|
Compagnie Des Phosphates De Gafsa
The Compagnie des phosphates de Gafsa ( ar, شركة فسفاط قفصة, Gafsa Phosphate Company) or CPG is a Tunisian phosphate mining company based in Gafsa, formed in the late 19th century during the French colonial era, and once the largest employer in the country. It was merged in 1994 with the Groupe chimique tunisien (CGT) to form the CPG-CGT group. Before the revolution of 2011 the company was the fifth largest phosphate producer in the world, but since then strikes and social unrest have caused production to drop by half. Foundation In April 1885 the French amateur geologist Philippe Thomas discovered rich layers of calcium phosphates on the north slope of Jebel Thelja in the Métlaoui region of western Tunisia. Further geological surveys and explorations found significant phosphate deposits to the south and north of the Île de Kasserine. The government at first offered a concession to exploit the phosphates only on condition of building a port to export the ore and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be defined as a permanent and densely settled place with administratively defined boundaries whose members work primarily on non-agricultural tasks. Cities generally have extensive systems for housing, transportation, sanitation, utilities, land use, production of goods, and communication. Their density facilitates interaction between people, government organisations and businesses, sometimes benefiting different parties in the process, such as improving efficiency of goods and service distribution. Historically, city-dwellers have been a small proportion of humanity overall, but following two centuries of unprecedented and rapid urbanization, more than half of the world population now lives in cities, which has had profound consequences for g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunis
''Tounsi'' french: Tunisois , population_note = , population_urban = , population_metro = 2658816 , population_density_km2 = , timezone1 = CET , utc_offset1 = +01:00 , timezone1_DST = , utc_offset1_DST = , postal_code_type = Postal code , postal_code = 1xxx, 2xxx , area_code_type = Calling code , area_code = 71 , iso_code = TN-11, TN-12, TN-13 and TN-14 , blank_name_sec2 = geoTLD , blank_info_sec2 = .tn , website = , footnotes = Tunis ( ar, تونس ') is the capital and largest city of Tunisia. The greater metropolitan area of Tunis, often referred to as " Grand Tunis", has about 2,700,000 inhabitants. , it is the third-largest city in the Maghreb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government-owned Companies Of Tunisia
State ownership, also called government ownership and public ownership, is the ownership of an industry, asset, or enterprise by the state or a public body representing a community, as opposed to an individual or private party. Public ownership specifically refers to industries selling goods and services to consumers and differs from public goods and government services financed out of a government's general budget. Public ownership can take place at the national, regional, local, or municipal levels of government; or can refer to non-governmental public ownership vested in autonomous public enterprises. Public ownership is one of the three major forms of property ownership, differentiated from private, collective/cooperative, and common ownership. In market-based economies, state-owned assets are often managed and operated as joint-stock corporations with a government owning all or a controlling stake of the company's shares. This form is often referred to as a state-o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
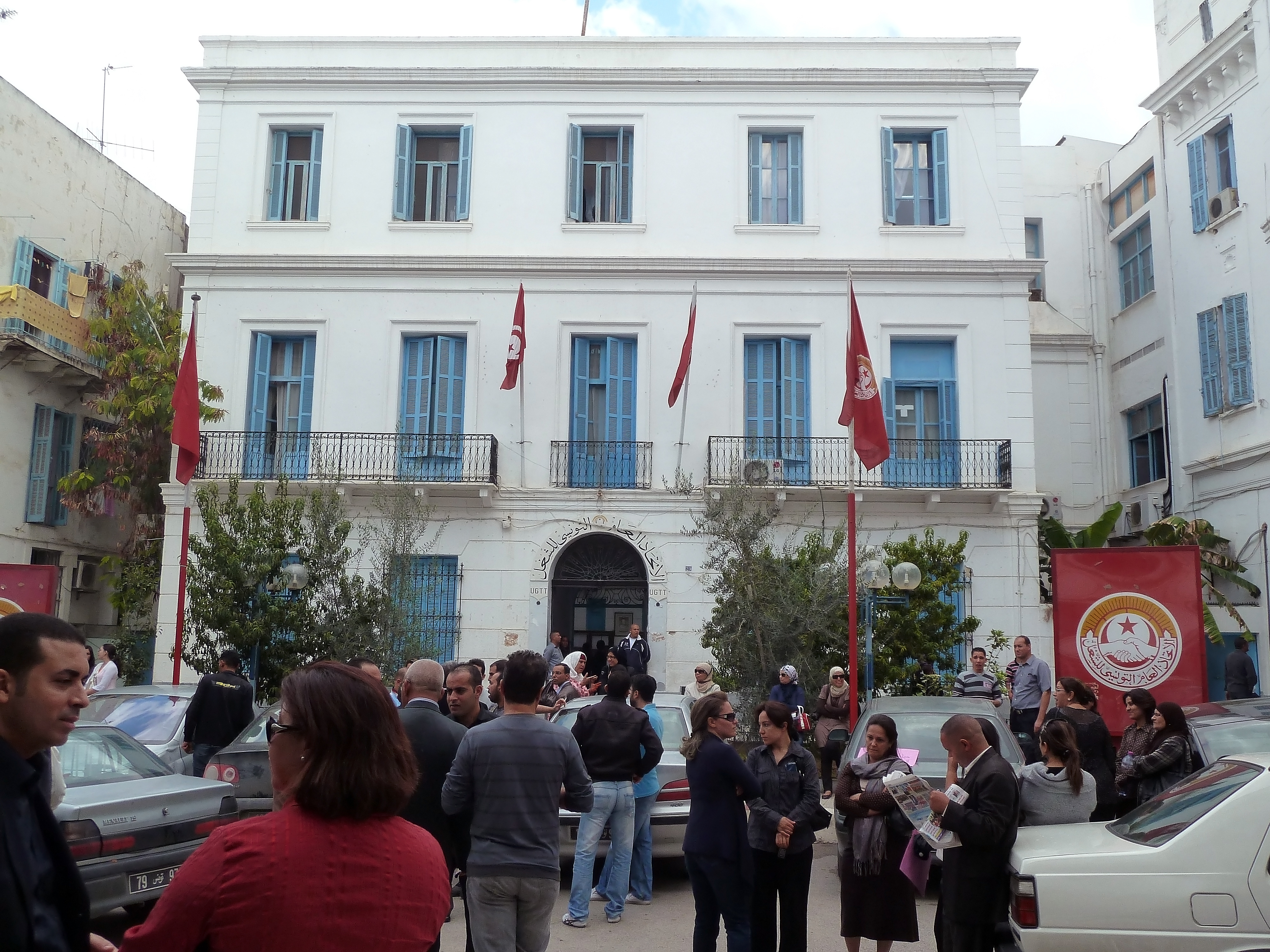
Tunisian General Labour Union
The Tunisian General Labour Union (french: Union Générale Tunisienne du Travail, ''UGTT''. ar, الاتحاد العام التونسي للشغل) is a national trade union center in Tunisia. It has a membership of more than one million and was founded January 20, 1946. The UGTT is affiliated with the International Trade Union Confederation and the Arab Trade Union Confederation. The UGTT worked together with the Tunisian Human Rights League, the Tunisian Confederation of Industry, Trade and Handicrafts and the Tunisian Order of Lawyers – collectively labelled the National Dialogue Quartet – to address the national discord following the Jasmine Revolution of 2011. The National Dialogue Quartet was announced as the laureate of the 2015 Nobel Peace Prize "for its decisive contribution to the building of a pluralistic democracy in Tunisia". Chairman (secretaries-general) *1946–1952: Farhat Hached Farhat Hached (; 2 February 1914 – 5 December 1952) was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zine El Abidine Ben Ali
Zine El Abidine Ben Ali ( ar, زين العابدين بن علي, translit=Zayn al-'Ābidīn bin 'Alī; 3 September 1936 – 19 September 2019), commonly known as Ben Ali ( ar, بن علي) or Ezzine ( ar, الزين), was a Tunisian politician who served as the 2nd president of Tunisia from 1987 to 2011. In that year, during the Tunisian revolution, he fled to Saudi Arabia. Ben Ali was appointed Prime Minister in October 1987. He assumed the Presidency on 7 November 1987 in a bloodless coup d'état that ousted President Habib Bourguiba by declaring him incompetent. Ben Ali was subsequently reelected with enormous majorities, each time exceeding 90% of the vote; his final re-election coming on 25 October 2009. Ben Ali was the penultimate surviving leader deposed in the Arab Spring who was survived by Egypt's Hosni Mubarak, the latter dying in February 2020. On 14 January 2011, following a month of protests against his rule, he fled to Saudi Arabia along with his wife Leïla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Train Loaded With Phosphate Rock, Metlaoui Tunisia-4298B
In rail transport, a train (from Old French , from Latin , "to pull, to draw") is a series of connected vehicles that run along a railway track and transport people or freight. Trains are typically pulled or pushed by locomotives (often known simply as "engines"), though some are self-propelled, such as multiple units. Passengers and cargo are carried in railroad cars, also known as wagons. Trains are designed to a certain gauge, or distance between rails. Most trains operate on steel tracks with steel wheels, the low friction of which makes them more efficient than other forms of transport. Trains have their roots in wagonways, which used railway tracks and were powered by horses or pulled by cables. Following the invention of the steam locomotive in the United Kingdom in 1804, trains rapidly spread around the world, allowing freight and passengers to move over land faster and cheaper than ever possible before. Rapid transit and trams were first built in the late 1800s to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diammonium Phosphate
Diammonium phosphate (DAP; IUPAC name diammonium hydrogen phosphate; chemical formula (NH4)2(HPO4) is one of a series of water-soluble ammonium phosphate salts that can be produced when ammonia reacts with phosphoric acid. Solid diammonium phosphate shows a dissociation pressure of ammonia as given by the following expression and equation: : At 100 °C, the dissociation pressure of diammonium phosphate is approximately 5 mmHg. According to the diammonium phosphate MSDS from CF Industries, Inc., decomposition starts as low as 70 °C: "Hazardous Decomposition Products: Gradually loses ammonia when exposed to air at room temperature. Decomposes to ammonia and monoammonium phosphate at around 70 °C (158 °F). At 155 °C (311 °F), DAP emits phosphorus oxides, nitrogen oxides and ammonia." Uses DAP is used as a fertilizer. When applied as plant food, it temporarily increases the soil pH, but over a long term the treated ground becomes more acidic than before, upon nitrif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triple Super Phosphate
Triple superphosphate is a component of fertilizer that primarily consists of monocalcium phosphate, Ca(H2PO4)2. Triple superphosphate is obtained by treating phosphate rock with phosphoric acid. Traditional routes for extraction of phosphate rock uses sulfuric acid gives single superphosphate, an approximate 1:1 mixture of Ca(H2PO4)2 and CaSO4 phosphogypsum). Double superphosphate refers to some average of triple- and single superphosphate, resulting from the extraction of phosphate rock with a mixture of phosphoric and sulfuric acids. Many fertilizers are derived from triple superphosphate, e.g. by blending with ammonium sulfate and potassium chloride Potassium chloride (KCl, or potassium salt) is a metal halide salt composed of potassium and chlorine. It is odorless and has a white or colorless vitreous crystal appearance. The solid dissolves readily in water, and its solutions have a salt .... Typical fertilizer-grade triple superphosphate contains 45% P2O5eq, single supe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphoric Acid
Phosphoric acid (orthophosphoric acid, monophosphoric acid or phosphoric(V) acid) is a colorless, odorless phosphorus-containing solid, and inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is commonly encountered as an 85% aqueous solution, which is a colourless, odourless, and non- volatile syrupy liquid. It is a major industrial chemical, being a component of many fertilizers. The compound is an acid. Removal of all three ions gives the phosphate ion . Removal of one or two protons gives dihydrogen phosphate ion , and the hydrogen phosphate ion , respectively. Phosphoric acid forms esters, called organophosphates. The name "orthophosphoric acid" can be used to distinguish this specific acid from other "phosphoric acids", such as pyrophosphoric acid. Nevertheless, the term "phosphoric acid" often means this specific compound; and that is the current IUPAC nomenclature. Production Phosphoric acid is produced industrially by one of two routes, wet processes and dry. We ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gujarat State Fertilizers And Chemicals
Gujarat State Fertilizers & Chemicals Limited (GSFC) is an Indian chemicals and fertilizers manufacturer, owned by the Government of Gujarat. GSFC was founded in 1962 and has its headquarters in Vadodara on the Ahmedabad Vadodara Expressway. It manufacturers plastics, nylons, fibers, industrial gases and varied chemicals including urea, ammonia, ammonium sulfate, sulfuric acid, phosphoric acid & diammonium phosphate, Caprolactam, Malemine, Methanol. Oil and gas discovered in Bombay High and South Basin triggered the birth of 8 new generation fertilizer plants to fulfill the growing food needs of India. In 1976, it set up a plant in Bharuch which trades as Gujarat Narmada Valley Fertilisers & Chemicals, also a subsidiary A subsidiary, subsidiary company or daughter company is a company owned or controlled by another company, which is called the parent company or holding company. Two or more subsidiaries that either belong to the same parent company or having a s ... of GSFC. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coromandel International
Coromandel International Limited is an Indian corporation founded in the early 1960s by IMC and Chevron Companies of USA and EID Parry, headquartered in Hyderabad, Telangana, India. Originally named Coromandel Fertilisers, the company is in the business of fertilizers, pesticides and specialty nutrients. The company is also in rural retail business in the states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka and Maharashtra through its Mana Gromor Centres. Coromandel International is part of Murugappa Group and a subsidiary of EID Parry, which holds 62.82% of the equity in the company. The company has sixteen manufacturing units located in the states of Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra, Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh and Jammu and Kashmir. Its product line includes Gromor, Godavari, Paramfos, Parry Gold and Parry Super. As of 2020 their revenues stood at ₹13,176.73 crore (US$1.8 billion) and their total assets were at ₹10,148.77 crore (US$1.4 billion). About Corom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)