|
Common Envelope
In astronomy, a common envelope (CE) is gas that contains a binary star system. The gas does not rotate at the same rate as the embedded binary system. A system with such a configuration is said to be in a common envelope phase or undergoing common envelope evolution. During a common envelope phase the embedded binary system is subject to drag forces from the envelope which cause the separation of the two stars to decrease. The phase ends either when the envelope is ejected to leave the binary system with much smaller orbital separation, or when the two stars become sufficiently close to merge and form a single star. A common envelope phase is short-lived relative to the lifetime of the stars involved. Evolution through a common envelope phase with ejection of the envelope can lead to the formation of a binary system composed of a compact object with a close companion. Cataclysmic variables, X-ray binaries and systems of close double white dwarfs or neutron stars are examples of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Envelope Phase - Ejection Or Merger
Common may refer to: Places * Common, a townland in County Tyrone, Northern Ireland * Boston Common, a central public park in Boston, Massachusetts * Cambridge Common, common land area in Cambridge, Massachusetts * Clapham Common, originally common land, now a park in London, UK * Common Moss, a townland in County Tyrone, Northern Ireland * Lexington Battle Green, Lexington Common, a common land area in Lexington, Massachusetts * Salem Common Historic District (Salem, Massachusetts), Salem Common Historic District, a common land area in Salem, Massachusetts People * Common (rapper) (born 1972), American hip hop artist, actor, and poet * Andrew Ainslie Common (born 1841), English amateur astronomer * Andrew Common (born 1889), British shipping director * John Common, American songwriter, musician and singer * Thomas Common (born 1850), Scottish translator and literary critic Arts, entertainment, and media * Common (film), ''Common'' (film), a 2014 BBC One film, written by Jimmy M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Supergiant
Red supergiants (RSGs) are stars with a supergiant luminosity class ( Yerkes class I) of spectral type K or M. They are the largest stars in the universe in terms of volume, although they are not the most massive or luminous. Betelgeuse and Antares are the brightest and best known red supergiants (RSGs), indeed the only first magnitude red supergiant stars. Classification Stars are classified as supergiants on the basis of their spectral luminosity class. This system uses certain diagnostic spectral lines to estimate the surface gravity of a star, hence determining its size relative to its mass. Larger stars are more luminous at a given temperature and can now be grouped into bands of differing luminosity. The luminosity differences between stars are most apparent at low temperatures, where giant stars are much brighter than main-sequence stars. Supergiants have the lowest surface gravities and hence are the largest and brightest at a particular temperature. The ''Yerkes'' o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post Common Envelope Binary
A post-common envelope binary (PCEB) or pre-cataclysmic variable is a binary system consisting of a white dwarf or hot subdwarf and a main-sequence star or a brown dwarf. The star or brown dwarf shared a common envelope with the white dwarf progenitor in the red giant phase. In this scenario the star or brown dwarf loses angular momentum as it orbits within the envelope, eventually leaving a main-sequence star and white dwarf in a short-period orbit. A PCEB will continue to lose angular momentum via magnetic braking and gravitational waves and will eventually begin mass-transfer, resulting in a cataclysmic variable. While there are thousands of PCEBs known, there are only a few eclipsing PCEBs, also called ePCEBs. Even more rare are PCEBs with a brown dwarf as the secondary. A brown dwarf with a mass lower than 20 might evaporate during the common envelope phase and therefore the secondary is supposed to have a mass higher than 20 . The material ejected from the common envelop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contact Binary
In astronomy, a contact binary is a binary star system whose component stars are so close that they touch each other or have merged to share their gaseous envelopes. A binary system whose stars share an envelope may also be called an overcontact binary. The term "contact binary" was introduced by astronomer Gerard Kuiper in 1941. Almost all known contact binary systems are eclipsing binaries; eclipsing contact binaries are known as W Ursae Majoris variables, after their type star, W Ursae Majoris. In a contact binary, both stars have filled their Roche lobes, allowing the more massive primary component to transfer both mass and luminosity to the secondary member. As a result, the components in a contact binary often have similar effective temperatures and luminosities, regardless of their respective masses. The rate of energy transfer between the components is dependent on their mass ratio and luminosity ratio. In cases where the stars are in geometric contact but the thermal c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary System (astronomy)
A binary system is a system of two astronomical bodies which are close enough that their gravitational attraction causes them to orbit each other around a barycenter ''(also see animated examples)''. More restrictive definitions require that this common center of mass is not located within the interior of either object, in order to exclude the typical planet–satellite systems and planetary systems. The most common binary systems are binary stars and binary asteroid, but brown dwarfs, planets, neutron stars, black holes and galaxies can also form binaries. A ''multiple system'' is like a binary system but consists of three or more objects such as for trinary stars and trinary asteroids. Classification In a binary system, the brighter object is referred to as primary, and the other the secondary. They are also classified based on orbit. Wide binaries are objects with orbits that keep them apart from one another. They evolve separately and have very little effect on each ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Star
A binary star is a system of two stars that are gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved using a telescope as separate stars, in which case they are called ''visual binaries''. Many visual binaries have long orbital periods of several centuries or millennia and therefore have orbits which are uncertain or poorly known. They may also be detected by indirect techniques, such as spectroscopy (''spectroscopic binaries'') or astrometry (''astrometric binaries''). If a binary star happens to orbit in a plane along our line of sight, its components will eclipse and transit each other; these pairs are called ''eclipsing binaries'', or, together with other binaries that change brightness as they orbit, ''photometric binaries''. If components in binary star systems are close enough they can gravitationally distort their mutual outer stellar atmospheres. In some cases, thes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ou 5
Ou 5, also known as IPHASXJ211420.0+434136, is a planetary nebula in the constellation of Cygnus. It was discovered by the IPHAS project in data taken on August 1, 2010, and independently by the French amateur astronomer Nicolas Outters in September 2012. Located two degrees east of the North American Nebula, it is an unusual planetary nebula because its central star is a short period eclipsing binary. Ou 5 showed signs of variability during the three occasions when IPHAS observed it. Because of that, members of the IPHAS team made follow-up photometric observations of the nebula during October and November 2013, using the 80 cm IAC80 telescope at the Teide Observatory. The derived light curve showed that the central star was an eclipsing binary, and the short orbital period (8.7 hours) implies that during the red giant phase which preceded the formation of the planetary nebula, the stars must have formed a common envelope binary. Passing through a common envelope stage is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
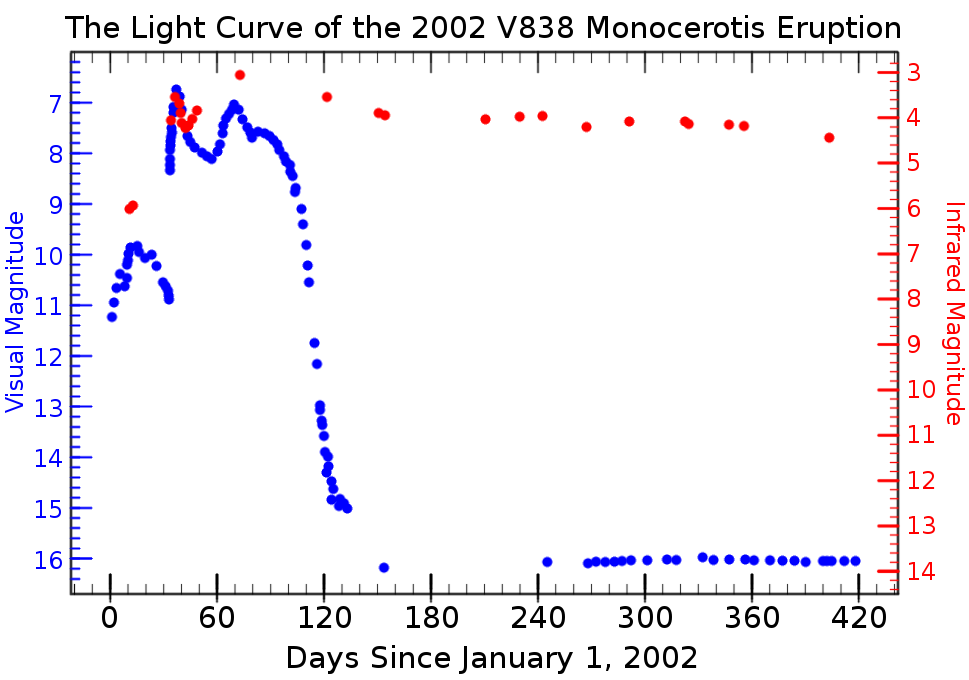
V838 Monocerotis
V838 Monocerotis (Nova Monocerotis 2002) is a spectroscopic binary star system in the constellation Monoceros (constellation), Monoceros about 19,000 light years (6 parsec, kpc) from the Sun. The previously unremarked star was observed in early 2002 experiencing a major outburst, and was possibly one of the List of largest known stars, largest known stars for a short period following the outburst. Originally believed to be a typical nova eruption, it was then identified as the first of a new class of eruptive variables known as luminous red novae. The reason for the outburst is still uncertain, but several conjectures have been put forward, including an eruption related to stellar death processes and a merger of a binary star or planets. The eruption occurred on one of two B3 main sequence stars in a close binary orbit. The erupting star became a very cool supergiant and for a while engulfed its companion. By 2009 the temperature of the supergiant had increased (since 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M31 RV
M31-RV is a possible red cataclysmic variable star located in the Andromeda Galaxy (M31) that experienced an outburst in 1988, which is similar to the outburst V838 Monocerotis experienced in 2002. Such objects have been called luminous red novae or intermediate-luminosity red transients. During the outburst, both V838 Mon and M31-RV reached a maximum absolute visual magnitude of -9.8. In 2006, the area around M31-RV was observed using the Hubble Space Telescope, but only red giants were seen. It is thought that the star either became too dim for Hubble to see, or the star is a companion of one of the red giants, or the star is one of the red giants themselves. M31-RV reached a peak visual magnitude of 17 before fading rapidly and showing dust formation. The most likely explanation states that these outbursts occur during stellar merger A stellar collision is the coming together of two stars caused by stellar dynamics within a star cluster, or by the orbital decay of a b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
V1309 Scorpii
V1309 Scorpii (also known as V1309 Sco) is a contact binary that merged into a single star in 2008 in a process known as a luminous red nova. It was the first star to provide conclusive evidence that contact binary systems end their evolution in a stellar merger. Its similarities to V838 Monocerotis and V4332 Sagittarii allowed scientists to identify these stars as merged contact binaries as well. Discovery V1309 Scorpii was discovered independently on 2 September 2008 by three groups: Koichi Nishiyama and Fujio Kabashima, Yukio Sakurai, and Guoyou Sun and Xing Gao. It was originally identified as a transient object located near the galactic bulge at right ascension ± 0s.01 and declination ± 0″.1. The astronomers who found it noted that it had been invisible to their 12 mag limit telescope just a few days prior to its discovery, indicating that it had recently gone nova. Before its eruption, its faintness and close proximity to USNO-B1.0 star 0592-0608962 (magnitud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M85 OT2006-1
M85 or M-85 may refer to: Military * M85 machine gun, a machine-gun used in the M60 Patton series of tanks * Zastava M85, an assault rifle developed and manufactured by Zastava Arms * Parker-Hale M85 a sniper rifle. Places * Messier 85, a lenticular galaxy in the constellation Coma Berenices * 85 Io, the asteroid #85, named "Io", a main belt asteroid Highways * M-85 (Michigan highway), a state highway in Michigan * M85 expressway (Hungary) * Mexican Federal Highway 85, a highway in Mexico * Mexican Federal Highway 85D, a toll highway in Mexico Transportation * Morin M85, a French homebuilt aircraft design * M85 fuel, an 85% methanol and 15% petrol blend Other uses * M 85, an age group for Masters athletics Masters athletics is a class of the sport of athletics for athletes of over 35 years of age. The events include track and field, road running and cross country running. Competitors are bracketed into five-year age groups (which promotes fair comp ... (athletes aged 35+) See ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)