|
Colne Bridge
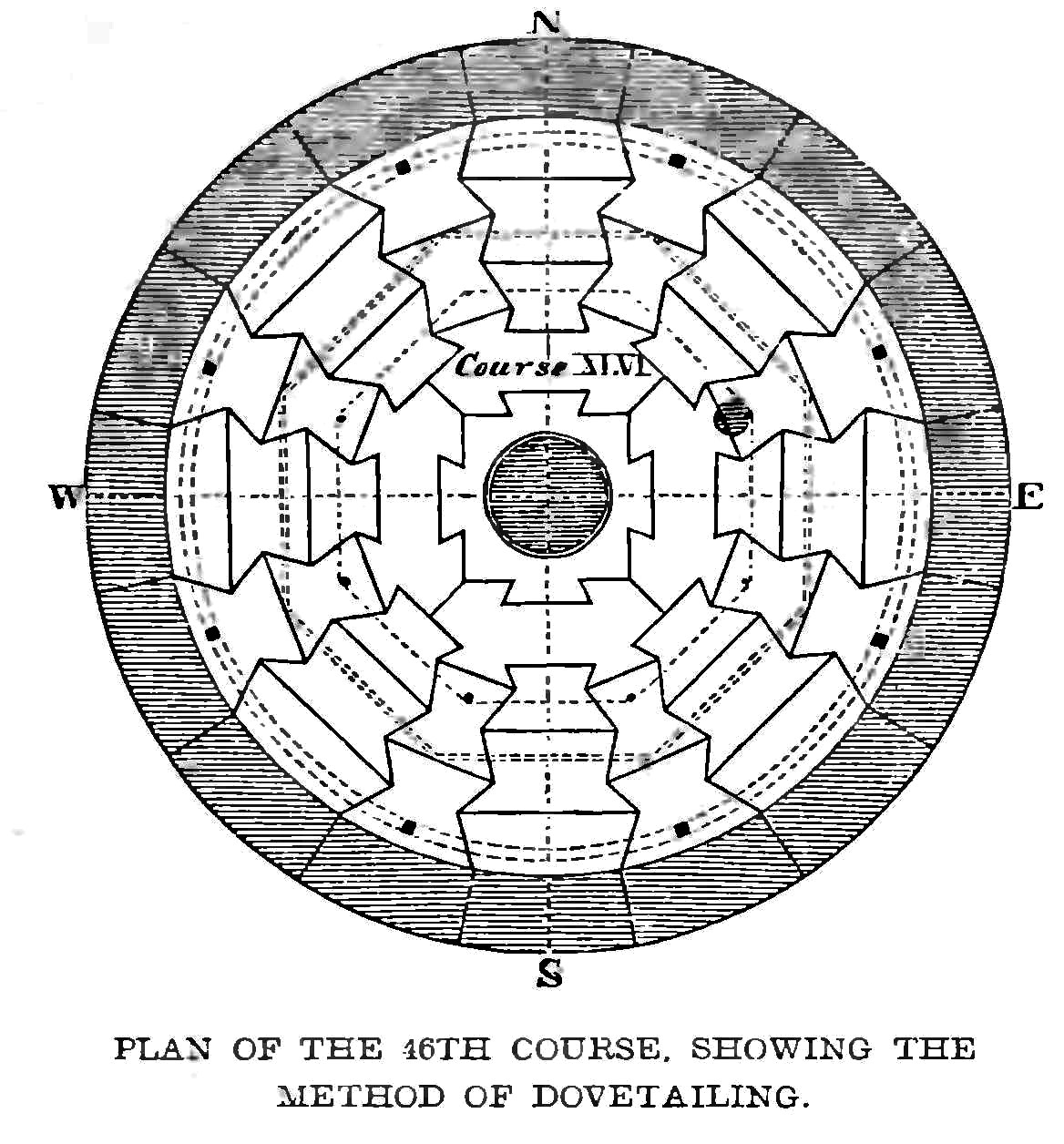
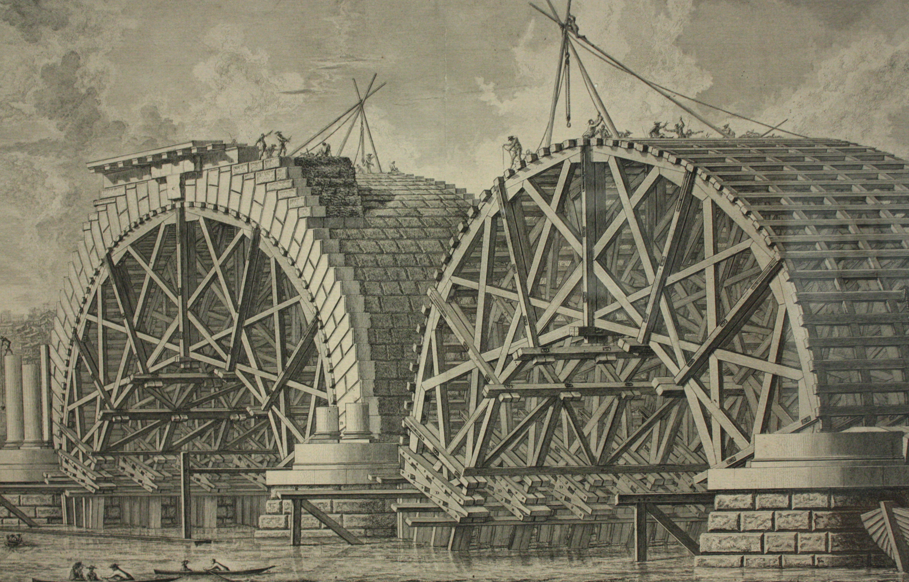
Colne Bridge () is an historic 18th-century bridge near Huddersfield, West Yorkshire, England. A Grade II listed stone-built arch bridge, it spans the River Colne between Bradley and Kirkheaton. A Colne Bridge was mentioned in the Fountains Abbey records of the 12th century. It gave its name to a village, and also to Colne Bridge Mill which was destroyed by fire in 1818. According to Ted Ruddock, Colne Bridge may have been the design inspiration for John Smeaton's work on the Blackfriars Bridge Blackfriars Bridge is a road and foot traffic bridge over the River Thames in London, between Waterloo Bridge and Blackfriars Railway Bridge, carrying the A201 road. The north end is in the City of London near the Inns of Court and Temple Chu .... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colne Bridge Mill
Colne Bridge Mill () was a factory, built in 1775, in the village of Colne Bridge near Bradley and Kirkheaton, Huddersfield, West Yorkshire, England, which was destroyed by fire on 14 February 1818. It was owned by the wealthy manufacturer Thomas Atkinson (1779–1838), who was also proprietor of another business at Bradley Mills, Huddersfield. Fire of 1818 Early in the morning of 14 February 1818, around 5 am, the fire was caused by a 10-year-old boy, James Thornton (), who was sent down into the Mill’s carding Carding is a mechanical process that disentangles, cleans and intermixes fibres to produce a continuous web or sliver (textiles), sliver suitable for subsequent processing. This is achieved by passing the fibres between differentially moving su ... room with a naked candle. The flame ignited the huge amounts of flammable material. Many were left trapped in the mill's upper floors. As the workers tried to escape and attempts were made to rescue them, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fountains Abbey
Fountains Abbey is one of the largest and best preserved ruined Cistercian monasteries in England. It is located approximately south-west of Ripon in North Yorkshire, near to the village of Aldfield. Founded in 1132, the abbey operated for 407 years, becoming one of the wealthiest monasteries in England until its dissolution, by order of Henry VIII, in 1539. In 1983, Studley Royal Park including the ruins of Fountains Abbey was purchased by the National Trust. The abbey is maintained by English Heritage. Foundation After a dispute and riot in 1132 at the Benedictine house of St Mary's Abbey in York, 13 monks were expelled, among them Saint Robert of Newminster. They were taken under the protection of Thurstan, Archbishop of York, who provided them with land in the valley of the River Skell, a tributary of the Ure. The enclosed valley had all the natural features needed for the creation of a monastery, providing shelter from the weather, stone and timber for building, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Colne, West Yorkshire
The River Colne in West Yorkshire is formed at the confluence of two brooks that originate in the Pennines close to Marsden. It flows in an easterly direction through the Colne Valley and Huddersfield towards Cooper Bridge where it flows into the River Calder. Course Brooks formed by rainwater high (between 300 and 480 metres AMSL) in the Pennines of West Yorkshire, flow down the hillsides through the small valleys known locally as ''cloughs'' to fill March Haigh and Redbrook Reservoirs. The Haigh Brook and Redbrook continue down the valley fed by more tributaries, until they converge at a scenic spot called Close Gate Bridge where the River Colne is formed. The river flows from west to east through the Colne Valley passing through Marsden, Slaithwaite and Milnsbridge to Huddersfield and then on to Cooper Bridge where it feeds the larger River Calder. Its tributaries include Wessenden Brook, Bradley Brook, Crimble Brook, Mag Brook, Fenay Brook, New Mill Dike and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arch Bridge
An arch bridge is a bridge with abutments at each end shaped as a curved arch. Arch bridges work by transferring the weight of the bridge and its loads partially into a horizontal thrust restrained by the abutments at either side. A viaduct (a long bridge) may be made from a series of arches, although other more economical structures are typically used today. History Possibly the oldest existing arch bridge is the Mycenaean Arkadiko Bridge in Greece from about 1300 BC. The stone corbel arch bridge is still used by the local populace. The well-preserved Hellenistic Eleutherna Bridge has a triangular corbel arch. The 4th century BC Rhodes Footbridge rests on an early voussoir arch. Although true arches were already known by the Etruscans and ancient Greeks, the Romans were – as with the vault and the dome – the first to fully realize the potential of arches for bridge construction. A list of Roman bridges compiled by the engineer Colin O'Connor featur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Listed Building
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern Ireland Environment Agency in Northern Ireland. The term has also been used in the Republic of Ireland, where buildings are protected under the Planning and Development Act 2000. The statutory term in Ireland is " protected structure". A listed building may not be demolished, extended, or altered without special permission from the local planning authority, which typically consults the relevant central government agency, particularly for significant alterations to the more notable listed buildings. In England and Wales, a national amenity society must be notified of any work to a listed building which involves any element of demolition. Exemption from secular listed building control is provided for some buildings in current use for worship, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huddersfield
Huddersfield is a market town in the Kirklees district in West Yorkshire, England. It is the administrative centre and largest settlement in the Kirklees district. The town is in the foothills of the Pennines. The River Holme's confluence into the similar-sized Colne to the south of the town centre which then flows into the Calder in the north eastern outskirts of the town. The rivers around the town provided soft water required for textile treatment in large weaving sheds, this made it a prominent mill town with an economic boom in the early part of the Victorian era Industrial Revolution. The town centre has much neoclassical Victorian architecture, one example is which is a Grade I listed building – described by John Betjeman as "the most splendid station façade in England" – and won the Europa Nostra award for architecture. It hosts the University of Huddersfield and three colleges: Greenhead College, Kirklees College and Huddersfield New College. The town ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Yorkshire
West Yorkshire is a metropolitan and ceremonial county in the Yorkshire and Humber Region of England. It is an inland and upland county having eastward-draining valleys while taking in the moors of the Pennines. West Yorkshire came into existence as a metropolitan county in 1974 after the reorganisation of the Local Government Act 1972 which saw it formed from a large part of the West Riding of Yorkshire. The county had a recorded population of 2.3 million in the 2011 Census making it the fourth-largest by population in England. The largest towns are Huddersfield, Castleford, Batley, Bingley, Pontefract, Halifax, Brighouse, Keighley, Pudsey, Morley and Dewsbury. The three cities of West Yorkshire are Bradford, Leeds and Wakefield. West Yorkshire consists of five metropolitan boroughs (City of Bradford, Calderdale, Kirklees, City of Leeds and City of Wakefield); it is bordered by the counties of Derbyshire to the south, Greater Manchester to the south-west, Lancash ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grade II Listed
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern Ireland Environment Agency in Northern Ireland. The term has also been used in the Republic of Ireland, where buildings are protected under the Planning and Development Act 2000. The statutory term in Ireland is " protected structure". A listed building may not be demolished, extended, or altered without special permission from the local planning authority, which typically consults the relevant central government agency, particularly for significant alterations to the more notable listed buildings. In England and Wales, a national amenity society must be notified of any work to a listed building which involves any element of demolition. Exemption from secular listed building control is provided for some buildings in current use for worship, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bradley, West Yorkshire
Bradley is a district of Huddersfield, West Yorkshire, England, 3 miles north-east of the town centre. It is generally just off the A62 Leeds Road and west of the River Colne and the Huddersfield Broad Canal. Located north of Deighton and east of Brackenhall (via Bradley bar), the area has two primary schools, a secondary school and three churches, (one Catholic, one Protestant and another converted to a gymnasium although the burial ground is still in use. See 'External Links' below for a detailed survey of all burials). * All Saints' Catholic College, previously All Saints' Catholic High School (which serves the towns of Brighouse and Huddersfield) is situated in the district. Built in 1960 and formerly two schools, (St Gregory's R.C. Grammar and St. Augustine's R.C. Secondary Modern) the two were combined in 1973 to form the currently large high school. * Bradley has a council estate with the Keldregate thoroughfare running parallel to Leeds Road (A62), as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirkheaton
Kirkheaton () is a village and former civil parish north-east of Huddersfield, now in the parish of Kirkburton, in the county of West Yorkshire, England, Historically, it is part of the West Riding of Yorkshire. It is in the Dalton ward of the Metropolitan Borough of Kirklees. In 1931 the parish had a population of 2,610. History The name Heaton comes from Old English "Heah" meaning high and "tun" meaning settlement along with Old Norse "Kirk" meaning church. Governance On 1 April 1938 the parish was abolished and merged with Kirkburton and Huddersfield. From 1894 to 1938 Kirkheaton was also an urban district. Parish Church The Parish church in Kirkheaton, dedicated to St John the Baptist, is one of the earliest churches in the area, there was a stone church on the site before the Norman Conquest. In the churchyard is a fine memorial to a disaster which shook the nation in 1818, a horrific fire in a local cotton mill, Colne Bridge Mill, in which 14 workers, all gir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Smeaton
John Smeaton (8 June 1724 – 28 October 1792) was a British civil engineer responsible for the design of bridges, canals, harbours and lighthouses. He was also a capable mechanical engineer and an eminent physicist. Smeaton was the first self-proclaimed "civil engineer", and is often regarded as the "father of civil engineering".Mark Denny (2007). "Ingenium: Five Machines That Changed the World". p. 34. JHU Press. He pioneered the use of hydraulic lime in concrete, using pebbles and powdered brick as aggregate. Smeaton was associated with the Lunar Society. Law and physics Smeaton was born in Austhorpe, Leeds, England. After studying at Leeds Grammar School he joined his father's law firm, but left to become a mathematical instrument maker (working with Henry Hindley), developing, among other instruments, a pyrometer to study material expansion. In 1750, his premises were in the Great Turnstile in Holborn. He was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society in 1753 and in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackfriars Bridge
Blackfriars Bridge is a road and foot traffic bridge over the River Thames in London, between Waterloo Bridge and Blackfriars Railway Bridge, carrying the A201 road. The north end is in the City of London near the Inns of Court and Temple Church, along with Blackfriars station. The south end is in the London Borough of Southwark, near the Tate Modern art gallery and the Oxo Tower. History The first fixed crossing at Blackfriars was a long toll bridge designed in an Italianate style by Robert Mylne and constructed with nine semi-elliptical arches of Portland stone. Beating designs by John Gwynn and George Dance, it took nine years to build, opening to the public in 1769. It was the third bridge across the Thames in the then built-up area of London, supplementing the ancient London Bridge, which dated from several centuries earlier, and Westminster Bridge. It was originally named "William Pitt Bridge" (after the Prime Minister William Pitt the Elder) as a dedication, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

.jpg)