|
Commonwealth Fusion Systems
Commonwealth Fusion Systems (CFS) is an American company founded in 2018 aiming to build a compact fusion power plant based on the ARC tokamak power plant concept. The company is based in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and is a spin-off of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). CFS has participated in the United States Department of Energy’s INFUSE public-private knowledge innovation scheme, with several national labs and universities. History CFS was founded in 2018 as a spin-off from the MIT Plasma Science and Fusion Center. After initial funding of $50 million in 2018 from the Italian multinational Eni, CFS closed its series A round of venture capital funding in 2019 with a total of US$ 115 million in funding from Eni, Bill Gates's Breakthrough Energy Ventures, Vinod Khosla's Khosla Ventures, and others. CFS raised an additional US$ 84 million in series A2 funding from Singapore's Temasek, Norway's Equinor, and Devonshire Investors, as well as from previous inve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Industry
The energy industry is the totality of all of the industries involved in the production and sale of energy, including fuel extraction, manufacturing, refining and distribution. Modern society consumes large amounts of fuel, and the energy industry is a crucial part of the infrastructure and maintenance of society in almost all countries. In particular, the energy industry comprises: * the fossil fuel industries, which include petroleum industries (oil companies, petroleum refiners, fuel transport and end-user sales at gas stations) coal industries (extraction and processing) and the natural gas industries ( natural gas extraction, and coal gas manufacture, as well as distribution and sales); * the electrical power industry, including electricity generation, electric power distribution and sales; * the nuclear power industry; * the renewable energy industry, comprising alternative energy and sustainable energy companies, including those involved in hydroelectric power, wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of Norway. Bouvet Island, located in the Subantarctic, is a dependency of Norway; it also lays claims to the Antarctic territories of Peter I Island and Queen Maud Land. The capital and largest city in Norway is Oslo. Norway has a total area of and had a population of 5,425,270 in January 2022. The country shares a long eastern border with Sweden at a length of . It is bordered by Finland and Russia to the northeast and the Skagerrak strait to the south, on the other side of which are Denmark and the United Kingdom. Norway has an extensive coastline, facing the North Atlantic Ocean and the Barents Sea. The maritime influence dominates Norway's climate, with mild lowland temperatures on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
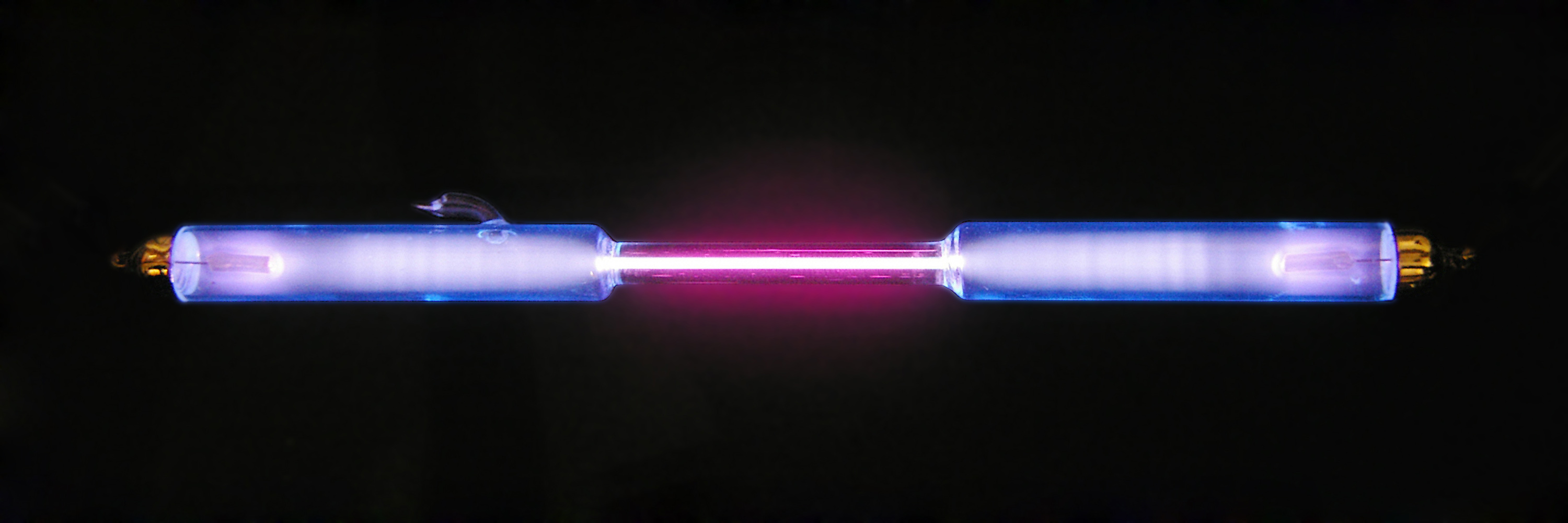
Tritium
Tritium ( or , ) or hydrogen-3 (symbol T or H) is a rare and radioactive isotope of hydrogen with half-life about 12 years. The nucleus of tritium (t, sometimes called a ''triton'') contains one proton and two neutrons, whereas the nucleus of the common isotope hydrogen-1 (''protium'') contains one proton and zero neutrons, and that of hydrogen-2 (''deuterium'') contains one proton and one neutron. Naturally occurring tritium is extremely rare on Earth. The atmosphere has only trace amounts, formed by the interaction of its gases with cosmic rays. It can be produced artificially by irradiating lithium metal or lithium-bearing ceramic pebbles in a nuclear reactor and is a low-abundance byproduct in normal operations of nuclear reactors. Tritium is used as the energy source in radioluminescent lights for watches, gun sights, numerous instruments and tools, and even novelty items such as self-illuminating key chains. It is used in a medical and scientific setting as a rad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deuterium
Deuterium (or hydrogen-2, symbol or deuterium, also known as heavy hydrogen) is one of two Stable isotope ratio, stable isotopes of hydrogen (the other being Hydrogen atom, protium, or hydrogen-1). The atomic nucleus, nucleus of a deuterium atom, called a deuteron, contains one proton and one neutron, whereas the far more common protium has no neutrons in the nucleus. Deuterium has a natural abundance in Earth's oceans of about one atom of deuterium among all atoms of hydrogen (see heavy water). Thus deuterium accounts for approximately 0.0156% by number (0.0312% by mass) of all the naturally occurring hydrogen in the oceans, while protium accounts for more than 99.98%. The abundance of deuterium changes slightly from one kind of natural water to another (see Vienna Standard Mean Ocean Water). (Tritium is yet another hydrogen isotope, with two neutrons, that is far more rare and is radioactive.) The name ''deuterium'' is derived from the Greek , meaning "second", to denot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superconducting Magnet
A superconducting magnet is an electromagnet made from coils of superconducting wire. They must be cooled to cryogenic temperatures during operation. In its superconducting state the wire has no electrical resistance and therefore can conduct much larger electric currents than ordinary wire, creating intense magnetic fields. Superconducting magnets can produce stronger magnetic fields than all but the strongest non-superconducting electromagnets, and large superconducting magnets can be cheaper to operate because no energy is dissipated as heat in the windings. They are used in Magnetic resonance imaging, MRI instruments in hospitals, and in scientific equipment such as Nuclear magnetic resonance, NMR spectrometers, mass spectrometers, Fusion power, fusion reactors and particle accelerators. They are also used for levitation, guidance and propulsion in a SCMaglev, magnetic levitation (maglev) railway system being constructed in Japan. Construction Cooling During operation, the mag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-temperature Superconductivity
High-temperature superconductors (abbreviated high-c or HTS) are defined as materials that behave as superconductors at temperatures above , the boiling point of liquid nitrogen. The adjective "high temperature" is only in respect to previously known superconductors, which function at even colder temperatures close to absolute zero. In absolute terms, these "high temperatures" are still far below ambient, and therefore require cooling. The first high-temperature superconductor was discovered in 1986, by IBM researchers Bednorz and Müller, who were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1987 "for their important break-through in the discovery of superconductivity in ceramic materials". Most high-c materials are type-II superconductors. The major advantage of high-temperature superconductors is that they can be cooled by using liquid nitrogen, as opposed to the previously known superconductors which require expensive and hard-to-handle coolants, primarily liquid helium. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
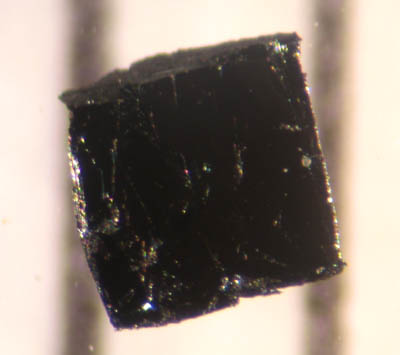
Yttrium Barium Copper Oxide
Yttrium barium copper oxide (YBCO) is a family of crystalline chemical compounds that display high-temperature superconductivity; it includes the first material ever discovered to become superconducting above the boiling point of liquid nitrogen (77 K) at about 93 K. Many YBCO compounds have the general formula Y Ba2 Cu3 O7−''x'' (also known as Y123), although materials with other Y:Ba:Cu ratios exist, such as Y Ba2 Cu4 Oy (Y124) or Y2 Ba4 Cu7 Oy (Y247). At present, there is no singularly recognised theory for high-temperature superconductivity. It is part of the more general group of rare-earth barium copper oxides (ReBCO) in which, instead of yttrium, other rare earths are present. History In April 1986, Georg Bednorz and Karl Müller, working at IBM in Zurich, discovered that certain semiconducting oxides became superconducting at relatively high temperature, in particular, a lanthanum barium copper oxide becomes superconducting at 35 K. This oxide was an oxyg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tesla (unit)
The tesla (symbol: T) is the unit of magnetic flux density (also called magnetic B-field strength) in the International System of Units (SI). One tesla is equal to one weber per square metre. The unit was announced during the General Conference on Weights and Measures in 1960 and is named in honour of Serbian-American electrical and mechanical engineer Nikola Tesla, upon the proposal of the Slovenian electrical engineer France Avčin. Definition A particle, carrying a charge of one coulomb (C), and moving perpendicularly through a magnetic field of one tesla, at a speed of one metre per second (m/s), experiences a force with magnitude one newton (N), according to the Lorentz force law. That is, : \text = \dfrac. As an SI derived unit, the tesla can also be expressed in terms of other units. For example, a magnetic flux of 1 weber (Wb) through a surface of one square meter is equal to a magnetic flux density of 1 tesla.''The International System of Units (SI), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wall Street Journal
''The Wall Street Journal'' is an American business-focused, international daily newspaper based in New York City, with international editions also available in Chinese and Japanese. The ''Journal'', along with its Asian editions, is published six days a week by Dow Jones & Company, a division of News Corp. The newspaper is published in the broadsheet format and online. The ''Journal'' has been printed continuously since its inception on July 8, 1889, by Charles Dow, Edward Jones, and Charles Bergstresser. The ''Journal'' is regarded as a newspaper of record, particularly in terms of business and financial news. The newspaper has won 38 Pulitzer Prizes, the most recent in 2019. ''The Wall Street Journal'' is one of the largest newspapers in the United States by circulation, with a circulation of about 2.834million copies (including nearly 1,829,000 digital sales) compared with ''USA Today''s 1.7million. The ''Journal'' publishes the luxury news and lifestyle magazine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-temperature Superconductivity
High-temperature superconductors (abbreviated high-c or HTS) are defined as materials that behave as superconductors at temperatures above , the boiling point of liquid nitrogen. The adjective "high temperature" is only in respect to previously known superconductors, which function at even colder temperatures close to absolute zero. In absolute terms, these "high temperatures" are still far below ambient, and therefore require cooling. The first high-temperature superconductor was discovered in 1986, by IBM researchers Bednorz and Müller, who were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1987 "for their important break-through in the discovery of superconductivity in ceramic materials". Most high-c materials are type-II superconductors. The major advantage of high-temperature superconductors is that they can be cooled by using liquid nitrogen, as opposed to the previously known superconductors which require expensive and hard-to-handle coolants, primarily liquid helium. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yahoo! Finance
Yahoo! Finance is a media property that is part of the Yahoo! network. It provides financial news, data and commentary including stock quotes, press releases, financial reports, and original content. It also offers some online tools for personal finance management. In addition to posting partner content from other web sites, it posts original stories by its team of staff journalists. It is ranked 20th by SimilarWeb on the list of largest news and media websites. In 2017 Yahoo! Finance added the feature to look at news surrounding cryptocurrency. It lists over 9,000 unique coins including Bitcoin and Ethereum Ethereum is a decentralized, open-source blockchain with smart contract functionality. Ether ( Abbreviation: ETH; sign: Ξ) is the native cryptocurrency of the platform. Among cryptocurrencies, ether is second only to bitcoin in market cap .... See also * Google Finance * MSN Money References * https://finance.yahoo.com/portfolios External links Yahoo! Fin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusion Industry Association
The Fusion Industry Association is a US-registered non-profit independent trade association for the international nuclear fusion industry. It is headquartered in Washington, D.C. It was founded in 2018 to advocate for policies to accelerate the arrival of fusion power. Its executive director is Andrew Holland, Chief Operating Officer of the American Security Project. The Fusion Industry Association has 28 members and 35 affiliate members, including nuclear reactor designers, engineering firms, suppliers, academic institutions, and various professional services with business in the nuclear fusion industry such as research consultancies. The emergence of the Fusion Industry Association can be traced back to the 2013 publication of a white paper on fusion energy by the American Security Project. The Fusion Industry Association's stated advocacy objectives are to encourage private sector fusion companies' partnering with the public sector for applied fusion research, to increa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |