|
Conical Intersection
In quantum chemistry, a conical intersection of two or more potential energy surfaces is the set of molecular geometry points where the potential energy surfaces are degenerate (intersect) and the non-adiabatic couplings between these states are non-vanishing. In the vicinity of conical intersections, the Born–Oppenheimer approximation breaks down and the coupling between electronic and nuclear motion becomes important, allowing non-adiabatic processes to take place. The location and characterization of conical intersections are therefore essential to the understanding of a wide range of important phenomena governed by non-adiabatic events, such as photoisomerization, photosynthesis, vision and the photostability of DNA. Conical intersections are also called molecular funnels or diabolic points as they have become an established paradigm for understanding reaction mechanisms in photochemistry as important as transitions states in thermal chemistry. This comes from the very impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diatomic Molecule
Diatomic molecules () are molecules composed of only two atoms, of the same or different chemical elements. If a diatomic molecule consists of two atoms of the same element, such as hydrogen () or oxygen (), then it is said to be homonuclear molecule, homonuclear. Otherwise, if a diatomic molecule consists of two different atoms, such as carbon monoxide () or nitric oxide (), the molecule is said to be heteronuclear molecule, heteronuclear. The bond in a homonuclear diatomic molecule is non-polar. The only chemical elements that form stable homonuclear diatomic molecules at standard temperature and pressure (STP) (or at typical laboratory conditions of 1 bar (pressure), bar and 25 °C) are the gases hydrogen (), nitrogen (), oxygen (), fluorine (), and chlorine (), and the liquid bromine (). The noble gases (helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon) are also gases at STP, but they are monatomic. The homonuclear diatomic gases and noble gases together are called "ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avoided Crossing
In quantum physics and quantum chemistry, an avoided crossing (AC, sometimes called intended crossing, non-crossing or anticrossing) is the phenomenon where two eigenvalues of a Hermitian matrix representing a quantum observable and depending on k continuous real parameters cannot become equal in value ("cross") except on a manifold of dimension k-2 . The phenomenon is also known as the von Neumann–Wigner theorem. In the case of a diatomic molecule (with one parameter, namely the bond length), this means that the eigenvalues cannot cross at all. In the case of a triatomic molecule, this means that the eigenvalues can coincide only at a single point (see conical intersection). This is particularly important in quantum chemistry. In the Born–Oppenheimer approximation, the electronic molecular Hamiltonian is diagonalized on a set of distinct molecular geometries (the obtained eigenvalues are the values of the adiabatic potential energy surfaces). The geometries for which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diabatic Representation
The diabatic representation as a mathematical tool for theoretical calculations of atomic collisions and of molecular interactions. One of the guiding principles in modern chemical dynamics and spectroscopy is that the motion of the nuclei in a molecule is slow compared to that of its electrons. This is justified by the large disparity between the mass of an electron, and the typical mass of a nucleus and leads to the Born–Oppenheimer approximation and the idea that the structure and dynamics of a chemical species are largely determined by nuclear motion on potential energy surfaces. The potential energy surfaces are obtained within the adiabatic or Born–Oppenheimer approximation. This corresponds to a representation of the molecular wave function where the variables corresponding to the molecular geometry and the electronic degrees of freedom are separated. The non separable terms are due to the nuclear kinetic energy terms in the molecular Hamiltonian and are said to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christopher Longuet-Higgins
Hugh Christopher Longuet-Higgins (11 April 1923 – 27 March 2004) was a British theoretical chemist and cognitive scientist. He was the Professor of Theoretical Chemistry at the University of Cambridge for 13 years until 1967 when he moved to the University of Edinburgh to work in the developing field of cognitive science. He made many significant contributions to our understanding of molecular science. He was also a gifted amateur musician, both as performer and composer, and was keen to advance the scientific understanding of this art. He was the founding editor of the journal ''Molecular Physics''. Education and early life Longuet-Higgins was born on 11 April 1923 at The Vicarage, Lenham, Kent, England, the elder son and second of the three children of Henry Hugh Longuet-Higgins (1886–1966), vicar of Lenham, and his wife, Albinia Cecil Bazeley. He was educated at The Pilgrims' School, Winchester, and Winchester College. At Winchester College he was one of the "gang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
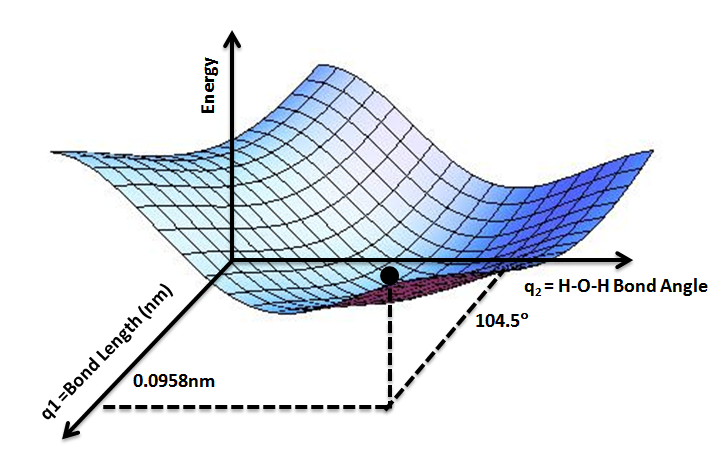
Potential Energy Surface
A potential energy surface (PES) or energy landscape describes the energy of a Physical system, system, especially a collection of atoms, in terms of certain Parameter, parameters, normally the positions of the atoms. The Surface (mathematics), surface might define the energy as a Function (mathematics), function of one or more coordinates; if there is only one coordinate, the surface is called a ''potential energy curve'' or energy profile. An example is the Morse/Long-range potential. It is helpful to use the analogy of a landscape: for a system with two Degrees of freedom (physics and chemistry), degrees of freedom (e.g. two bond lengths), the value of the energy (analogy: the height of the land) is a function of two bond lengths (analogy: the coordinates of the position on the ground). The PES concept finds application in fields such as physics, chemistry and biochemistry, especially in the theoretical sub-branches of these subjects. It can be used to theoretically explore p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jahn–Teller Effect
The Jahn–Teller effect (JT effect or JTE) is an important mechanism of spontaneous symmetry breaking in molecular and solid-state systems which has far-reaching consequences in different fields, and is responsible for a variety of phenomena in spectroscopy, stereochemistry, crystal chemistry, molecular and solid-state physics, and materials science. The effect is named for Hermann Arthur Jahn and Edward Teller, who first reported studies about it in 1937. Simplified overview The Jahn–Teller effect, sometimes also referred to as Jahn–Teller distortion, describes the geometrical distortion of molecules and ions that results from certain electron configurations. The Jahn–Teller theorem essentially states that any non-linear molecule with a spatially degenerate energy level, degenerate electronic ground state will undergo a geometrical distortion that removes that degeneracy, because the distortion lowers the overall energy of the species. For a description of another type of geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Shell
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is , meaning that the 1s, 2s, and 2p subshells are occupied by two, two, and six electrons, respectively. Electronic configurations describe each electron as moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by the nuclei and all the other electrons. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions. According to the laws of quantum mechanics, a level of energy is associated with each electron configuration. In certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon. Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
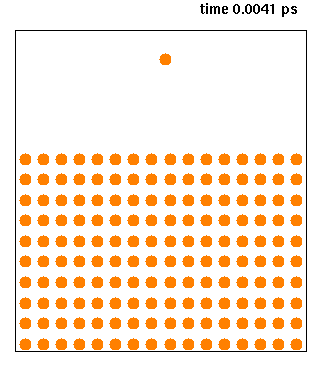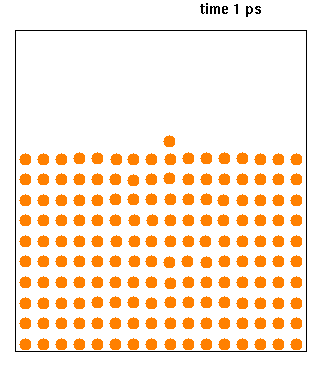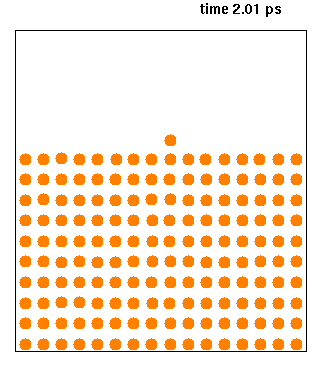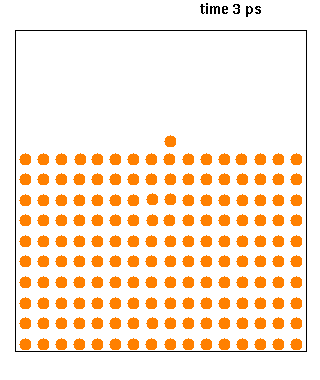
Molecular Dynamics
Molecular dynamics (MD) is a computer simulation method for analyzing the Motion (physics), physical movements of atoms and molecules. The atoms and molecules are allowed to interact for a fixed period of time, giving a view of the dynamics (mechanics), dynamic "evolution" of the system. In the most common version, the trajectory, trajectories of atoms and molecules are determined by Numerical integration, numerically solving Newton's laws of motion, Newton's equations of motion for a system of interacting particles, where Force (physics), forces between the particles and their potential energy, potential energies are often calculated using interatomic potentials or molecular mechanics, molecular mechanical Force field (chemistry), force fields. The method is applied mostly in chemical physics, materials science, and biophysics. Because molecular systems typically consist of a vast number of particles, it is impossible to determine the properties of such complex systems analyt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthogonal Complement
In the mathematical fields of linear algebra and functional analysis, the orthogonal complement of a subspace W of a vector space V equipped with a bilinear form B is the set W^\perp of all vectors in V that are orthogonal to every vector in W. Informally, it is called the perp, short for perpendicular complement. It is a subspace of V. Example Let V = (\R^5, \langle \cdot, \cdot \rangle) be the vector space equipped with the usual dot product \langle \cdot, \cdot \rangle (thus making it an inner product space), and let W = \, with \mathbf = \begin 1 & 0\\ 0 & 1\\ 2 & 6\\ 3 & 9\\ 5 & 3\\ \end. then its orthogonal complement W^\perp = \ can also be defined as W^\perp = \, being \mathbf = \begin -2 & -3 & -5 \\ -6 & -9 & -3 \\ 1 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end. The fact that every column vector in \mathbf is orthogonal to every column vector in \mathbf can be checked by direct computation. The fact that the spans of these vectors are orthogonal then follows by bilinearity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotation (mathematics)
Rotation in mathematics is a concept originating in geometry. Any rotation is a motion of a certain space that preserves at least one point. It can describe, for example, the motion of a rigid body around a fixed point. Rotation can have a sign (as in the sign of an angle): a clockwise rotation is a negative magnitude so a counterclockwise turn has a positive magnitude. A rotation is different from other types of motions: translations, which have no fixed points, and (hyperplane) reflections, each of them having an entire -dimensional flat of fixed points in a - dimensional space. Mathematically, a rotation is a map. All rotations about a fixed point form a group under composition called the rotation group (of a particular space). But in mechanics and, more generally, in physics, this concept is frequently understood as a coordinate transformation (importantly, a transformation of an orthonormal basis), because for any motion of a body there is an inverse transformat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spin–orbit Interaction
In quantum mechanics, the spin–orbit interaction (also called spin–orbit effect or spin–orbit coupling) is a relativistic interaction of a particle's spin with its motion inside a potential. A key example of this phenomenon is the spin–orbit interaction leading to shifts in an electron's atomic energy levels, due to electromagnetic interaction between the electron's magnetic dipole, its orbital motion, and the electrostatic field of the positively charged nucleus. This phenomenon is detectable as a splitting of spectral lines, which can be thought of as a Zeeman effect product of two effects: the apparent magnetic field seen from the electron perspective due to special relativity and the magnetic moment of the electron associated with its intrinsic spin due to quantum mechanics. For atoms, energy level splitting produced by the spin–orbit interaction is usually of the same order in size as the relativistic corrections to the kinetic energy and the zitterbewegung ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |