|
Collodaria
Collodaria is a unicellular order (organisms within the order are called Collodarians) under the phylum Radiozoa (or Radiolaria) and the infrakingdom Rhizaria. Like most of the Radiolaria taxonomy, Collodaria was first described by Ernst Haeckel, a German scholar who published three volumes of manuscript describing the extensive samples of Radiolaria collected by the voyage of HMS ''Challenger''. Recent molecular phylogenetic studies concluded that there are Collodaria contains three families, Sphaerozodae, Collosphaeridae, and Collophidilidae. Story and origin Ernst Haeckel is the main contributor to species description in the phylum Radiolaria, which contains the order Collodaria. Members of Collodaria were first described in 1862. In 1881, ''Collodaria'' was defined by Haeckel in 1881 as “ Spumellaria without latticed shell.” The story behind this order involved the historic voyage of HMS ''Challenger''. As recorded in the manuscript of "Report on the Scientific Resu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiolaria
The Radiolaria, also called Radiozoa, are protozoa of diameter 0.1–0.2 mm that produce intricate mineral skeletons, typically with a central capsule dividing the cell into the inner and outer portions of endoplasm and ectoplasm. The elaborate mineral skeleton is usually made of silica. They are found as zooplankton throughout the global ocean. As zooplankton, radiolarians are primarily heterotrophic, but many have photosynthetic endosymbionts and are, therefore, considered mixotrophs. The skeletal remains of some types of radiolarians make up a large part of the cover of the ocean floor as siliceous ooze. Due to their rapid change as species and intricate skeletons, radiolarians represent an important diagnostic fossil found from the Cambrian onwards. Description Radiolarians have many needle-like pseudopods supported by bundles of microtubules, which aid in the radiolarian's buoyancy. The cell nucleus and most other organelles are in the endoplasm, while the ectoplasm is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
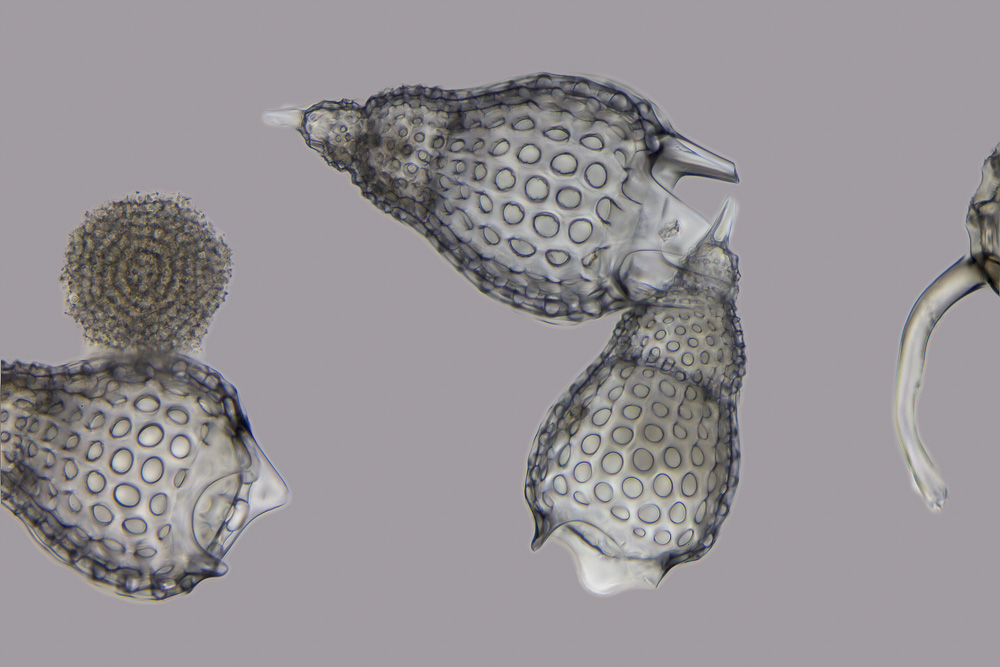
Polycystines
The polycystines are a group of radiolarians. They include the vast majority of the fossil radiolaria, as their skeletons are abundant in marine sediments, making them one of the most common groups of microfossils. These skeletons are composed of opaline silica. In some it takes the form of relatively simple spicules, but in others it forms more elaborate lattices, such as concentric spheres with radial spines or sequences of conical chambers. Two of the orders belonging to this group are the radially-symmetrical Spumellaria, dating back to the late Cambrian period, and the bilaterally-symmetrical Nasselaria, whose origin is placed within the lower Devonian The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, whe .... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycystine
The polycystines are a group of radiolarians. They include the vast majority of the fossil radiolaria, as their skeletons are abundant in marine sediments, making them one of the most common groups of microfossils. These skeletons are composed of opaline silica. In some it takes the form of relatively simple spicules, but in others it forms more elaborate lattices, such as concentric spheres with radial spines or sequences of conical chambers. Two of the orders belonging to this group are the radially-symmetrical Spumellaria, dating back to the late Cambrian period, and the bilaterally-symmetrical Nasselaria, whose origin is placed within the lower Devonian The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, w .... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microphyte
Microalgae or microphytes are microscopic algae invisible to the naked eye. They are phytoplankton typically found in freshwater and marine systems, living in both the water column and sediment. They are unicellular species which exist individually, or in chains or groups. Depending on the species, their sizes can range from a few micrometers (μm) to a few hundred micrometers. Unlike higher plants, microalgae do not have roots, stems, or leaves. They are specially adapted to an environment dominated by viscous forces. Microalgae, capable of performing photosynthesis, are important for life on earth; they produce approximately half of the atmospheric oxygen and use the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide to grow photoautotrophically. "Marine photosynthesis is dominated by microalgae, which together with cyanobacteria, are collectively called phytoplankton." Microalgae, together with bacteria, form the base of the food web and provide energy for all the trophic levels above them. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizaria Orders
The Rhizaria are an ill-defined but species-rich supergroup of mostly unicellular eukaryotes. Except for the Chlorarachniophytes and three species in the genus Paulinella in the phylum Cercozoa, they are all non-photosynthethic, but many foraminifera and radiolaria have a symbiotic relationship with unicellular algae. A multicellular form, ''Guttulinopsis vulgaris'', a cellular slime mold, has also been described. This group was used by Cavalier-Smith in 2002, although the term "Rhizaria" had been long used for clades within the currently recognized taxon. Being described mainly from rDNA sequences, they vary considerably in form, having no clear morphological distinctive characters (synapomorphies), but for the most part they are amoeboids with filose, reticulose, or microtubule-supported pseudopods. In the absence of an apomorphy, the group is ill-defined, and its composition has been very fluid. Some Rhizaria possess mineral exoskeleton (thecae or loricas), which is in differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxopodida
''Sticholonche'' is a genus of radiolarians with a single species, ''Sticholonche zanclea'', found in open oceans at depths of 99–510 metres. It is generally considered a heliozoan, placed in its own order, called the Taxopodida. However it has also been classified as an unusual radiolarian, and this has gained support from genetic studies, which place it near the Acantharea. ''Sticholonche'' are usually around 200 μm, though this varies considerably, and have a bilaterally symmetric shape, somewhat flattened and widened at the front. The axopods are arranged into distinct rows, six of which lie in a dorsal groove and are rigid, and the rest of which are mobile. These are used primarily for buoyancy, rather than feeding. They also have fourteen groups of prominent spines, and many smaller spicule Spicules are any of various small needle-like anatomical structures occurring in organisms Spicule may also refer to: * Spicule (sponge), small skeletal elements of sea spon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraphyly
In taxonomy (general), taxonomy, a group is paraphyletic if it consists of the group's most recent common ancestor, last common ancestor and most of its descendants, excluding a few Monophyly, monophyletic subgroups. The group is said to be paraphyletic ''with respect to'' the excluded subgroups. In contrast, a monophyletic group (a clade) includes a common ancestor and ''all'' of its descendants. The terms are commonly used in phylogenetics (a subfield of biology) and in the tree model of historical linguistics. Paraphyletic groups are identified by a combination of Synapomorphy and apomorphy, synapomorphies and symplesiomorphy, symplesiomorphies. If many subgroups are missing from the named group, it is said to be polyparaphyletic. The term was coined by Willi Hennig to apply to well-known taxa like Reptilia (reptiles) which, as commonly named and traditionally defined, is paraphyletic with respect to mammals and birds. Reptilia contains the last common ancestor of reptiles a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nassellaria
Nassellaria is an order of Rhizaria belonging to the class Radiolaria. The organisms of this order are characterized by a skeleton cross link with a cone or ring. Introduction Nassellaria is an order of Radiolaria under the class Polycystina. These organisms are unicellular eukaryotic heterotrophic plankton typically with a siliceous cone-shaped skeleton. The most common group of radiolarians are the polycystine radiolarians, which are divided into two subgroups: the spumellarians and the nassellarians. Both spumellarians and nassellarians are common chert-forming microfossils and are important in stratigraphical dating, as the oldest radiolarians are Precambrian in age. The nassellarians appear in the fossil record much later than their other polycystine relatives, the spumellarians. spumellarians can be seen as far back as the Precambrian, whereas nassellarians do not begin to appear until the Carboniferous. Nassellarians are believed to be have been increasing in species di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sticholonche
''Sticholonche'' is a genus of radiolarians with a single species, ''Sticholonche zanclea'', found in open oceans at depths of 99–510 metres. It is generally considered a heliozoan, placed in its own order, called the Taxopodida. However it has also been classified as an unusual radiolarian, and this has gained support from genetic studies, which place it near the Acantharea. ''Sticholonche'' are usually around 200 μm, though this varies considerably, and have a bilaterally symmetric shape, somewhat flattened and widened at the front. The axopods are arranged into distinct rows, six of which lie in a dorsal groove and are rigid, and the rest of which are mobile. These are used primarily for buoyancy, rather than feeding. They also have fourteen groups of prominent spines, and many smaller spicule Spicules are any of various small needle-like anatomical structures occurring in organisms Spicule may also refer to: * Spicule (sponge), small skeletal elements of sea spong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acantharea
The Acantharea (Acantharia) are a group of radiolarian protozoa, distinguished mainly by their strontium sulfate skeletons. Acantharians are heterotrophic marine microplankton that range in size from about 200 microns in diameter up to several millimeters. Some acantharians have photosynthetic endosymbionts and hence are considered mixotrophs. Morphology Acantharian skeletons are composed of strontium sulfate, SrSO4, in the form of mineral celestine crystal. Celestine is named for the delicate blue colour of its crystals, and is the heaviest mineral in the ocean. The denseness of their celestite ensures acantharian shells function as mineral ballast, resulting in fast sedimentation to bathypelagic depths. High settling fluxes of acantharian cysts have been observed at times in the Iceland Basin and the Southern Ocean, as much as half of the total gravitational organic carbon flux. Material was copied from this source, which is available under Creative Commons Attribut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838 by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ''zōḗ'' (), "life", meaning "ancient life" ). It is the longest of the Phanerozoic eras, lasting from , and is subdivided into six geologic periods (from oldest to youngest): # Cambrian # Ordovician # Silurian # Devonian # Carboniferous # Permian The Paleozoic comes after the Neoproterozoic Era of the Proterozoic Eon and is followed by the Mesozoic Era. The Paleozoic was a time of dramatic geological, climatic, and evolutionary change. The Cambrian witnessed the most rapid and widespread diversification of life in Earth's history, known as the Cambrian explosion, in which most modern phyla first appeared. Arthropods, molluscs, fish, amphibians, reptiles, and synapsids all evolved during the Paleozoic. Life began in the ocean bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micropaleontology
Micropaleontology (American spelling; spelled micropalaeontology in European usage) is the branch of paleontology ( palaeontology) that studies microfossils, or fossils that require the use of a microscope to see the organism, its morphology and its characteristic details. Microfossils Microfossils are fossils that are generally between 0.001mm and 1 mm in size, the study of which requires the use of light or electron microscopy. Fossils which can be studied by the naked eye or low-powered magnification, such as a hand lens, are referred to as macrofossils. For example, some colonial organisms, such as Bryozoa (especially the Cheilostomata) have relatively large colonies, but are classified by fine skeletal details of the small individuals of the colony. In another example, many fossil genera of Foraminifera, which are protists are known from shells (called "tests") that were as big as coins, such as the genus '' Nummulites''. Microfossils are a common feature o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |