|
Conditional Entropy
In information theory, the conditional entropy quantifies the amount of information needed to describe the outcome of a random variable Y given that the value of another random variable X is known. Here, information is measured in shannons, nats, or hartleys. The ''entropy of Y conditioned on X'' is written as \Eta(Y, X). Definition The conditional entropy of Y given X is defined as where \mathcal X and \mathcal Y denote the support sets of X and Y. ''Note:'' Here, the convention is that the expression 0 \log 0 should be treated as being equal to zero. This is because \lim_ \theta\, \log \theta = 0. Intuitively, notice that by definition of expected value and of conditional probability, \displaystyle H(Y, X) can be written as H(Y, X) = \mathbb (X,Y)/math>, where f is defined as \displaystyle f(x,y) := -\log\Big(\frac\Big) = -\log(p(y, x)). One can think of \displaystyle f as associating each pair \displaystyle (x, y) with a quantity measuring the information conten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chain Rule (probability)
In probability theory, the chain rule (also called the general product rule) permits the calculation of any member of the joint distribution of a set of random variables using only conditional probabilities. The rule is useful in the study of Bayesian networks, which describe a probability distribution in terms of conditional probabilities. Chain rule for events Two events The chain rule for two random events Event may refer to: Gatherings of people * Ceremony, an event of ritual significance, performed on a special occasion * Convention (meeting), a gathering of individuals engaged in some common interest * Event management, the organization of ev ... A and B says P(A \cap B) = P(B \mid A) \cdot P(A). Example This rule is illustrated in the following example. Urn 1 has 1 black ball and 2 white balls and Urn 2 has 1 black ball and 3 white balls. Suppose we pick an urn at random and then select a ball from that urn. Let event A be choosing the first urn: P(A) = P(\overline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conditional Quantum Entropy
The conditional quantum entropy is an entropy measure used in quantum information theory. It is a generalization of the conditional entropy of classical information theory. For a bipartite state \rho^, the conditional entropy is written S(A, B)_\rho, or H(A, B)_\rho, depending on the notation being used for the von Neumann entropy. The quantum conditional entropy was defined in terms of a conditional density operator \rho_ by Nicolas Cerf and Chris Adami, who showed that quantum conditional entropies can be negative, something that is forbidden in classical physics. The negativity of quantum conditional entropy is a sufficient criterion for quantum non-separability. In what follows, we use the notation S(\cdot) for the von Neumann entropy, which will simply be called "entropy". Definition Given a bipartite quantum state \rho^, the entropy of the joint system AB is S(AB)_\rho \ \stackrel\ S(\rho^), and the entropies of the subsystems are S(A)_\rho \ \stackrel\ S(\rho^A) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutual Information
In probability theory and information theory, the mutual information (MI) of two random variables is a measure of the mutual dependence between the two variables. More specifically, it quantifies the " amount of information" (in units such as shannons (bits), nats or hartleys) obtained about one random variable by observing the other random variable. The concept of mutual information is intimately linked to that of entropy of a random variable, a fundamental notion in information theory that quantifies the expected "amount of information" held in a random variable. Not limited to real-valued random variables and linear dependence like the correlation coefficient, MI is more general and determines how different the joint distribution of the pair (X,Y) is from the product of the marginal distributions of X and Y. MI is the expected value of the pointwise mutual information (PMI). The quantity was defined and analyzed by Claude Shannon in his landmark paper " A Mathematic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entropy (information Theory)
In information theory, the entropy of a random variable is the average level of "information", "surprise", or "uncertainty" inherent to the variable's possible outcomes. Given a discrete random variable X, which takes values in the alphabet \mathcal and is distributed according to p: \mathcal\to , 1/math>: \Eta(X) := -\sum_ p(x) \log p(x) = \mathbb \log p(X), where \Sigma denotes the sum over the variable's possible values. The choice of base for \log, the logarithm, varies for different applications. Base 2 gives the unit of bits (or " shannons"), while base ''e'' gives "natural units" nat, and base 10 gives units of "dits", "bans", or " hartleys". An equivalent definition of entropy is the expected value of the self-information of a variable. The concept of information entropy was introduced by Claude Shannon in his 1948 paper "A Mathematical Theory of Communication",PDF archived froherePDF archived frohere and is also referred to as Shannon entropy. Shannon's theory def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conditional Quantum Entropy
The conditional quantum entropy is an entropy measure used in quantum information theory. It is a generalization of the conditional entropy of classical information theory. For a bipartite state \rho^, the conditional entropy is written S(A, B)_\rho, or H(A, B)_\rho, depending on the notation being used for the von Neumann entropy. The quantum conditional entropy was defined in terms of a conditional density operator \rho_ by Nicolas Cerf and Chris Adami, who showed that quantum conditional entropies can be negative, something that is forbidden in classical physics. The negativity of quantum conditional entropy is a sufficient criterion for quantum non-separability. In what follows, we use the notation S(\cdot) for the von Neumann entropy, which will simply be called "entropy". Definition Given a bipartite quantum state \rho^, the entropy of the joint system AB is S(AB)_\rho \ \stackrel\ S(\rho^), and the entropies of the subsystems are S(A)_\rho \ \stackrel\ S(\rho^A) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Information Theory
Quantum information is the information of the state of a quantum system. It is the basic entity of study in quantum information theory, and can be manipulated using quantum information processing techniques. Quantum information refers to both the technical definition in terms of Von Neumann entropy and the general computational term. It is an interdisciplinary field that involves quantum mechanics, computer science, information theory, philosophy and cryptography among other fields. Its study is also relevant to disciplines such as cognitive science, psychology and neuroscience. Its main focus is in extracting information from matter at the microscopic scale. Observation in science is one of the most important ways of acquiring information and measurement is required in order to quantify the observation, making this crucial to the scientific method. In quantum mechanics, due to the uncertainty principle, non-commuting Observable, observables cannot be precisely measured simu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Mechanics
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science. Classical physics, the collection of theories that existed before the advent of quantum mechanics, describes many aspects of nature at an ordinary ( macroscopic) scale, but is not sufficient for describing them at small (atomic and subatomic) scales. Most theories in classical physics can be derived from quantum mechanics as an approximation valid at large (macroscopic) scale. Quantum mechanics differs from classical physics in that energy, momentum, angular momentum, and other quantities of a bound system are restricted to discrete values ( quantization); objects have characteristics of both particles and waves (wave–particle duality); and there are limit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uncertainty Principle
In quantum mechanics, the uncertainty principle (also known as Heisenberg's uncertainty principle) is any of a variety of mathematical inequalities asserting a fundamental limit to the accuracy with which the values for certain pairs of physical quantities of a particle, such as position, ''x'', and momentum, ''p'', can be predicted from initial conditions. Such variable pairs are known as complementary variables or canonically conjugate variables; and, depending on interpretation, the uncertainty principle limits to what extent such conjugate properties maintain their approximate meaning, as the mathematical framework of quantum physics does not support the notion of simultaneously well-defined conjugate properties expressed by a single value. The uncertainty principle implies that it is in general not possible to predict the value of a quantity with arbitrary certainty, even if all initial conditions are specified. Introduced first in 1927 by the German physicist Wern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estimator
In statistics, an estimator is a rule for calculating an estimate of a given quantity based on observed data: thus the rule (the estimator), the quantity of interest (the estimand) and its result (the estimate) are distinguished. For example, the sample mean is a commonly used estimator of the population mean. There are point and interval estimators. The point estimators yield single-valued results. This is in contrast to an interval estimator, where the result would be a range of plausible values. "Single value" does not necessarily mean "single number", but includes vector valued or function valued estimators. ''Estimation theory'' is concerned with the properties of estimators; that is, with defining properties that can be used to compare different estimators (different rules for creating estimates) for the same quantity, based on the same data. Such properties can be used to determine the best rules to use under given circumstances. However, in robust statistics, statistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joint Probability Density Function
In probability theory, a probability density function (PDF), or density of a continuous random variable, is a function whose value at any given sample (or point) in the sample space (the set of possible values taken by the random variable) can be interpreted as providing a ''relative likelihood'' that the value of the random variable would be close to that sample. Probability density is the probability per unit length, in other words, while the ''absolute likelihood'' for a continuous random variable to take on any particular value is 0 (since there is an infinite set of possible values to begin with), the value of the PDF at two different samples can be used to infer, in any particular draw of the random variable, how much more likely it is that the random variable would be close to one sample compared to the other sample. In a more precise sense, the PDF is used to specify the probability of the random variable falling ''within a particular range of values'', as opposed t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Random Variate
In probability and statistics, a random variate or simply variate is a particular outcome of a ''random variable'': the random variates which are other outcomes of the same random variable might have different values ( random numbers). A random deviate or simply deviate is the difference of random variate with respect to the distribution central location (e.g., mean), often divided by the standard deviation of the distribution (i.e., as a standard score). Random variates are used when simulating processes driven by random influences ( stochastic processes). In modern applications, such simulations would derive random variates corresponding to any given probability distribution from computer procedures designed to create random variates corresponding to a uniform distribution, where these procedures would actually provide values chosen from a uniform distribution of pseudorandom numbers. Procedures to generate random variates corresponding to a given distribution are known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
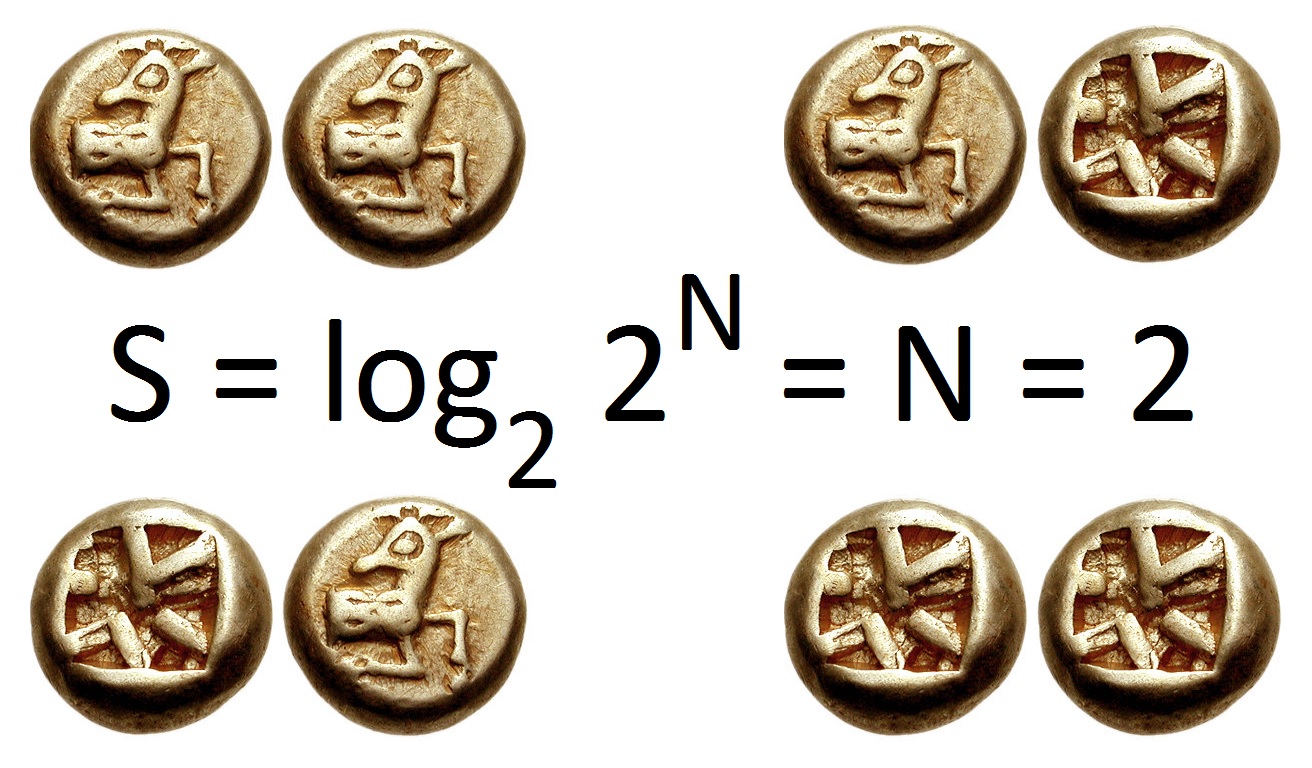
.jpg)


