|
Concurrent ML
Concurrent ML (CML) is a concurrent extension of the Standard ML programming language characterized by its ability to allow programmers to create composable communication abstractions that are first-class rather than built into the language. The design of CML and its primitive operations have been adopted in several other programming languages such as GNU Guile, Racket, and Manticore. Concepts Many programming languages that support concurrency offer communication channels that allow the exchange of values between processes or threads running concurrently in a system. Communications established between processes may follow a specific protocol, requiring the programmer to write functions to establish the required pattern of communication. Meanwhile, a communicating system often requires establishing multiple channels, such as to multiple servers, and then choosing between the available channels when new data is available. This can be accomplished using polling, such as wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concurrent Computing
Concurrent computing is a form of computing in which several computations are executed '' concurrently''—during overlapping time periods—instead of ''sequentially—''with one completing before the next starts. This is a property of a system—whether a program, computer, or a network—where there is a separate execution point or "thread of control" for each process. A ''concurrent system'' is one where a computation can advance without waiting for all other computations to complete. Concurrent computing is a form of modular programming. In its paradigm an overall computation is factored into subcomputations that may be executed concurrently. Pioneers in the field of concurrent computing include Edsger Dijkstra, Per Brinch Hansen, and C.A.R. Hoare. Introduction The concept of concurrent computing is frequently confused with the related but distinct concept of parallel computing, Pike, Rob (2012-01-11). "Concurrency is not Parallelism". ''Waza conference'', 11 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thread (computing)
In computer science, a thread of execution is the smallest sequence of programmed instructions that can be managed independently by a scheduler, which is typically a part of the operating system. The implementation of threads and processes differs between operating systems. In Modern Operating Systems, Tanenbaum shows that many distinct models of process organization are possible.TANENBAUM, Andrew S. Modern Operating Systems. 1992. Prentice-Hall International Editions, ISBN 0-13-595752-4. In many cases, a thread is a component of a process. The multiple threads of a given process may be executed concurrently (via multithreading capabilities), sharing resources such as memory, while different processes do not share these resources. In particular, the threads of a process share its executable code and the values of its dynamically allocated variables and non- thread-local global variables at any given time. History Threads made an early appearance under the name of "t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concurrent Programming Languages
Concurrent computing is a form of computing in which several computations are executed '' concurrently''—during overlapping time periods—instead of ''sequentially—''with one completing before the next starts. This is a property of a system—whether a program, computer, or a network—where there is a separate execution point or "thread of control" for each process. A ''concurrent system'' is one where a computation can advance without waiting for all other computations to complete. Concurrent computing is a form of modular programming. In its paradigm an overall computation is factored into subcomputations that may be executed concurrently. Pioneers in the field of concurrent computing include Edsger Dijkstra, Per Brinch Hansen, and C.A.R. Hoare. Introduction The concept of concurrent computing is frequently confused with the related but distinct concept of parallel computing, Pike, Rob (2012-01-11). "Concurrency is not Parallelism". ''Waza conference'', 11 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Programming Language Design
A programming language is a system of notation for writing computer program, computer programs. Most programming languages are text-based formal languages, but they may also be visual programming language, graphical. They are a kind of computer language. The description of a programming language is usually split into the two components of Syntax (programming languages), syntax (form) and semantics (computer science), semantics (meaning), which are usually defined by a formal language. Some languages are defined by a specification document (for example, the C (programming language), C programming language is specified by an International Organization for Standardization, ISO Standard) while other languages (such as Perl) have a dominant Programming language implementation, implementation that is treated as a reference implementation, reference. Some languages have both, with the basic language defined by a standard and extensions taken from the dominant implementation being commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Programming Constructs
Program, programme, programmer, or programming may refer to: Business and management * Program management, the process of managing several related projects * Time management * Program, a part of planning Arts and entertainment Audio * Programming (music), generating music electronically * Radio programming, act of scheduling content for radio * Synthesizer programmer, a person who develops the instrumentation for a piece of music Video or television * Broadcast programming, scheduling content for television * Program music, a type of art music that attempts to render musically an extra-musical narrative * Synthesizer patch or program, a synthesizer setting stored in memory * "Program", an instrumental song by Linkin Park from '' LP Underground Eleven'' * Programmer, a film on the lower half of a double feature bill; see B-movie Science and technology * Computer program, a set of instructions that describes how to perform a specific task to a computer. * Computer programming, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
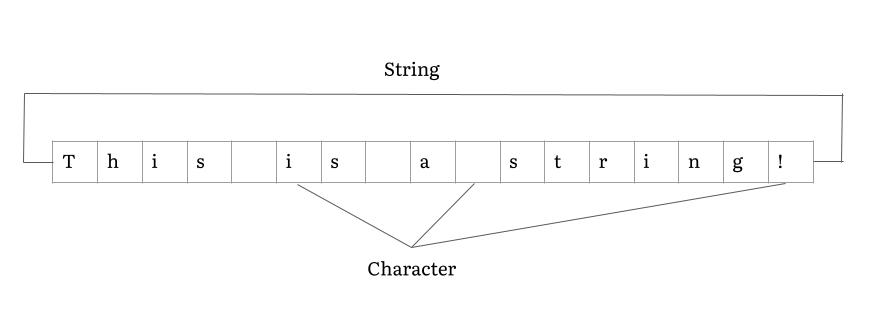
String (computer Science)
In computer programming, a string is traditionally a sequence of characters, either as a literal constant or as some kind of variable. The latter may allow its elements to be mutated and the length changed, or it may be fixed (after creation). A string is generally considered as a data type and is often implemented as an array data structure of bytes (or words) that stores a sequence of elements, typically characters, using some character encoding. ''String'' may also denote more general arrays or other sequence (or list) data types and structures. Depending on the programming language and precise data type used, a variable declared to be a string may either cause storage in memory to be statically allocated for a predetermined maximum length or employ dynamic allocation to allow it to hold a variable number of elements. When a string appears literally in source code, it is known as a string literal or an anonymous string. In formal languages, which are used in mathemati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thread (computer Science)
In computer science, a thread of execution is the smallest sequence of programmed instructions that can be managed independently by a scheduler, which is typically a part of the operating system. The implementation of threads and processes differs between operating systems. In Modern Operating Systems, Tanenbaum shows that many distinct models of process organization are possible.TANENBAUM, Andrew S. Modern Operating Systems. 1992. Prentice-Hall International Editions, ISBN 0-13-595752-4. In many cases, a thread is a component of a process. The multiple threads of a given process may be executed concurrently (via multithreading capabilities), sharing resources such as memory, while different processes do not share these resources. In particular, the threads of a process share its executable code and the values of its dynamically allocated variables and non- thread-local global variables at any given time. History Threads made an early appearance under the name of "task ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coupling (computer Programming)
In software engineering, coupling is the degree of interdependence between software modules; a measure of how closely connected two routines or modules are; the strength of the relationships between modules. Coupling is usually contrasted with cohesion. Low coupling often correlates with high cohesion, and vice versa. Low coupling is often thought to be a sign of a well-structured computer system and a good design, and when combined with high cohesion, supports the general goals of high readability and maintainability. History The software quality metrics of coupling and cohesion were invented by Larry Constantine in the late 1960s as part of a structured design, based on characteristics of “good” programming practices that reduced maintenance and modification costs. Structured design, including cohesion and coupling, were published in the article ''Stevens, Myers & Constantine'' (1974) and the book ''Yourdon & Constantine'' (1979), and the latter subsequently became st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blocking (computing)
In computing, a process is an instance of a computer program that is being executed. A process always exists in exactly one process state. A process that is blocked is one that is waiting for some event, such as a resource becoming available or the completion of an I/O operation. In a multitasking computer system, individual tasks, or threads of execution, must share the resources of the system. Shared resources include: the CPU, network and network interfaces, memory and disk. When one task is using a resource, it is generally not possible, or desirable, for another task to access it. The techniques of mutual exclusion are used to prevent this concurrent use. When the other task is blocked, it is unable to execute until the first task has finished using the shared resource. Programming languages and scheduling algorithms are designed to minimize the over-all effect blocking. A process that blocks may prevent local work-tasks from progressing. In this case "blocking" often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Select (Unix)
is a system call and application programming interface (API) in Unix-like and POSIX-compliant operating systems for examining the status of file descriptors of open input/output channels. The select system call is similar to the ' facility introduced in UNIX System V and later operating systems. However, with the c10k problem, both select and poll have been superseded by the likes of kqueue, epoll, /dev/poll and I/O completion ports. One common use of select outside of its stated use of waiting on filehandles is to implement a portable sub-second sleep. This can be achieved by passing NULL for all three fd_set arguments, and the duration of the desired sleep as the timeout argument. In the C programming language, the select system call is declared in the header file sys/select.h or unistd.h, and has the following syntax: int select(int nfds, fd_set *readfds, fd_set *writefds, fd_set *errorfds, struct timeval *timeout); fd_set type arguments may be manipulated with four ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polling (computer Science)
Polling, or polled operation, in computer science, refers to actively sampling the status of an external device by a client program as a synchronous activity. Polling is most often used in terms of input/output (), and is also referred to as polled or software-driven . A good example of hardware implementation is a watchdog timer. Description Polling is the process where the computer or controlling device waits for an external device to check for its readiness or state, often with low-level hardware. For example, when a printer is connected via a parallel port, the computer waits until the printer has received the next character. These processes can be as minute as only reading one bit. This is sometimes used synonymously with ' busy-wait' polling. In this situation, when an operation is required, the computer does nothing other than check the status of the device until it is ready, at which point the device is accessed. In other words, the computer waits until the device ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Server (computing)
In computing, a server is a piece of computer hardware or software (computer program) that provides functionality for other programs or devices, called " clients". This architecture is called the client–server model. Servers can provide various functionalities, often called "services", such as sharing data or resources among multiple clients, or performing computation for a client. A single server can serve multiple clients, and a single client can use multiple servers. A client process may run on the same device or may connect over a network to a server on a different device. Typical servers are database servers, file servers, mail servers, print servers, web servers, game servers, and application servers. Client–server systems are usually most frequently implemented by (and often identified with) the request–response model: a client sends a request to the server, which performs some action and sends a response back to the client, typically with a result or ackn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |