|
Concordia Publishing House
Concordia Publishing House (CPH), founded in 1869, is the official publishing arm of the Lutheran Church–Missouri Synod (LCMS). Headquartered in St. Louis, Missouri, at 3558 S. Jefferson Avenue, CPH publishes the synod's official monthly magazine, ''The Lutheran Witness,'' and the synod's hymnals, including '' The Lutheran Hymnal'' (1941), '' Lutheran Worship'' (1982), and '' Lutheran Service Book'' (2006). It publishes a wide range of resources for churches, schools, and homes and is the publisher of the world's most widely circulated daily devotional resource, '' Portals of Prayer''. Its children's books, known as Arch Books, have been published in millions of copies. Concordia Publishing House is the oldest publishing company west of the Mississippi River and the world's largest distinctly Lutheran publishing house. History Background In 1849, the LCMS created a publication society to provide "the most inexpensive and most general distribution of orthodox evangelical L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concordia Publishing House Logo
Concordia (mythology) is the Roman goddess who embodies agreement in marriage and society. Concordia may also refer to: Businesses and organizations Educational institutions * Concordia University (other), for Concordia University, Concordia College and Concordia Seminary * Concordia Academy (other) * Concordia High School (other) * Concordia Lutheran High School (other) * Concordia International School Shanghai, Pudong, China * Concordia Junior-Senior High School, Concordia, Kansas * Concordia Normal School, Kansas (closed 1878) * Great Western Business and Normal College, or Concordia Normal School and Business College, or Concordia Business College, in Concordia, Kansas, U.S. (closed 1930s) * Concordia Language Villages, a world-language and culture education program Other businesses and organizations * Concordia Association of Manchukuo, a 1930s–1940s political party * Concordia Healthcare, now Advanz Pharma, multinational p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drawing Of Concordia Publishing House In 1870
Drawing is a Visual arts, visual art that uses an instrument to mark paper or another two-dimensional surface, or a digital representation of such. Traditionally, the instruments used to make a drawing include pencils, crayons, and ink pens, sometimes in combination. More modern tools include Stylus (computing), computer styluses with graphics tablets and gamepads in Virtual reality, VR drawing software. A drawing instrument releases a small amount of material onto a surface, leaving a visible mark. The most common support for drawing is paper, although other materials, such as Paperboard, cardboard, vellum, wood, plastic, leather, canvas, and Lumber, board, have been used. Temporary drawings may be made on a blackboard or whiteboard. Drawing has been a popular and fundamental means of public expression throughout human history. It is one of the simplest and most efficient means of communicating ideas. The wide availability of drawing instruments makes drawing one of the most comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Spurgeon
Charles Haddon Spurgeon (19 June 1834 – 31st January 1892) was an English Particular Baptist preacher. Spurgeon remains highly influential among Christians of various denominations, to some of whom he is known as the "Prince of Preachers." He was a strong figure in the Baptist tradition, defending the 1689 London Baptist Confession of Faith, and opposing the liberal and pragmatic theological tendencies in the Church of his day. Spurgeon was pastor of the congregation of the New Park Street Chapel (later the Metropolitan Tabernacle) in London for 38 years. He was part of several controversies with the Baptist Union of Great Britain and later he left the denomination over doctrinal convictions. While at the Metropolitan Tabernacle, he built an Almshouse and the Stockwell Orphanage. He encouraged his congregation to engage actively with the poor of Victorian London. He also founded Spurgeon's College, which was named after him posthumously. Spurgeon authored sermons, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Georg Walch
Johann Georg Walch (17 June 1693 – 13 January 1775) was a German Lutheran theologian. Life He was born in Meiningen, where his father, Georg Walch, was general superintendent. He studied at Leipzig and Jena, amongst his teachers being J. F. Buddeus, whose only daughter he married. He published in 1716 a work, ''Historia critica Latinae linguae'', which soon came into wide use. Two years later he became professor extraordinarius of philosophy at Jena. In 1719, he was appointed professor ordinarius of rhetoric, in 1721 of poetry, and in 1724 professor extraordinarius of theology. In 1728 he became professor ordinarius of theology, and in 1730 professor primarius. His theological position was that of moderate orthodoxy, greatly influenced by the philosophy and controversies of the Deistic period. His university lectures and published works ranged over the wide fields of church history in its various branches, particularly the literature and the controversies of the church, dogm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Independent Evangelical-Lutheran Church
The Independent Evangelical-Lutheran Church (, abbreviated SELK) is a confessional Lutheran church body of Germany. It is a member of the European Lutheran Conference and of the International Lutheran Council (ILC) (of which the Lutheran Church – Missouri Synod of North America is also a member). The SELK has about 33,000 members in 174 congregations. The seat of SELK is in Hanover. History In 1817, Frederick William III of Prussia, King Frederick William III of Prussia ordered the Lutheran and Continental Reformed church, Reformed churches in his territory to unite, forming the Prussian Union of churches, Evangelical Church of the Prussian Union, a predecessor to today's Union of Evangelical Churches. As the uniting of Lutheran and Reformed Christians in Germany proceeded, some Lutheran groups dissented and formed independent churches, especially in Prussia, Saxony, Hanover, and Hesse. These Lutherans held that Reformed doctrine and Lutheran doctrine are contradictory on man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concordia Journal
Concordia Seminary is a Lutheran seminary in Clayton, Missouri. The institution's primary mission is to train pastors, deaconesses, missionaries, chaplains, and church leaders for the Lutheran Church–Missouri Synod (LCMS). Founded in 1839, the seminary initially resided in Perry County, Missouri. In 1849, it was moved to St. Louis, and in 1926, the current campus was built. The St. Louis institution was at one time considered the "theoretical" (academic) seminary of the LCMS while Concordia Theological Seminary in Fort Wayne was considered the "practical" seminary, although those distinctions no longer exist. Concordia Seminary currently offers a Master of Divinity degree leading to ordination, as well as Master of Arts, Master of Sacred Theology, Doctor of Ministry, and Doctor of Philosophy degrees. The seminary is considered theologically conservative. It does not train women for ordination as pastors. However, it does offer a program by which women may be rostered as deac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anzeiger Des Westens
The ''Anzeiger des Westens'' (literally "Gazette of the West") was the first German-language newspaper in St. Louis, Missouri, United States. Alongside the ''Westliche Post'' and the '' Illinois Staats-Zeitung'', it became one of the three most prominent German-language papers in the Midwestern United States, serving the German-American population with news and features. During the 1840s, it is believed to have had the largest circulation of any newspaper in Missouri, regardless of language.''Catholicism and American Freedom,'', John McGreevy Norton and Co., New York 2003, p. 22-23. History Early years The ''Anzeiger'' was founded by Heinrich Bimpage and B.T.O. Festen, and its first issue appeared in June 1835. At first it was issued as a weekly. For years, the paper was the leading source of German-American thought throughout the Midwest. William Weber became editor early in 1836. He had been a German student. His republican sympathies and involvement in the Polish uprising of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
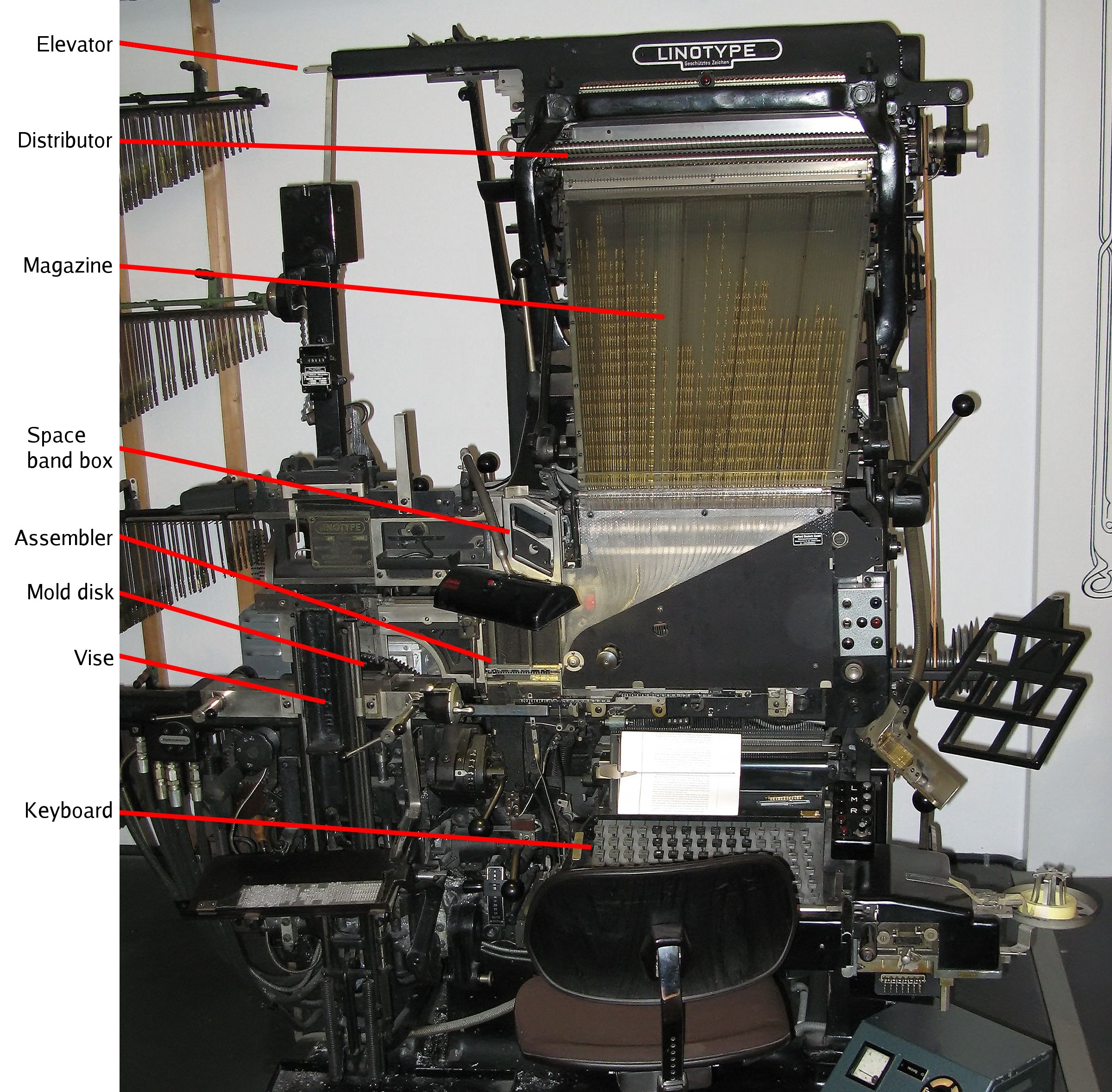
Linotype Machine
The Linotype machine ( ) is a "line casting" machine used in printing which is manufactured and sold by the former Mergenthaler Linotype Company and related It was a hot metal typesetting system that cast lines of metal type for one-time use. Linotype became one of the mainstays for typesetting, especially small-size body text, for newspapers, magazines, and posters from the late 19th century to the 1970s and 1980s, when it was largely replaced by phototypesetting and digital typesetting. The name of the machine comes from producing an entire line of metal Sort (typesetting), type at once, hence a ''line-o'-type''. It was a significant improvement over the previous industry standard of letter-by-letter manual typesetting using a composing stick and shallow subdivided trays, called "cases". The Linotype machine operator enters text on a 90-character keyboard. The machine assembles ''matrices'', or molds for the letter forms, in a line. The assembled line is then cast as a sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pan-American Exposition
The Pan-American Exposition was a world's fair held in Buffalo, New York, United States, from May 1 through November 2, 1901. The fair occupied of land on the western edge of what is now Delaware Park–Front Park System, Delaware Park, extending from Delaware Avenue to Elmwood Avenue and northward to Great Arrow Avenue. It is remembered today primarily for being the location of the Assassination of William McKinley, assassination of United States President William McKinley at the Temple of Music on September 6, 1901. The exposition was illuminated at night. Thomas A. Edison, Inc. filmed it during the day and a Panning (camera), pan of it at night. History The Pan-American Exposition, often referred to as "The Rainbow City", received national attention in the press and elsewhere a couple of years before, during and after it occurred During the course of the exposition more than 8,000,000 visitors came to the event. The event was organized by the Pan-American Exposition Company, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World's Columbian Exposition
The World's Columbian Exposition, also known as the Chicago World's Fair, was a world's fair held in Chicago from May 5 to October 31, 1893, to celebrate the 400th anniversary of Christopher Columbus's arrival in the New World in 1492. The centerpiece of the Fair, held in Jackson Park, was a large water pool representing the voyage that Columbus took to the New World. Chicago won the right to host the fair over several competing cities, including New York City, Washington, D.C., and St. Louis. The exposition was an influential social and cultural event and had a profound effect on American architecture, the arts, American industrial optimism, and Chicago's image. The layout of the Chicago Columbian Exposition was predominantly designed by John Wellborn Root, Daniel Burnham, Frederick Law Olmsted, and Charles B. Atwood. It was the prototype of what Burnham and his colleagues thought a city should be. It was designed to follow Beaux-Arts principles of design, namely ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louisiana Purchase Exposition
The Louisiana Purchase Exposition, informally known as the St. Louis World's Fair, was an World's fair, international exposition held in St. Louis, St. Louis, Missouri, United States, from April 30 to December 1, 1904. Local, state, and federal funds totaling $15 million (equivalent to $ in ) were used to finance the event. More than 60 countries and 43 of the then-45 American states maintained exhibition spaces at the fair, which was attended by nearly 19.7 million people. Historians generally emphasize the prominence of the themes of Race (human categorization), race and imperialism, and the fair's long-lasting impact on intellectuals in the fields of history, architecture, and anthropology. From the point of view of the memory of the average person who attended the fair, it primarily promoted entertainment, consumer goods, and popular culture. The monumental Greco-Roman architecture of this and other fairs of the era did much to influence permanent new buildings and master p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |