|
Collateral Eminence
The collateral eminence is an elongated swelling lying lateral parallel with the hippocampus The hippocampus (: hippocampi; via Latin from Ancient Greek, Greek , 'seahorse'), also hippocampus proper, is a major component of the brain of humans and many other vertebrates. In the human brain the hippocampus, the dentate gyrus, and the .... It corresponds with the medial part of the collateral fissure, and its size depends on the depth and direction of this fissure. It is continuous behind with a flattened triangular area, the trigone of the lateral ventricle, situated between the posterior and inferior horn. It is not always present. References Cerebrum Anatomical variations {{neuroscience-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
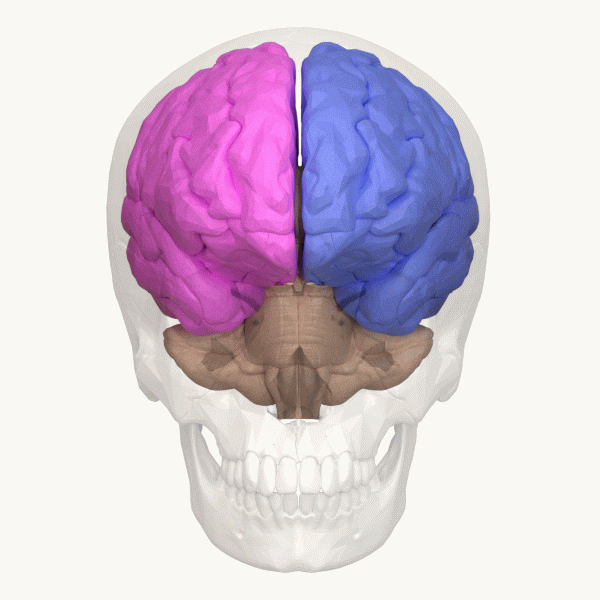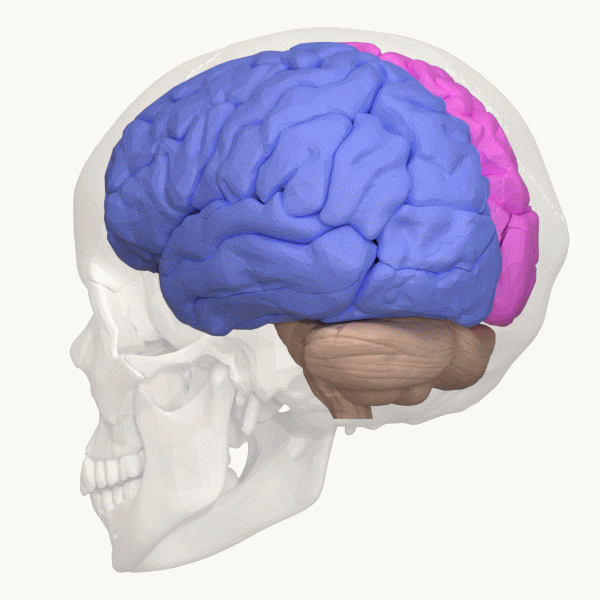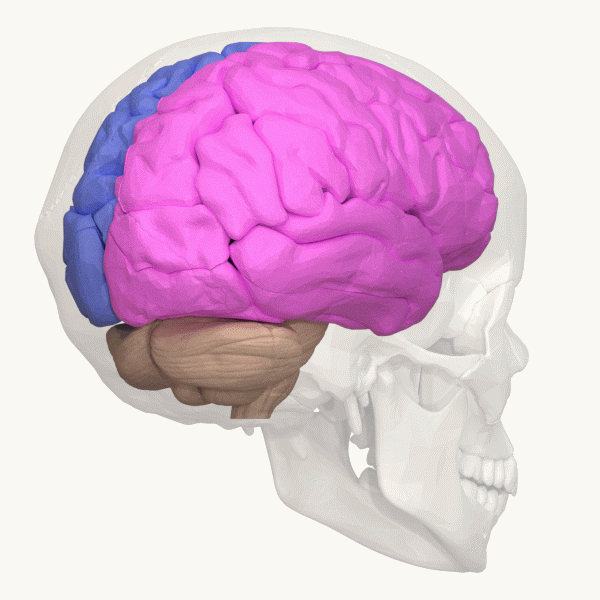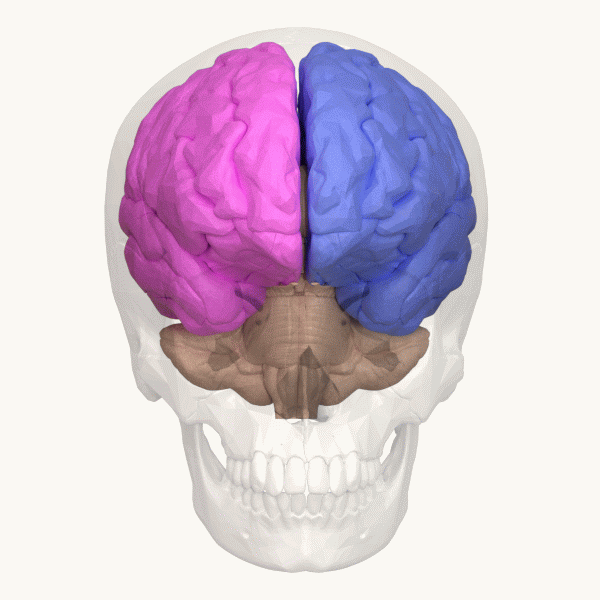
Lateralization Of Brain Function
The lateralization of brain function (or hemispheric dominance/ lateralization) is the tendency for some neural functions or cognitive processes to be specialized to one side of the brain or the other. The median longitudinal fissure separates the human brain into two distinct cerebral hemispheres connected by the corpus callosum. Both hemispheres exhibit Brain asymmetry, brain asymmetries in both structure and neuronal network composition associated with specialized function. Lateralization of brain structures has been studied using both healthy and split-brain patients. However, there are numerous counterexamples to each generalization and each human's brain develops differently, leading to unique lateralization in individuals. This is different from specialization, as lateralization refers only to the function of one structure divided between two hemispheres. Specialization is much easier to observe as a trend, since it has a stronger Anthropology, anthropological history. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippocampus
The hippocampus (: hippocampi; via Latin from Ancient Greek, Greek , 'seahorse'), also hippocampus proper, is a major component of the brain of humans and many other vertebrates. In the human brain the hippocampus, the dentate gyrus, and the subiculum are components of the hippocampal formation located in the limbic system. The hippocampus plays important roles in the Memory consolidation, consolidation of information from short-term memory to long-term memory, and in spatial memory that enables Navigation#Navigation in spatial cognition, navigation. In humans, and other primates the hippocampus is located in the archicortex, one of the three regions of allocortex, in each cerebral hemisphere, hemisphere with direct neural projections to, and reciprocal indirect projections from the neocortex. The hippocampus, as the medial pallium, is a structure found in all vertebrates. In Alzheimer's disease (and other forms of dementia), the hippocampus is one of the first regions of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medial Longitudinal Fasciculus
The medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) is a prominent bundle of nerve fibres which pass within the ventral/anterior portion of periaqueductal gray of the mesencephalon (midbrain). It contains the interstitial nucleus of Cajal, responsible for oculomotor control, head posture, and vertical eye movement. The MLF interconnects interneurons of each abducens nucleus with motor neurons of the contralateral oculomotor nucleus; thus, the MLF mediates coordination of horizontal (side to side) eye movements, ensuring the two eyes move in unison (thus also enabling saccadic eye movements). The MLF also contains fibers projecting from the vestibular nuclei to the oculomotor and trochlear nuclei as well as the interstitial nucleus of Cajal; these connections ensure that eye movements are coordinated with head movements (as sensed by the vestibular system). The medial longitudinal fasciculus is the main central connection for the oculomotor nerve, trochlear nerve, and abduce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collateral Fissure
The collateral fissure is a large sulcus on the tentorial surface of the cerebral hemisphere and extends from near the occipital pole to within a short distance of the temporal pole. It is also known as the medial occipitotemporal sulcus. Behind, it lies below and lateral to the calcarine fissure, from which it is separated by the lingual gyrus; in front, it is situated between the parahippocampal gyrus and the anterior part of the fusiform gyrus. Additional images File:Gray738.png, Coronal section through posterior cornua of lateral ventricle The lateral ventricles are the two largest ventricular system, ventricles of the brain and contain cerebrospinal fluid. Each cerebral hemisphere contains a lateral ventricle, known as the left or right lateral ventricle, respectively. Each later .... (Collateral fissure labeled at bottom center.) File:Hippocampal Limbic Connections Functions - Sanjoy Sanyal (Cropped from 5m28s to 6m30s) Collateral sulcus.webm, Human brain diss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trigone Of The Lateral Ventricle
The lateral ventricles are the two largest ventricles of the brain and contain cerebrospinal fluid. Each cerebral hemisphere contains a lateral ventricle, known as the left or right lateral ventricle, respectively. Each lateral ventricle resembles a C-shaped cavity that begins at an inferior horn in the temporal lobe, travels through a body in the parietal lobe and frontal lobe, and ultimately terminates at the interventricular foramina where each lateral ventricle connects to the single, central third ventricle. Along the path, a posterior horn extends backward into the occipital lobe, and an anterior horn extends farther into the frontal lobe. Structure Each lateral ventricle takes the form of an elongated curve, with an additional anterior-facing continuation emerging inferiorly from a point near the posterior end of the curve; the junction is known as the ''trigone of the lateral ventricle''. The centre of the superior curve is referred to as the ''body'', while the thre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebrum
The cerebrum (: cerebra), telencephalon or endbrain is the largest part of the brain, containing the cerebral cortex (of the two cerebral hemispheres) as well as several subcortical structures, including the hippocampus, basal ganglia, and olfactory bulb. In the human brain, the cerebrum is the uppermost region of the central nervous system. The cerebrum prenatal development, develops prenatally from the forebrain (prosencephalon). In mammals, the Dorsum (biology), dorsal telencephalon, or Pallium (neuroanatomy), pallium, develops into the cerebral cortex, and the ventral telencephalon, or Pallium (neuroanatomy), subpallium, becomes the basal ganglia. The cerebrum is also divided into approximately symmetric Lateralization of brain function, left and right cerebral hemispheres. With the assistance of the cerebellum, the cerebrum controls all voluntary actions in the human body. Structure The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain. Depending upon the position of the animal, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |