|
Color Calibration
The aim of color calibration is to measure and/or adjust the color response of a device (input or output) to a known state. In International Color Consortium (ICC) terms, this is the basis for an additional color characterization of the device and later profiling. In non-ICC workflows, calibration sometimes refers to establishing a known relationship to a standard color space in one go. The device that is to be calibrated is sometimes known as a ''calibration source''; the color space that serves as a standard is sometimes known as a ''calibration target''. Color calibration is a requirement for all devices taking an active part in a color management, color-managed workflow and is used by many industries, such as television production, gaming, photography, engineering, chemistry, medicine, and more. Information flow and output distortion Input data can come from device sources like digital cameras, image scanners, or any other measuring devices. Those inputs can be either mono ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Color Consortium
The International Color Consortium (ICC) was formed in 1993 by eight vendors in order to create an open, vendor-neutral color management system which would function transparently across all operating systems and software packages. Overview The ICC specification, currently on version 4.4, allows for matching of color when moved between applications and operating systems, from the point of creation to the final output, whether display or print. This specification is technically identical to ISO 15076-1:2010, available from ISO. The ICC profile describes the color attributes of a particular device or viewing requirement by defining a mapping between the source or target color space and a ''profile connection space'' (PCS). The ICC defines the specification precisely but does not define algorithms or processing details. As such, applications or systems that work with different ICC profiles are allowed to vary. ICC has also published a preliminary specification for iccMAX, a n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Point
A white point (often referred to as reference white or target white in technical documents) is a set of tristimulus values or chromaticity coordinates that serve to define the color "white" in image capture, encoding, or reproduction. Depending on the application, different definitions of white are needed to give acceptable results. For example, photographs taken indoors may be lit by incandescent lights, which are relatively orange compared to daylight. Defining "white" as daylight will give unacceptable results when attempting to color-correct a photograph taken with incandescent lighting. Illuminants An illuminant is characterized by its relative spectral power distribution (SPD). The white point of an illuminant is the chromaticity of a white object under the illuminant, and can be specified by chromaticity coordinates, such as the ''x'', ''y'' coordinates on the CIE 1931 chromaticity diagram (hence the use of the relative SPD and not the absolute SPD, because the white ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
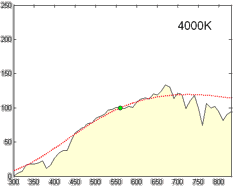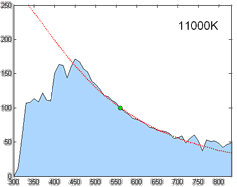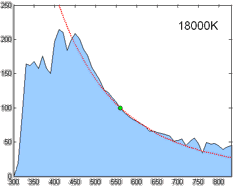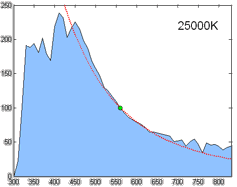
CIE Standard Illuminant D65
A standard illuminant is a theoretical source of visible light with a spectral power distribution that is published. Standard illuminants provide a basis for comparing images or colors recorded under different lighting. CIE illuminants The International Commission on Illumination (usually abbreviated CIE for its French name) is the body responsible for publishing all of the well-known standard illuminants. Each of these is known by a letter or by a letter-number combination. Illuminants A, B, and C were introduced in 1931, with the intention of respectively representing average incandescent light, direct sunlight, and average daylight. Illuminants D (1967) represent variations of daylight, illuminant E is the equal-energy illuminant, while illuminants F (2004) represent fluorescent lamps of various composition. There are instructions on how to experimentally produce light sources ("standard sources") corresponding to the older illuminants. For the relatively newer ones (such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamut
In color reproduction and colorimetry, a gamut, or color gamut , is a convex set containing the colors that can be accurately represented, i.e. reproduced by an output device (e.g. printer or display) or measured by an input device (e.g. camera or visual system). Devices with a larger gamut can represent more colors. Similarly, gamut may also refer to the colors within a defined color space, which is not linked to a specific device. A trichromatic gamut is often visualized as a color triangle. A less common usage defines gamut as the subset of colors contained within an image, scene or video. Introduction The term ''gamut'' was adopted from the field of music, where the medieval Latin expression "gamma ut" meant the lowest tone of the G scale and, in time, came to imply the entire range of musical notes of which musical melodies are composed. William Shakespeare, Shakespeare's use of the term in ''The Taming of the Shrew'' is sometimes attributed to the author / musician Thom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
On-screen Display
An on-screen display (OSD) is an image superimposed on a screen picture, commonly used by modern television sets, VCRs, and DVD players to display information such as volume, channel, and time. History In the past, most adjustments on TV sets were performed with analog controls such as potentiometers and switches. This was used more recently also in monochrome portable TVs. After remote controls were invented, digital adjustments became common. They needed an external display, which was LED, LCD, or VFD based. Including this display increased manufacturing costs. When electronics became more advanced, it became clear that adding some extra devices for an OSD was cheaper than adding a second display device. TV screens had become much bigger and could display much more information than a small second display. OSDs display graphical information superimposed over the picture, which is done by synchronizing the reading from OSD video memory with the TV signal. Some of the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
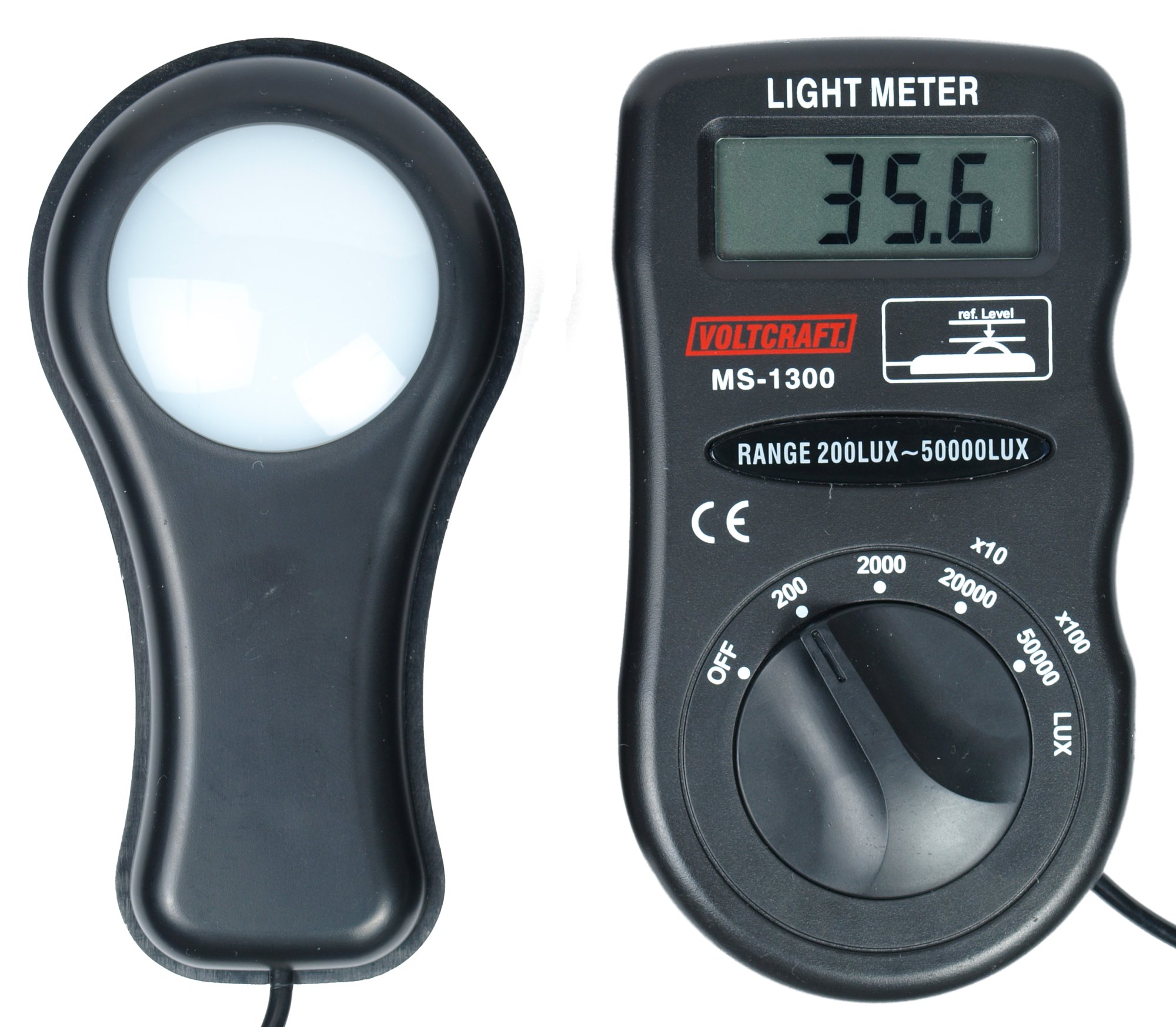
Tristimulus Colorimeter
A tristimulus colorimeter, colloquially shortened to ''colorimeter'' or ''colourimeter'', is used in digital imaging to profile and calibrate output devices. It takes a limited number of wideband spectral energy readings along the visible spectrum by using filtered photodetectors; e.g. silicon photodiodes. A colorimeter with the known value of absolute error allows measuring (x,y)-chromaticity coordinates in red, green, blue and white colors. Measured values are used for calculation of LCD profile coefficients. Originally, three glass filters whose transmittance spectra mimicked the CIE color matching functions (shown below) were employed. A filter bank may be used to decompose the individual color matching functions if more accuracy is desired. A camera or colorimeter is said to be ''colorimetric'' if it satisfies the by (1868–1945) (also called the "Maxwell–Ives criterion"), reducing observer metamerism color errors, if the product of the spectral responsivity of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lab Color Space
The CIELAB color space, also referred to as ''L*a*b*'', is a color space defined by the International Commission on Illumination (abbreviated CIE) in 1976. It expresses color as three values: ''L*'' for perceptual lightness and ''a*'' and ''b*'' for the four Unique hues, unique colors of human vision: red, green, blue and yellow. CIELAB was intended as a perceptually uniform space, where a given numerical change corresponds to a similar perceived change in color. While the LAB space is not truly perceptually uniform, it nevertheless is useful in industry for detecting small differences in color. Like the CIE 1931 color space, CIEXYZ space it derives from, CIELAB color space is a device-independent, "standard observer" model. The colors it defines are not relative to any particular device such as a computer monitor or a printer, but instead relate to the CIE 1931 color space#CIE standard observer, CIE standard observer which is an averaging of the results of color matching expe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RGB Color Space
RGB color spaces are a category of additive colorimetric color spaces specifying part of its absolute color space definition using the RGB color model. RGB color spaces are commonly found describing the mapping of the RGB color model to human perceivable color, but some RGB color spaces use imaginary (non-real-world) primaries and thus can not be displayed directly. Like any color space, while the specifications in this category use the RGB color model to describe their space, it is not mandatory to use that model to signal pixel color values. Broadcast TV color spaces like NTSC, PAL, Rec. 709, Rec. 2020 additionally describe a translation from RGB to YCbCr and that is how they are usually signalled for transmission, but an image can be stored as either RGB or YCbCr. This demonstrates using the singular term "RGB color space" can be misleading, since a chosen color space or signalled colour can be described by any appropriate color model. However the singular can be seen in spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photometer
A photometer is an instrument that measures the strength of electromagnetic radiation in the range from ultraviolet to infrared and including the visible spectrum. Most photometers convert light into an electric current using a photoresistor, photodiode, or photomultiplier. Photometers measure: *Illuminance * Irradiance * Light absorption * Scattering of light * Reflection of light *Fluorescence *Phosphorescence * Luminescence Historically, photometry was done by estimation, comparing the luminous flux of a source with a standard source. By the 19th century, common photometers included Rumford's photometer, which compared the depths of shadows cast by different light sources, and Ritchie's photometer, which relied on equal illumination of surfaces. Another type was based on the extinction of shadows. Modern photometers utilize photoresistors, photodiodes or photomultipliers to detect light. Some models employ photon counting, measuring light by counting individual photons. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Mapping
Image color transfer is a function that maps (transforms) the colors of one (source) image to the colors of another (target) image. A color mapping may be referred to as the algorithm that results in the mapping function or the algorithm that transforms the image colors. The image modification process is sometimes called ''color transfer'' or, when grayscale images are involved, ''brightness transfer function (BTF)''; it may also be called ''photometric camera calibration'' or ''radiometric camera calibration''. The term ''image color transfer'' is a bit of a misnomer since most common algorithms transfer both color and shading. (Indeed, the example shown on this page predominantly transfers shading other than a small orange region within the image that is adjusted to yellow.) Algorithms There are two types of image color transfer algorithms: those that employ the statistics of the colors of two images, and those that rely on a given pixel correspondence between the images. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |