|
Communicating Finite-state Machine
In computer science, a communicating finite-state machine is a finite-state machine labeled with "receive" and "send" operations over some alphabet of channels. They were introduced by Brand and Zafiropulo,D. Brand and P. Zafiropulo. On communicating finite-state machines. Journal of the ACM, 30(2):323–342, 1983. and can be used as a model of concurrent processes like Petri nets A Petri net, also known as a place/transition net (PT net), is one of several mathematical modeling languages for the description of distributed systems. It is a class of discrete event dynamic system. A Petri net is a directed bipartite grap .... Communicating finite-state machines are used frequently for modeling a communication protocol since they make it possible to detect major protocol design errors, including boundedness, deadlocks, and unspecified receptions.Rosier, Louis E; Gouda, Mohamed G. Deciding Progress for a Class of Communicating Finite State Machines. Austin: University of Texas at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, applied disciplines (including the design and implementation of Computer architecture, hardware and Software engineering, software). Algorithms and data structures are central to computer science. The theory of computation concerns abstract models of computation and general classes of computational problem, problems that can be solved using them. The fields of cryptography and computer security involve studying the means for secure communication and preventing security vulnerabilities. Computer graphics (computer science), Computer graphics and computational geometry address the generation of images. Programming language theory considers different ways to describe computational processes, and database theory concerns the management of re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finite-state Machine
A finite-state machine (FSM) or finite-state automaton (FSA, plural: ''automata''), finite automaton, or simply a state machine, is a mathematical model of computation. It is an abstract machine that can be in exactly one of a finite number of ''State (computer science), states'' at any given time. The FSM can change from one state to another in response to some Input (computer science), inputs; the change from one state to another is called a ''transition''. An FSM is defined by a list of its states, its initial state, and the inputs that trigger each transition. Finite-state machines are of two types—Deterministic finite automaton, deterministic finite-state machines and Nondeterministic finite automaton, non-deterministic finite-state machines. For any non-deterministic finite-state machine, an equivalent deterministic one can be constructed. The behavior of state machines can be observed in many devices in modern society that perform a predetermined sequence of actions d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concurrency (computer Science)
Concurrency refers to the ability of a system to execute multiple tasks through simultaneous execution or time-sharing (context switching), sharing resources and managing interactions. Concurrency improves responsiveness, throughput, and scalability in modern computing, including: * Operating systems and embedded systems * Distributed systems, parallel computing, and high-performance computing * Database systems, web applications, and cloud computing Related concepts Concurrency is a broader concept that encompasses several related ideas, including: * Parallelism (simultaneous execution on multiple processing units). Parallelism executes tasks independently on multiple CPU cores. Concurrency allows for multiple ''threads of control'' at the program level, which can use parallelism or time-slicing to perform these tasks. Programs may exhibit parallelism only, concurrency only, both parallelism and concurrency, neither. * Multi-threading and multi-processing (shared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
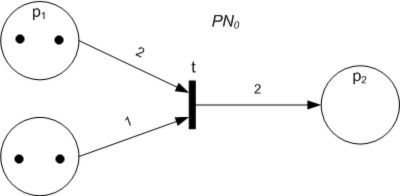
Petri Nets
A Petri net, also known as a place/transition net (PT net), is one of several mathematical modeling languages for the description of distributed systems. It is a class of discrete event dynamic system. A Petri net is a directed bipartite graph that has two types of elements: places and transitions. Place elements are depicted as white circles and transition elements are depicted as rectangles. A place can contain any number of tokens, depicted as black circles. A transition is enabled if all places connected to it as inputs contain at least one token. Some sources state that Petri nets were invented in August 1939 by Carl Adam Petri — at the age of 13 — for the purpose of describing chemical processes. Like industry standards such as UML activity diagrams, Business Process Model and Notation, and event-driven process chains, Petri nets offer a graphical notation for stepwise processes that include choice, iteration, and concurrent execution. Unlike these standards, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concurrency (computer Science)
Concurrency refers to the ability of a system to execute multiple tasks through simultaneous execution or time-sharing (context switching), sharing resources and managing interactions. Concurrency improves responsiveness, throughput, and scalability in modern computing, including: * Operating systems and embedded systems * Distributed systems, parallel computing, and high-performance computing * Database systems, web applications, and cloud computing Related concepts Concurrency is a broader concept that encompasses several related ideas, including: * Parallelism (simultaneous execution on multiple processing units). Parallelism executes tasks independently on multiple CPU cores. Concurrency allows for multiple ''threads of control'' at the program level, which can use parallelism or time-slicing to perform these tasks. Programs may exhibit parallelism only, concurrency only, both parallelism and concurrency, neither. * Multi-threading and multi-processing (shared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |