|
Complex Convexity
Complex convexity is a general term in complex geometry. Definition A set \Omega in \Complex^n is called if its intersection with any complex line is contractible. Background In complex geometry and analysis, the notion of convexity and its generalizations play an important role in understanding function behavior. Examples of classes of functions with a rich structure are, in addition to the convex functions, the subharmonic functions and the plurisubharmonic functions. Geometrically, these classes of functions correspond to convex domains and pseudoconvex domains, but there are also other types of domains, for instance lineally convex domains which can be generalized using convex analysis Convex analysis is the branch of mathematics devoted to the study of properties of convex functions and convex sets, often with applications in convex minimization, a subdomain of optimization theory. Convex sets A subset C \subseteq X of s .... A great deal is already known abou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex Geometry
In mathematics, complex geometry is the study of geometric structures and constructions arising out of, or described by, the complex numbers. In particular, complex geometry is concerned with the study of spaces such as complex manifolds and complex algebraic varieties, functions of several complex variables, and holomorphic constructions such as holomorphic vector bundles and coherent sheaves. Application of transcendental methods to algebraic geometry falls in this category, together with more geometric aspects of complex analysis. Complex geometry sits at the intersection of algebraic geometry, differential geometry, and complex analysis, and uses tools from all three areas. Because of the blend of techniques and ideas from various areas, problems in complex geometry are often more tractable or concrete than in general. For example, the classification of complex manifolds and complex algebraic varieties through the minimal model program and the construction of moduli spaces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex Analysis
Complex analysis, traditionally known as the theory of functions of a complex variable, is the branch of mathematical analysis that investigates Function (mathematics), functions of complex numbers. It is helpful in many branches of mathematics, including algebraic geometry, number theory, analytic combinatorics, applied mathematics; as well as in physics, including the branches of hydrodynamics, thermodynamics, and particularly quantum mechanics. By extension, use of complex analysis also has applications in engineering fields such as nuclear engineering, nuclear, aerospace engineering, aerospace, mechanical engineering, mechanical and electrical engineering. As a differentiable function of a complex variable is equal to its Taylor series (that is, it is Analyticity of holomorphic functions, analytic), complex analysis is particularly concerned with analytic functions of a complex variable (that is, holomorphic functions). History Complex analysis is one of the classical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
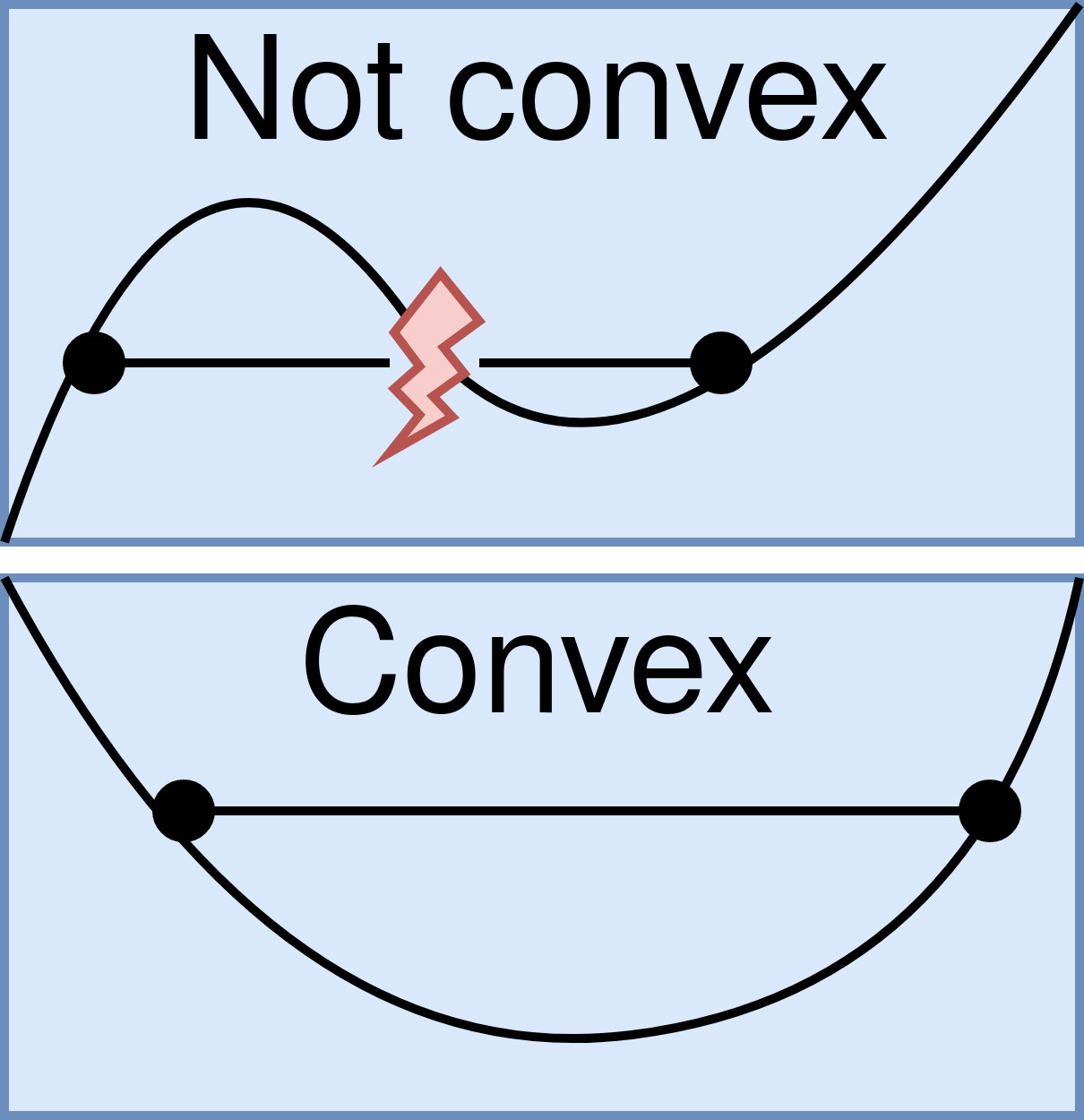
Convex Function
In mathematics, a real-valued function is called convex if the line segment between any two points on the graph of a function, graph of the function lies above the graph between the two points. Equivalently, a function is convex if its epigraph (mathematics), epigraph (the set of points on or above the graph of the function) is a convex set. A twice-differentiable function of a single variable is convex if and only if its second derivative is nonnegative on its entire domain. Well-known examples of convex functions of a single variable include the quadratic function x^2 and the exponential function e^x. In simple terms, a convex function refers to a function whose graph is shaped like a cup \cup, while a concave function's graph is shaped like a cap \cap. Convex functions play an important role in many areas of mathematics. They are especially important in the study of optimization problems where they are distinguished by a number of convenient properties. For instance, a st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Function (mathematics)
In mathematics, a function from a set to a set assigns to each element of exactly one element of .; the words map, mapping, transformation, correspondence, and operator are often used synonymously. The set is called the domain of the function and the set is called the codomain of the function.Codomain ''Encyclopedia of Mathematics'Codomain. ''Encyclopedia of Mathematics''/ref> The earliest known approach to the notion of function can be traced back to works of Persian mathematicians Al-Biruni and Sharaf al-Din al-Tusi. Functions were originally the idealization of how a varying quantity depends on another quantity. For example, the position of a planet is a ''function'' of time. Historically, the concept was elaborated with the infinitesimal calculus at the end of the 17th century, and, until the 19th century, the functions that were considered were differentiable (that is, they had a high degree of regularity). The concept of a function was formalized at the end of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subharmonic Function
In mathematics, subharmonic and superharmonic functions are important classes of function (mathematics), functions used extensively in partial differential equations, complex analysis and potential theory. Intuitively, subharmonic functions are related to convex functions of one variable as follows. If the graph of a function, graph of a convex function and a line intersect at two points, then the graph of the convex function is ''below'' the line between those points. In the same way, if the values of a subharmonic function are no larger than the values of a harmonic function on the ''boundary'' of a ball (mathematics), ball, then the values of the subharmonic function are no larger than the values of the harmonic function also ''inside'' the ball. ''Superharmonic'' functions can be defined by the same description, only replacing "no larger" with "no smaller". Alternatively, a superharmonic function is just the additive inverse, negative of a subharmonic function, and for this rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plurisubharmonic Function
In mathematics, plurisubharmonic functions (sometimes abbreviated as psh, plsh, or plush functions) form an important class of functions used in complex analysis. On a Kähler manifold, plurisubharmonic functions form a subset of the subharmonic functions. However, unlike subharmonic functions (which are defined on a Riemannian manifold) plurisubharmonic functions can be defined in full generality on complex analytic spaces. Formal definition A function :f \colon G \to \cup\, with ''domain'' G \subset ^n is called plurisubharmonic if it is upper semi-continuous, and for every complex line :\\subset ^n with a, b \in ^n the function z \mapsto f(a + bz) is a subharmonic function on the set :\. In ''full generality'', the notion can be defined on an arbitrary complex manifold or even a complex analytic space X as follows. An upper semi-continuous function :f \colon X \to \cup \ is said to be plurisubharmonic if and only if for any holomorphic map \varphi\colon\Delta\to X the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convex Analysis
Convex analysis is the branch of mathematics devoted to the study of properties of convex functions and convex sets, often with applications in convex minimization, a subdomain of optimization theory. Convex sets A subset C \subseteq X of some vector space X is if it satisfies any of the following equivalent conditions: #If 0 \leq r \leq 1 is real and x, y \in C then r x + (1 - r) y \in C. #If 0 is a if holds for any real 0 is called if \operatorname f \neq \varnothing and f(x) > -\infty for x \in \operatorname f. Alternatively, this means that there exists some x in the domain of f at which f(x) \in \mathbb and f is also equal to -\infty. In words, a function is if its domain is not empty, it never takes on the value -\infty, and it also is not identically equal to +\infty. If f : \mathbb^n \to \infty, \infty/math> is a proper convex function then there exist some vector b \in \mathbb^n and some r \in \mathbb such that :f(x) \geq x \cdot b - r for every x where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex Analysis
Complex analysis, traditionally known as the theory of functions of a complex variable, is the branch of mathematical analysis that investigates Function (mathematics), functions of complex numbers. It is helpful in many branches of mathematics, including algebraic geometry, number theory, analytic combinatorics, applied mathematics; as well as in physics, including the branches of hydrodynamics, thermodynamics, and particularly quantum mechanics. By extension, use of complex analysis also has applications in engineering fields such as nuclear engineering, nuclear, aerospace engineering, aerospace, mechanical engineering, mechanical and electrical engineering. As a differentiable function of a complex variable is equal to its Taylor series (that is, it is Analyticity of holomorphic functions, analytic), complex analysis is particularly concerned with analytic functions of a complex variable (that is, holomorphic functions). History Complex analysis is one of the classical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |