|
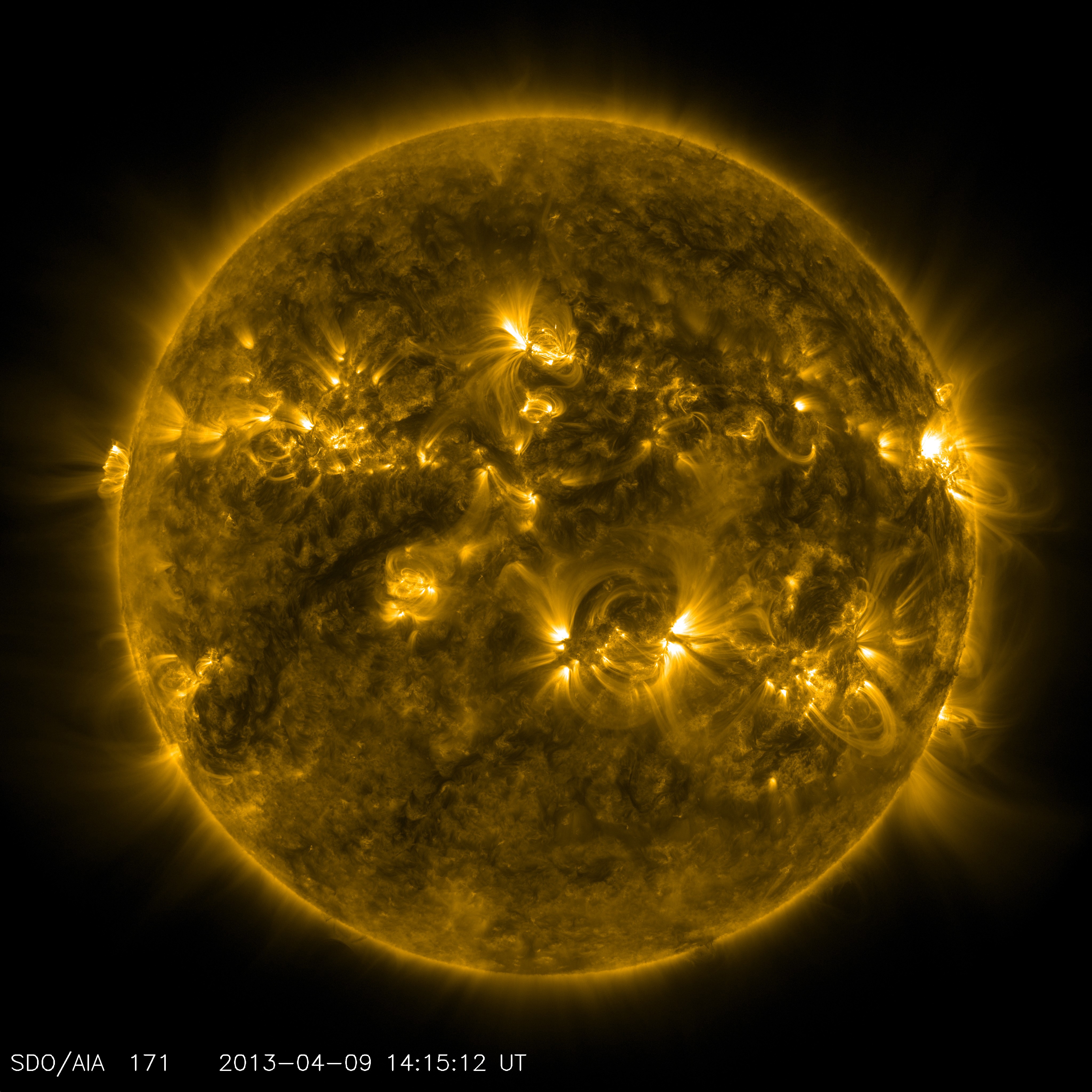
Computational Magnetohydrodynamics
Computational magnetohydrodynamics (CMHD) is a rapidly developing branch of magnetohydrodynamics that uses numerical methods and algorithms to solve and analyze problems that involve electrically conducting fluids. Most of the methods used in CMHD are borrowed from the well established techniques employed in Computational fluid dynamics. The complexity mainly arises due to the presence of a magnetic field and its coupling with the fluid. One of the important issues is to numerically maintain the \nabla \cdot = 0 (conservation of magnetic flux) condition, from Maxwell's equations, to avoid the presence of unrealistic effects, namely magnetic monopoles, in the solutions. Open-source MHD software * Pencil CodeCompressible resistive MHD, intrinsically divergence free, embedded particles module, finite-difference explicit scheme, high-order derivatives, Fortran95 and C, parallelized up to hundreds of thousands coresSource codeis available.br> RAMSES is an open source program to model as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetohydrodynamics
Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD; also called magneto-fluid dynamics or hydromagnetics) is the study of the magnetic properties and behaviour of electrically conducting fluids. Examples of such magnetofluids include plasmas, liquid metals, salt water, and electrolytes. The word ''magnetohydrodynamics'' is derived from ' meaning magnetic field, ' meaning water, and ' meaning movement. The field of MHD was initiated by Hannes Alfvén, for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1970. The fundamental concept behind MHD is that magnetic fields can induce currents in a moving conductive fluid, which in turn polarizes the fluid and reciprocally changes the magnetic field itself. The set of equations that describe MHD are a combination of the Navier–Stokes equations of fluid dynamics and Maxwell’s equations of electromagnetism. These differential equations must be solved simultaneously, either analytically or numerically. History The first record ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elmer FEM Solver
Elmer is computational tool for multi-physics problems. It has been developed by CSC in collaboration with Finnish universities, research laboratories and industry. Elmer FEM solver is free and open-source software, subject to the requirements of the GNU General Public License (GPL), version 2 or any later. Elmer includes physical models of fluid dynamics, structural mechanics, electromagnetics, heat transfer and acoustics, for example. These are described by partial differential equations which Elmer solves by the Finite Element Method (FEM). Elmer comprises several different parts: * ElmerGrid – A mesh conversion tool, which can be used to convert differing mesh formats into Elmer-suitable meshes. * ElmerGUI – A graphical interface which can be used on an existing mesh to assign physical models, this generates a "case file" which describes the problem to be solved. Does not show the whole ElmerSolver functionality in GUI. * ElmerSolver – The numerical solver which performs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma Modeling
Plasma modeling refers to solving equations of motion that describe the state of a plasma. It is generally coupled with Maxwell's equations for electromagnetic fields or Poisson's equation for electrostatic fields. There are several main types of plasma models: single particle, kinetic, fluid, hybrid kinetic/fluid, gyrokinetic and as system of many particles. Single particle description The single particle model describes the plasma as individual electrons and ions moving in imposed (rather than self-consistent) electric and magnetic fields. The motion of each particle is thus described by the Lorentz Force Law. In many cases of practical interest, this motion can be treated as the superposition of a relatively fast circular motion around a point called the guiding center and a relatively slow drift of this point. Kinetic description The kinetic model is the most fundamental way to describe a plasma, resultantly producing a distribution function :f(\vec,\vec,t) where the independ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Flow Meter
A ''magnetic flow meter'' (mag meter, electromagnetic flow meter) is a transducer that measures fluid flow by the voltage induced across the liquid by its flow through a magnetic field. A magnetic field is applied to the metering tube, which results in a potential difference proportional to the flow velocity perpendicular to the flux lines. The physical principle at work is electromagnetic induction. The magnetic flow meter requires a conducting fluid, for example, water that contains ions, and an electrical insulating pipe surface, for example, a rubber-lined steel tube. If the magnetic field direction were constant, electrochemical and other effects at the electrodes would make the potential difference difficult to distinguish from the fluid flow induced potential difference. To show this in modern magnetic flowmeters, the magnetic field is constantly reversed, cancelling out the electrochemical potential difference, which does not change direction with the magnetic field. Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetohydrodynamic Turbulence
Magnetohydrodynamic turbulence concerns the chaotic regimes of magnetofluid flow at high Reynolds number. Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) deals with what is a quasi-neutral fluid with very high conductivity. The fluid approximation implies that the focus is on macro length-and-time scales which are much larger than the collision length and collision time respectively. Incompressible MHD equations The incompressible MHD equations for constant mass density, \rho=1 , are : \begin \frac + \mathbf \cdot \nabla \mathbf & = -\nabla p + \mathbf \cdot \nabla \mathbf + \nu \nabla^2 \mathbf \\ pt \frac + \mathbf \cdot \nabla \mathbf & = \mathbf \cdot \nabla \mathbf + \eta \nabla^2 \mathbf \\ pt \nabla \cdot \mathbf & = 0 \\ pt\nabla \cdot \mathbf & = 0. \end where u, B, ''p'' represent the velocity, magnetic, and total pressure (thermal+magnetic) fields, \nu and \eta represent kinematic viscosity and magnetic diffusivity. The third equation is the incompressibility condition. In t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SoftwareX
''SoftwareX'' is a biannual peer-reviewed open-access scientific journal covering scientific software. It is published by Elsevier, and its editors-in-chief are Kate Keahey, Randall Sobie, and David Wallom. The journal has an official GitHub repository where the software/code of all publications are archived. Articles are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in the following bibliographic databases: *Emerging Sources Citation Index * Inspec *Scopus Scopus is Elsevier's abstract and citation database launched in 2004. Scopus covers nearly 36,377 titles (22,794 active titles and 13,583 inactive titles) from approximately 11,678 publishers, of which 34,346 are peer-reviewed journals in top-l ... References External links *{{Official website, https://www.journals.elsevier.com/softwarex Creative Commons Attribution-licensed journals Open access journals Computer science journals Elsevier acade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dielectric Heating
Dielectric heating, also known as electronic heating, radio frequency heating, and high-frequency heating, is the process in which a radio frequency (RF) alternating electric field, or radio wave or microwave electromagnetic radiation heats a dielectric material. At higher frequencies, this heating is caused by molecular dipole rotation within the dielectric. Mechanism Molecular rotation occurs in materials containing polar molecules having an electrical dipole moment, with the consequence that they will align themselves in an electromagnetic field. If the field is oscillating, as it is in an electromagnetic wave or in a rapidly oscillating electric field, these molecules rotate continuously by aligning with it. This is called dipole rotation, or dipolar polarisation. As the field alternates, the molecules reverse direction. Rotating molecules push, pull, and collide with other molecules (through electrical forces), distributing the energy to adjacent molecules and atoms in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma (physics)
Plasma () 1, where \nu_ is the electron gyrofrequency and \nu_ is the electron collision rate. It is often the case that the electrons are magnetized while the ions are not. Magnetized plasmas are ''anisotropic'', meaning that their properties in the direction parallel to the magnetic field are different from those perpendicular to it. While electric fields in plasmas are usually small due to the plasma high conductivity, the electric field associated with a plasma moving with velocity \mathbf in the magnetic field \mathbf is given by the usual Lorentz force, Lorentz formula \mathbf = -\mathbf\times\mathbf, and is not affected by Debye shielding. Mathematical descriptions To completely describe the state of a plasma, all of the particle locations and velocities that describe the electromagnetic field in the plasma region would need to be written down. However, it is generally not practical or necessary to keep track of all the particles in a plasma. Therefore, plasma physicist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finite Volume Method
The finite volume method (FVM) is a method for representing and evaluating partial differential equations in the form of algebraic equations. In the finite volume method, volume integrals in a partial differential equation that contain a divergence term are converted to surface integrals, using the divergence theorem. These terms are then evaluated as fluxes at the surfaces of each finite volume. Because the flux entering a given volume is identical to that leaving the adjacent volume, these methods are conservative. Another advantage of the finite volume method is that it is easily formulated to allow for unstructured meshes. The method is used in many computational fluid dynamics packages. "Finite volume" refers to the small volume surrounding each node point on a mesh. Finite volume methods can be compared and contrasted with the finite difference methods, which approximate derivatives using nodal values, or finite element methods, which create local approximations of a soluti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finite Element Method
The finite element method (FEM) is a popular method for numerically solving differential equations arising in engineering and mathematical modeling. Typical problem areas of interest include the traditional fields of structural analysis, heat transfer, fluid flow, mass transport, and electromagnetic potential. The FEM is a general numerical method for solving partial differential equations in two or three space variables (i.e., some boundary value problems). To solve a problem, the FEM subdivides a large system into smaller, simpler parts that are called finite elements. This is achieved by a particular space discretization in the space dimensions, which is implemented by the construction of a mesh of the object: the numerical domain for the solution, which has a finite number of points. The finite element method formulation of a boundary value problem finally results in a system of algebraic equations. The method approximates the unknown function over the domain. The sim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OpenFOAM
OpenFOAM (for "Open-source Field Operation And Manipulation") is a C++ toolbox for the development of customized numerical solvers, and pre-/post-processing utilities for the solution of continuum mechanics problems, most prominently including computational fluid dynamics (CFD). The OpenFOAM software is used in research organisations, academic institutes and across many types of industries, for example, automotive, manufacturing, process engineering and environmental engineering. OpenFOAM is open-source software which is freely available and licensed under the GNU General Public License Version 3, with the following variants: # OpenFOAM, released by OpenCFD Ltd. (with the name trademarked since 2007) first released as open-source in 2004. (Note: since 2012, OpenCFD Ltd is wholly-owned subsidiary of ESI Group) # FOAM-Extend, released by Wikki Ltd. (since 2009) # OpenFOAM, released by OpenFOAM Foundation. (since 2011) History The name FOAM has been claimed to appear for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NVIDIA
Nvidia CorporationOfficially written as NVIDIA and stylized in its logo as VIDIA with the lowercase "n" the same height as the uppercase "VIDIA"; formerly stylized as VIDIA with a large italicized lowercase "n" on products from the mid 1990s to early-mid 2000s. Though unofficial, second letter capitalization of NVIDIA, i.e. nVidia, may be found within enthusiast communities and publications. ( ) is an American multinational technology company incorporated in Delaware and based in Santa Clara, California. It is a software and fabless company which designs graphics processing units (GPUs), application programming interface (APIs) for data science and high-performance computing as well as system on a chip units (SoCs) for the mobile computing and automotive market. Nvidia is a global leader in artificial intelligence hardware and software. Its professional line of GPUs are used in workstations for applications in such fields as architecture, engineering and construction, media ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |