|
Colombo Racecourse
Colombo Racecourse ( si, කොළඹ තුරඟ තරඟ පිටිය) is a historical harness racing course in the Cinnamon Gardens, Colombo. During the Second World War, it was used as a temporary airfield. In 2012, it was redeveloped as the Colombo Racecourse Sports Complex to become the first International Rugby Union ground in Sri Lanka to host all the national rugby union side's home matches. In 2014, the ground went through a major renovation, which included installation of floodlights and the conversion of a substantial part of the grandstand into a shopping and dining complex. The ground hosted the 2022 SAFF U-17 Championship. History Horse racing Officially opened for horse racing in 1893 after it was moved from the Colpitty Race Course, as one of the best in terms of design, facilities, and size in the East. In 1922 a totalisator was installed becoming the first race course in the East to have one. The Colombo Turf Club was based here with its own pavilion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colombo
Colombo ( ; si, කොළඹ, translit=Koḷam̆ba, ; ta, கொழும்பு, translit=Koḻumpu, ) is the executive and judicial capital and largest city of Sri Lanka by population. According to the Brookings Institution, Colombo metropolitan area has a population of 5.6 million, and 752,993 in the Municipality. It is the financial centre of the island and a tourist destination. It is located on the west coast of the island and adjacent to the Greater Colombo area which includes Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte, the legislative capital of Sri Lanka, and Dehiwala-Mount Lavinia. Colombo is often referred to as the capital since Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte is itself within the urban/suburban area of Colombo. It is also the administrative capital of the Western Province and the district capital of Colombo District. Colombo is a busy and vibrant city with a mixture of modern life, colonial buildings and monuments. Due to its large harbour and its strategic position along ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by Kingdom of England, English and Kingdom of Scotland, Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Kingdom of France, France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the British Armed Forces, UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the middle decades of the 17th century, and through the 18th century, the Royal Navy vied with the Dutch Navy and later with the French Navy for maritime supremacy. From the mid 18th century, it was the world's most powerful navy until the World War II, Second World War. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superiority ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
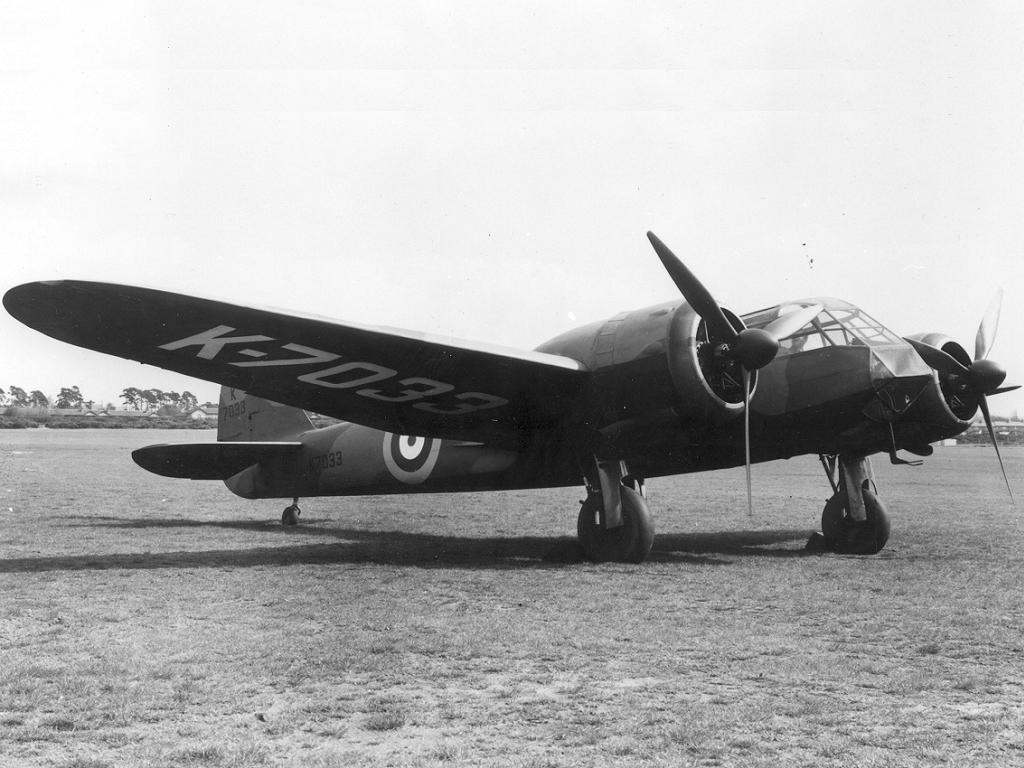
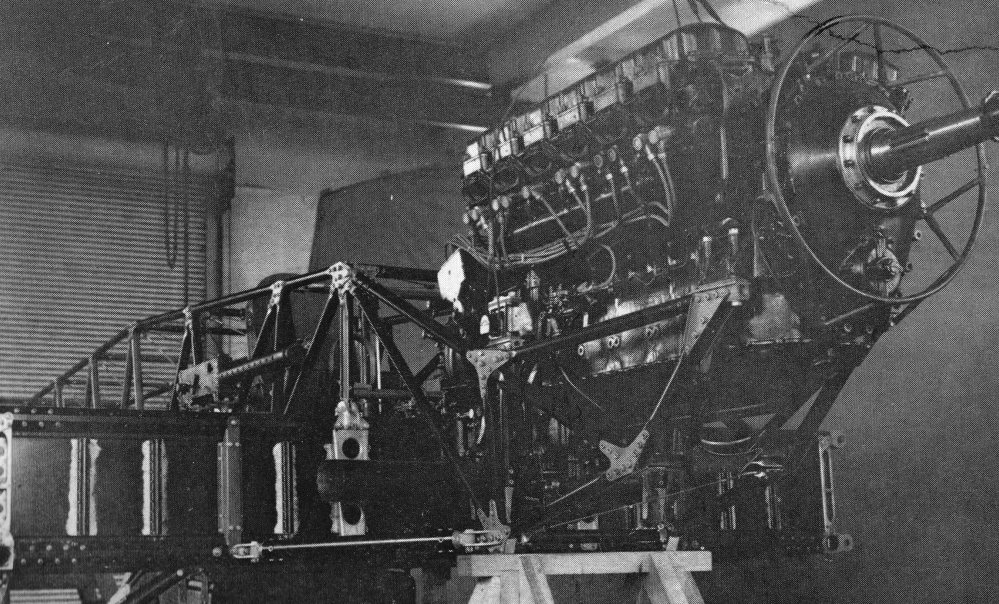
Bristol Blenheim
The Bristol Blenheim is a British light bomber aircraft designed and built by the Bristol Aeroplane Company (Bristol) which was used extensively in the first two years of the Second World War, with examples still being used as trainers until the end of the war. Development began with the ''Type 142'', a civil airliner, in response to a challenge from Lord Rothermere to produce the fastest commercial aircraft in Europe. The ''Type 142'' first flew in April 1935, and the Air Ministry, impressed by its performance, ordered a modified design as the ''Type 142M'' for the Royal Air Force (RAF) as a bomber. Deliveries of the newly named Blenheim to RAF squadrons commenced on 10 March 1937. In service the Type 142M became the Blenheim Mk.I which would be developed into the longer Type 149, designated the Blenheim Mk.IV, except in Canada where Fairchild Canada built the Type 149 under licence as the Bolingbroke. The Type 160 Bisley was also developed from the Blenheim, but was already o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawker Hurricanes
The Hawker Hurricane is a British single-seat fighter aircraft of the 1930s–40s which was designed and predominantly built by Hawker Aircraft Ltd. for service with the Royal Air Force (RAF). It was overshadowed in the public consciousness by the Supermarine Spitfire during the Battle of Britain in 1940, but the Hurricane inflicted 60 percent of the losses sustained by the Luftwaffe in the campaign, and fought in all the major theatres of the Second World War. The Hurricane originated from discussions between RAF officials and aircraft designer Sir Sydney Camm about a proposed monoplane derivative of the Hawker Fury biplane in the early 1930s. Despite an institutional preference for biplanes and lack of interest by the Air Ministry, Hawker refined their monoplane proposal, incorporating several innovations which became critical to wartime fighter aircraft, including retractable landing gear and the more powerful Rolls-Royce Merlin engine. The Air Ministry ordered Hawker's ''Int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal College, Colombo
Royal College, Colombo is a Single-sex education, selective entry boys' school located in Cinnamon Gardens, Cinnamon Gardens, Colombo, Sri Lanka. Started as a private school by Rev Joseph Marsh in 1835, it was established as the Colombo Academy by Sir Robert Wilmot-Horton, 3rd Baronet, Sir Robert Wilmot-Horton in January 1836, as part of the implementation of the recommendations of the Colebrooke Cameron Commission (1833), and was the first State school, government-run secondary school for boys in the island. Royal College is the first Lists of schools in Sri Lanka, public school in Sri Lanka and is often referred to as the "Eton College, Eton of Sri Lanka". The school was founded in the Public school (United Kingdom), British public school tradition, based on the recommendations of the Colebrooke Cameron Commission (1833), and having been named the Royal College, Colombo in 1881 with consent from Queen Victoria, it became the first school to gain the prefix, "Royal", outside o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Hospital
A military hospital is a hospital owned and operated by a military. They are often reserved for the use of military personnel and their dependents, but in some countries are made available to civilians as well. They may or may not be located on a military base; many are not. In the United Kingdom and Germany, British military hospitals have been closed; military personnel are usually treated in a special wing of a designated civilian hospital, in the UK, these are referred to as a Ministry of Defence Hospital Unit. Service personnel injured in combat operations are normally treated at the Royal Centre for Defence Medicine. Examples Asia Azerbaijan * Central Clinical Hospital * Baku Military Garrison Hospital * Military Hospital of Frontiers * Central Customs Hospital * Hospital of the Ministry of Internal Affairs * Central Military Hospital * Military Hospital of the Ministry of National Security * Polyclinic of the Army Medical Department of the Ministry of National S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Don Stephen Senanayake
Don Stephen Senanayake ( si, දොන් ස්ටීවන් සේනානායක,; ta, டி. எஸ். சேனநாயக்கா; 21 October 1884 – 22 March 1952) was a Ceylonese statesman. He was the first Prime Minister of Ceylon having emerged as the leader of the Sri Lankan independence movement that led to the establishment of self-rule in Ceylon. He is considered as the "Father of the Nation". Born to an entrepreneur from the village of Botale, Senanayake was educated at S. Thomas' College, Mutwal before briefly working as a clerk in the Surveyor General's Department. Joining the family business, he managed the family own estates and the Kahatagaha Graphite Mine. Long with his brothers, Senanayake became active in the temperance movement which grew into the independence movement following 1915 Sinhalese-Muslim riots, in which the Senanayake brothers were imprisoned without charges for 46 days. He was elected unopposed in 1924 to the Legisla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
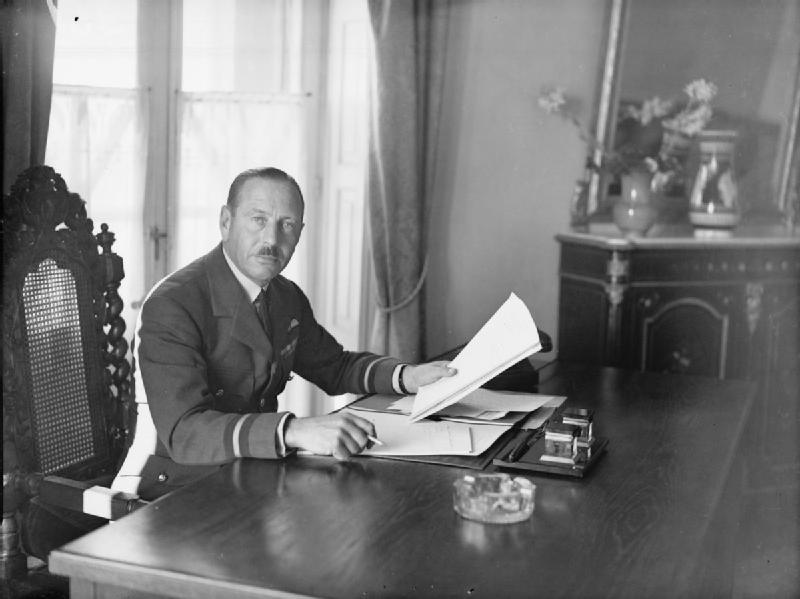
John D'Albiac
Air Marshal Sir John Henry D'Albiac, (28 January 1894 – 20 August 1963) was a senior commander in the Royal Air Force during the Second World War. Notably he was the British air commander for the Battle of Greece. Biography D'Albiac was educated at the Seabrook Lodge School in Kent, Framlingham College and the Royal Military College, Sandhurst. He was commissioned into the Royal Marine Artillery in 1914 but seconded to the Royal Naval Air Service during the following year. In 1916, whilst serving in France as an aeroplane observer, D'Albiac was awarded the Distinguished Service Order The Distinguished Service Order (DSO) is a military decoration of the United Kingdom, as well as formerly of other parts of the Commonwealth, awarded for meritorious or distinguished service by officers of the armed forces during wartime, typi .... After serving as Station Commander at RAF Scopwick he transferred to the RAF on its establishment in 1918 and served on the Staff at Head ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Vice Marshal
Air vice-marshal (AVM) is a two-star air officer rank which originated in and continues to be used by the Royal Air Force. The rank is also used by the air forces of many countries which have historical British influence and it is sometimes used as the English translation of an equivalent rank in countries which have a non-English air force-specific rank structure. Air vice-marshal is a two-star rank and has a NATO ranking code of OF-7. It is equivalent to a rear-admiral in the Royal Navy or a major-general in the British Army or the Royal Marines. In other NATO forces, such as the United States Armed Forces and the Canadian Armed Forces, the equivalent two-star rank is major general. The rank of air vice-marshal is immediately senior to the rank air commodore and immediately subordinate to the rank of air marshal. Since before the Second World War it has been common for air officers commanding RAF groups to hold the rank of air vice-marshal. In small air forces su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Officer Commanding, Ceylon
General Officer Commanding, Ceylon (also known as ''Commander of Troops'' or ''Officer Commanding His/Her Majesties Troops, Ceylon'') was the designation of the General Officer appointed to command all British Army units stationed in the island of Ceylon during the British colonial administration of the island. The post was succeeded by the Commander of the Ceylon Army. History The post entitled the holder a seat in the Executive Council of Ceylon and the Legislative Council of Ceylon, advised the Governor of Ceylon on military matters. Apart from British Army units that were deployed for garrison duty in the island, the officer held command over the Ceylon Defence Force if mobilized. However mobilization could be carried out only under orders from the Governor. Following independence in 1948, the command was split. With the creation of the Ceylon Army, it head had was referred to as the Commander of the Ceylon Army and the British troops in Ceylon came under the command of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geoffrey Layton
Admiral Sir Geoffrey Layton, (20 April 1884 – 4 September 1964) was a Royal Navy officer. He was in command of the submarine when, under attack from German vessels, it ran aground off the Danish coast during the First World War. Despite this incident, he rose to senior command in the Second World War and retired in 1947. His final appointment had been as Commander-in-Chief, Portsmouth. Early life and career Layton was the son of a Liverpool solicitor, George Layton, and was educated at Eastman's Royal Naval Academy. He joined the Royal Navy as a naval cadet on 15 May 1899 on HMS ''Britannia''. Following this he served as a midshipman aboard cruisers in the English Channel and off the south coast of the United States. Layton took his lieutenant's course and was promoted to that rank on 30 November 1905. He then he joined the submarine branch of the navy, in which he had his first command. From 1910 he did two years general service and returned to submarines in 1912, comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |