|
Conestoga Town
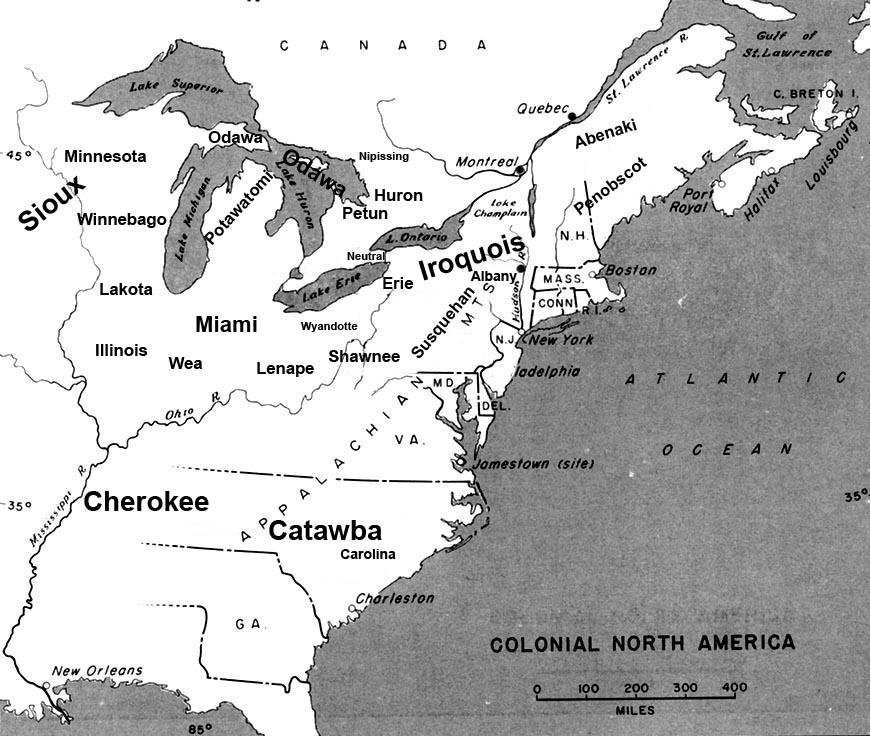
Conestoga Town is an historic archaeological site memorializing the Native American tribal village which stood on the site from the late 17th into the mid-18th-century; it is located at what is now Manor Township in Lancaster County, Pennsylvania. The town is a settlement at the southern end of the once vast range of the Susquehannock nation or Conestoga Indian nation, which once extended from the northern reaches of Maryland to the along the southern width of southern New York State and southern Catskills where a related people, the Five Nations of the Iroquois Confederacy held western settlement in check for 200 years. Their territory encompassed the entire drainage basin of the Susquehanna River which shares the tribe's root name and extended to the drainage divides of the flanking mountains both to the East to the Delaware nation and to the West to Shawnee lands. The town is the earliest established known surviving settlement of the tribe, and it is known that William Penn hims ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manor Township, Lancaster County, Pennsylvania
Manor Township is a second-class township in west-central Lancaster County, Pennsylvania, United States. As of the 2020 census it had a population of 21,920. History to 1763 Manor Township takes its name from the Manor of Conestoga, which was originally surveyed and reserved for William Penn in 1719, although there is evidence that William Penn visited this area prior to 1690. At this time, the area was Susquehannock territory, and the Susquehannock tribe themselves were the largest tribe in the Susquehanna Valley and had their center of the community within the Turkey Hill part of this territory. The Quaker government thus had surveyors lay off a large area bounded by the Little Conestoga Creek near what is now Millersville to the Susquehanna River and the Conestoga Creek. When the land was ceded by William Penn to their ancestors in the 1690s, the Susquehannock tribe had lived on the land for quite some time. Their ancestors were Conestoga Native Americans, many of whom w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Penn
William Penn ( – ) was an English writer and religious thinker belonging to the Religious Society of Friends (Quakers), and founder of the Province of Pennsylvania, a North American colony of England. He was an early advocate of democracy and religious freedom, notable for his good relations and successful treaties with the Lenape Native Americans. In 1681, King Charles II handed over a large piece of his North American land holdings along the North Atlantic Ocean coast to Penn to pay the debts the king had owed to Penn's father, the admiral and politician Sir William Penn. This land included the present-day states of Pennsylvania and Delaware. Penn immediately set sail and took his first step on American soil, sailing up the Delaware Bay and Delaware River, past earlier Swedish and Dutch riverfront colonies, in New Castle (now in Delaware) in 1682. On this occasion, the colonists pledged allegiance to Penn as their new proprietor, and the first Pennsylvania General A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites In Lancaster County, Pennsylvania
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the advent of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites On The National Register Of Historic Places In Pennsylvania
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, archaeological site, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conestoga, Pennsylvania
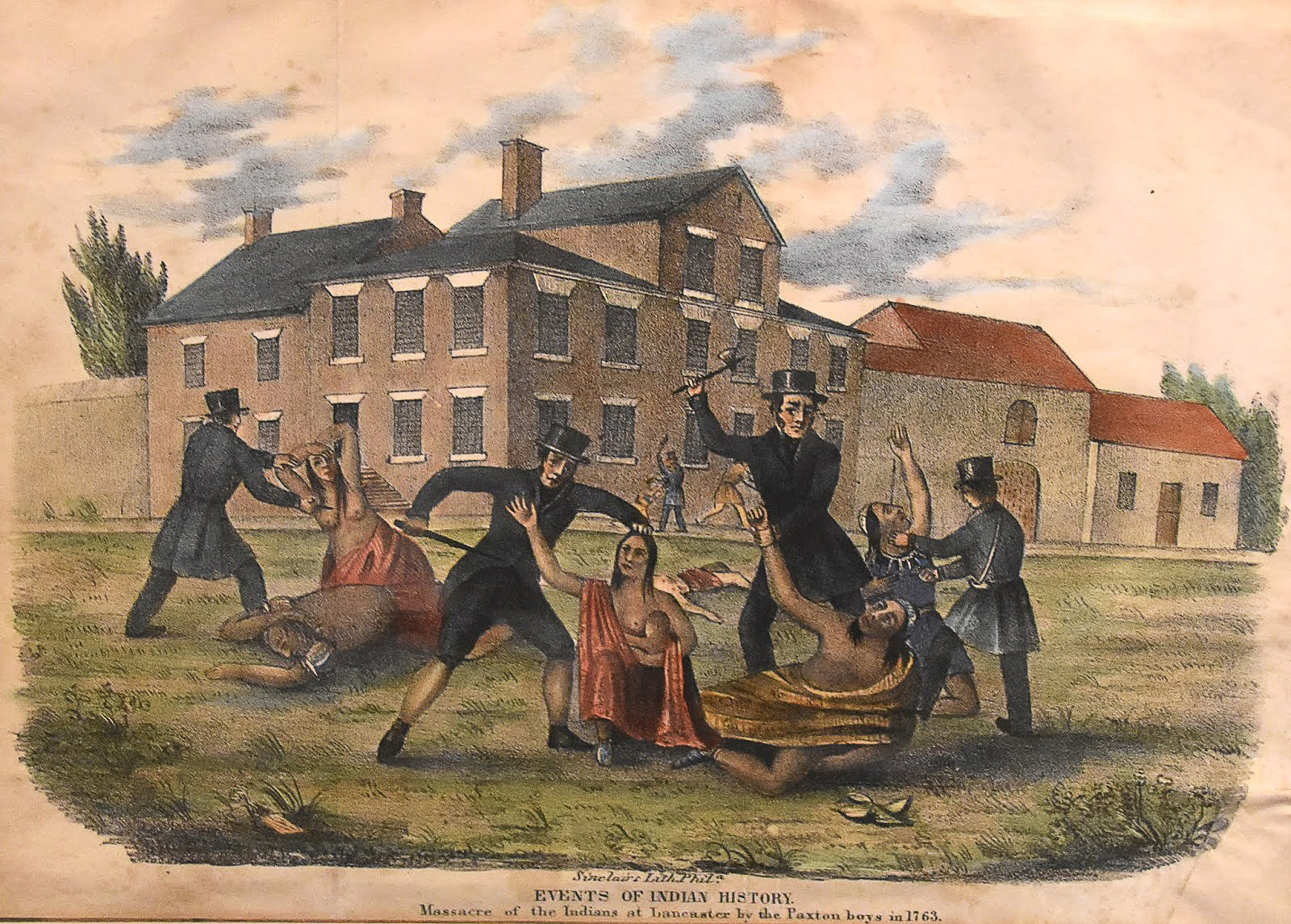
Conestoga is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Conestoga Township, Lancaster County, Pennsylvania, in the United States. At the 2010 census the population was 1,258. The Conestoga post office serves ZIP code 17516. History Conestoga was first called "Conestoga Manor" by William Penn, founder of Pennsylvania.Conestoga, PA The name was derived from the Conestoga () people, a peaceful tribe that adopted . Their principal village in the area was located nearby. In 1763 some 20 Conestoga were massacred by the |
National Register Of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance or "great artistic value". A property listed in the National Register, or located within a National Register Historic District, may qualify for tax incentives derived from the total value of expenses incurred in preserving the property. The passage of the National Historic Preservation Act (NHPA) in 1966 established the National Register and the process for adding properties to it. Of the more than one and a half million properties on the National Register, 95,000 are listed individually. The remainder are contributing resources within historic districts. For most of its history, the National Register has been administered by the National Park Service (NPS), an agency within the U.S. Department of the Interior. Its goals are to help property owners and inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paxton Boys
The Paxton Boys were Pennsylvania's most aggressive colonists according to historian Kevin Kenny. While not many specifics are known about the individuals in the group their overall profile is clear. Paxton Boys Lived in hill country northwest of Lancaster County and across the Susquehanna River in Cumberland County. Due to their westward position, they were considered the frontier at the time and consistently targeted during Indian wars and conflicts. Due to the lack of support from the local Provincial Government, The Paxton boys formed a vigilante group in 1763 to defend themselves during the French and Indian War and Pontiac's War. Using their Presbyterianism faith, Paxton Boy's leadership declared that Native Americans were “Cainites”(A biblical representation of evil) and believed that they needed to be destroyed. The Paxton Boys did not limit their hate to Native Tribes but also “Whites, Quakers, and German Moravians, when they believed that these groups too jeopardize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conestoga River
The Conestoga River, also referred to as Conestoga Creek, is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed August 8, 2011 tributary of the Susquehanna River flowing through the center of Lancaster County, Pennsylvania, United States. Geography Its headwaters rise mostly in southern Berks County and northeastern Lancaster County, in an area known as "Bortz's Swamp" or "Penngall Field" (a small area rises in Chester County). The East Branch and West Branch of the Conestoga join to form the main river just north of Morgantown, and the stream flows from northeast to southwest for more than , passing close to the center of Lancaster and ending at Safe Harbor along the Susquehanna River, approximately north of the Pennsylvania-Maryland state line. The principal tributaries of the Conestoga River are Cocalico Creek, Mill Creek, and Little Conestoga Creek; they drain into the Conestoga River watershed in the order ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Susquehannock
The Susquehannock people, also called the Conestoga by some English settlers or Andastes were Iroquoian Native Americans who lived in areas adjacent to the Susquehanna River and its tributaries, ranging from its upper reaches in the southern part of what is now New York (near the lands of the Five Nations of the Iroquois Confederacy), through eastern and central Pennsylvania west of the Poconos and the upper Delaware River (near the lands of the Lenape), with lands extending beyond the mouth of the Susquehanna in Maryland along the west bank of the Potomac at the north end of the Chesapeake Bay. Evidence of their habitation has also been found in northern West Virginia and portions of southwestern Pennsylvania, which could be reached via the gaps of the Allegheny or several counties to the south, via the Cumberland Narrows pass which held the Nemacolin Trail. Both passes abutted their range and could be reached through connecting valleys from the West Branch Susquehanna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Site
An archaeological site is a place (or group of physical sites) in which evidence of past activity is preserved (either prehistoric or historic or contemporary), and which has been, or may be, investigated using the discipline of archaeology and represents a part of the archaeological record. Sites may range from those with few or no remains visible above ground, to buildings and other structures still in use. Beyond this, the definition and geographical extent of a "site" can vary widely, depending on the period studied and the theoretical approach of the archaeologist. Geographical extent It is almost invariably difficult to delimit a site. It is sometimes taken to indicate a settlement of some sort although the archaeologist must also define the limits of human activity around the settlement. Any episode of deposition such as a hoard or burial can form a site as well. Development-led archaeology undertaken as cultural resources management has the disadvantage (or the ben ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drainage Divide
A drainage divide, water divide, ridgeline, watershed, water parting or height of land is elevated terrain that separates neighboring drainage basins. On rugged land, the divide lies along topographical ridges, and may be in the form of a single range of hills or mountains, known as a dividing range. On flat terrain, especially where the ground is marshy, the divide may be difficult to discern. A triple divide is a point, often a summit, where three drainage basins meet. A ''valley floor divide'' is a low drainage divide that runs across a valley, sometimes created by deposition or stream capture. Major divides separating rivers that drain to different seas or oceans are continental divides. The term ''height of land'' is used in Canada and the United States to refer to a drainage divide. It is frequently used in border descriptions, which are set according to the "doctrine of natural boundaries". In glaciated areas it often refers to a low point on a divide where it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Susquehanna River
The Susquehanna River (; Lenape: Siskëwahane) is a major river located in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, overlapping between the lower Northeast and the Upland South. At long, it is the longest river on the East Coast of the United States. By watershed area, it is the 16th-largest river in the United States,Susquehanna River Trail Pennsylvania Fish and Boat Commission, accessed March 25, 2010.Susquehanna River , Green Works Radio, accessed March 25, 2010. and also the longest river in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)