningitidis''. Different versions are effective against some or all of the following types of meningococcus: A, B, C, W-135, and Y. The vaccines are between 85 and 100% effective for at least two years. They result in a decrease in meningitis and sepsis among populations where they are widely used. They are given either by injection into a muscle or just under the skin. The World Health Organization recommends that countries with a moderate or high rate of disease or with frequent outbreaks should routinely vaccinate. In countries with a low risk of disease, they recommend that high risk groups should be immunized. In the African meningitis belt efforts to immunize all people between the ages of one and thirty with the meningococcal A conjugate vaccine are ongoing. In Canada and the United States the vaccines effective against four types of meningococcus (A, C, W, and Y) are recommended rout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neisseria Meningitidis
''Neisseria meningitidis'', often referred to as meningococcus, is a Gram-negative bacterium that can cause meningitis and other forms of meningococcal disease such as meningococcemia, a life-threatening sepsis. The bacterium is referred to as a coccus because it is round, and more specifically a diplococcus because of its tendency to form pairs. About 10% of adults are carriers of the bacteria in their nasopharynx. As an exclusively human pathogen, it is the main cause of bacterial meningitis in children and young adults, causing developmental impairment and death in about 10% of cases. It causes the only form of bacterial meningitis known to occur epidemically, mainly in Africa and Asia. It occurs worldwide in both epidemic and endemic form. ''N. meningitidis'' is spread through saliva and respiratory secretions during coughing, sneezing, kissing, chewing on toys and through sharing a source of fresh water. It has also been reported to be transmitted through oral sex and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)



.jpg)