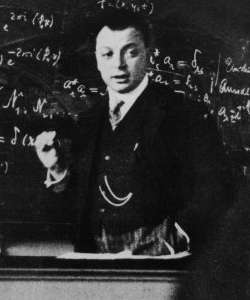|
Coincidence
A coincidence is a remarkable concurrence of events or circumstances that have no apparent causal connection with one another. The perception of remarkable coincidences may lead to supernatural, occult, or paranormal claims, or it may lead to belief in fatalism, which is a doctrine that events will happen in the exact manner of a predetermined plan. In general, the perception of coincidence, for lack of more sophisticated explanations, can serve as a link to folk psychology and philosophy. From a statistical perspective, coincidences are inevitable and often less remarkable than they may appear intuitively. Usually coincidences are chance events with underestimated probability. An example is the birthday problem, which shows that the probability of two persons having the same birthday already exceeds 50% in a group of only 23 persons. Etymology The first known usage of the word is from c. 1605 with the meaning "exact correspondence in substance or nature" from the French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synchronicity
Synchronicity (german: Synchronizität) is a concept first introduced by analytical psychologist Carl G. Jung "to describe circumstances that appear meaningfully related yet lack a causal connection." In contemporary research, synchronicity experiences refer to one's subjective experience that coincidences between events in one's mind and the outside world may be causally unrelated to each other yet have some other unknown connection. Jung held that this was a healthy, even necessary, function of the human mind that can become harmful within psychosis. Jung developed the theory of synchronicity as a hypothetical noncausal principle serving as the intersubjective or philosophically objective connection between these seemingly meaningful coincidences. Mainstream science generally regards that any such hypothetical principle either does not exist or falls outside the bounds of science. After first coining the term in the late 1920s or early 30s, Jung further developed the conc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Kammerer
Paul Kammerer (17 August 1880, in Vienna – 23 September 1926, in Puchberg am Schneeberg) was an Austrian biologist who studied and advocated Lamarckism, the theory that organisms may pass to their offspring characteristics acquired in their lifetime. Biography Education He began his academic career at the Vienna Academy by studying music but graduated with a degree in biology.Koestler, Arthur (1973). ''The Case of the Midwife Toad''. Vintage (first published 1971). Biological research Kammerer's work in biology largely involved altering the breeding and development of amphibians. He made ovoviviparous fire salamanders become viviparous, and viviparous alpine salamanders become ovoviviparous. In lesser-known experiments, he manipulated and bred olms. He made olms produce live young and bred dark-colored olms with full vision. He supported the Lamarckian theory of heritability of acquired characteristics, and he experimented extensively in an effort to prove the theory. Kamm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Jung
Carl Gustav Jung ( ; ; 26 July 1875 – 6 June 1961) was a Swiss psychiatrist and psychoanalyst who founded analytical psychology. Jung's work has been influential in the fields of psychiatry, anthropology, archaeology, literature, philosophy, psychology, and religious studies. Jung worked as a research scientist at the Burghölzli psychiatric hospital, in Zurich, under Eugen Bleuler. During this time, he came to the attention of Sigmund Freud, the founder of psychoanalysis. The two men conducted a The Freud/Jung Letters, lengthy correspondence and collaborated, for a while, on a joint vision of human psychology. Freud saw the younger Jung as the heir he had been seeking to take forward his "new science" of psychoanalysis and to this end secured his appointment as president of his newly founded International Psychoanalytical Association. Jung's research and personal vision, however, made it difficult for him to follow his older colleague's doctrine and they parted ways. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Roots Of Coincidence
''The Roots of Coincidence'' is a 1972 book by Arthur Koestler. It is an introduction to theories of parapsychology, including extrasensory perception and psychokinesis. Koestler postulates links between modern physics, their interaction with time and paranormal phenomena. It is influenced by Carl Jung's concept of synchronicity and the seriality of Paul Kammerer. Marks, David. (2000). '' The Psychology of the Psychic'' (2nd Edition). Prometheus Books. pp. 227- 246. In the book Koestler argues that science needs to take the possibility of the occurrence of phenomena that are outside our common sense view of the world more seriously and study them. He concludes that paranormal events are rare, unpredictable and capricious and need a paradoxical combination of skillful scientific experiment with a childlike excitement to be seen and recorded. The psychologist David Marks initially was critical of Koestler's book for endorsing pseudoscience. Marks noted that Koestler uncritically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Correlation Does Not Imply Causation
The phrase "correlation does not imply causation" refers to the inability to legitimately deduce a cause-and-effect relationship between two events or variables solely on the basis of an observed association or correlation between them. The idea that "correlation implies causation" is an example of a questionable-cause logical fallacy, in which two events occurring together are taken to have established a cause-and-effect relationship. This fallacy is also known by the Latin phrase ''cum hoc ergo propter hoc'' ('with this, therefore because of this'). This differs from the fallacy known as ''post hoc ergo propter hoc'' ("after this, therefore because of this"), in which an event following another is seen as a necessary consequence of the former event, and from conflation, the errant merging of two events, ideas, databases, etc., into one. As with any logical fallacy, identifying that the reasoning behind an argument is flawed does not necessarily imply that the resulting con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law Of Truly Large Numbers
The law of truly large numbers (a statistical adage), attributed to Persi Diaconis and Frederick Mosteller, states that with a large enough number of independent samples, any highly implausible (i.e. unlikely in any single sample, but with constant probability strictly greater than 0 in any sample) result is likely to be observed. Because we never find it notable when likely events occur, we highlight unlikely events and notice them more. The law is often used to falsify different pseudo-scientific claims; as such, it is sometimes criticized by fringe scientists. The law is meant to make a statement about probabilities and statistical significance: in large enough masses of statistical data, even minuscule fluctuations attain statistical significance. Thus in truly large numbers of observations, it is paradoxically easy to find significant correlations, in large numbers, which still do not lead to causal theories (see: spurious correlation), and which by their collective number, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paranormal
Paranormal events are purported phenomena described in popular culture, folk, and other non-scientific bodies of knowledge, whose existence within these contexts is described as being beyond the scope of normal scientific understanding. Notable paranormal beliefs include those that pertain to extrasensory perception (for example, telepathy), spiritualism and the pseudosciences of ghost hunting, cryptozoology, and ufology. Proposals regarding the paranormal are different from scientific hypotheses or speculations extrapolated from scientific evidence because scientific ideas are grounded in empirical observations and experimental data gained through the scientific method. In contrast, those who argue for the existence of the paranormal explicitly do not base their arguments on empirical evidence but rather on anecdote, testimony, and suspicion. The standard scientific models give the explanation that what appears to be paranormal phenomena is usually a misinterpretation, mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supernatural
Supernatural refers to phenomena or entities that are beyond the laws of nature. The term is derived from Medieval Latin , from Latin (above, beyond, or outside of) + (nature) Though the corollary term "nature", has had multiple meanings since the ancient world, the term "supernatural" emerged in the Middle Ages and did not exist in the ancient world. The supernatural is featured in folklore and religious contexts, but can also feature as an explanation in more secular contexts, as in the cases of superstitions or belief in the paranormal. The term is attributed to non-physical entities, such as angels, demons, gods, and spirits. It also includes claimed abilities embodied in or provided by such beings, including magic, telekinesis, levitation, precognition, and extrasensory perception. The philosophy of naturalism contends that nothing exists beyond the natural world, and as such approaches supernatural claims with skepticism. Etymology and history of the concept Occurr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolfgang Pauli
Wolfgang Ernst Pauli (; ; 25 April 1900 – 15 December 1958) was an Austrian theoretical physicist and one of the pioneers of quantum physics. In 1945, after having been nominated by Albert Einstein, Pauli received the Nobel Prize in Physics for his "decisive contribution through his discovery of a new law of Nature, the exclusion principle or Pauli principle". The discovery involved spin theory, which is the basis of a theory of the structure of matter. Early years Pauli was born in Vienna to a chemist, Wolfgang Joseph Pauli (''né'' Wolf Pascheles, 1869–1955), and his wife, Bertha Camilla Schütz; his sister was Hertha Pauli, a writer and actress. Pauli's middle name was given in honor of his godfather, physicist Ernst Mach. Pauli's paternal grandparents were from prominent families of Prague; his great-grandfather was the publisher Wolf Pascheles. Pauli's mother, Bertha Schütz, was raised in her mother's Roman Catholic religion; Pauli was raised as a Roman Catholic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birthday Problem
In probability theory, the birthday problem asks for the probability that, in a set of randomly chosen people, at least two will share a birthday. The birthday paradox is that, counterintuitively, the probability of a shared birthday exceeds 50% in a group of only 23 people. The birthday paradox is a veridical paradox: it appears wrong, but is in fact true. While it may seem surprising that only 23 individuals are required to reach a 50% probability of a shared birthday, this result is made more intuitive by considering that the comparisons of birthdays will be made between every possible pair of individuals. With 23 individuals, there are (23 × 22) / 2 = 253 pairs to consider, much more than half the number of days in a year. Real-world applications for the birthday problem include a cryptographic attack called the birthday attack, which uses this probabilistic model to reduce the complexity of finding a collision for a hash function, as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apophenia
Apophenia () is the tendency to perceive meaningful connections between unrelated things. The term (German: ' from the Greek verb ''ἀποφαίνειν'' (apophaínein)) was coined by psychiatrist Klaus Conrad in his 1958 publication on the beginning stages of schizophrenia. He defined it as "unmotivated seeing of connections ccompanied bya specific feeling of abnormal meaningfulness". He described the early stages of delusional thought as self-referential over-interpretations of actual sensory perceptions, as opposed to hallucinations. Apophenia has also come to describe a human propensity to unreasonably seek patterns in random information, such as can occur while gambling. Introduction Apophenia can be considered a commonplace effect of brain function. Taken to an extreme, however, it can be a symptom of psychiatric dysfunction, for example, as a symptom in paranoid schizophrenia, where a patient sees hostile patterns (for example, a conspiracy to persecute them) in ordin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Cars Parking
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to orange and opposite violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–740 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a secondary color (made from magenta and yellow) in the CMYK color model, and is the complementary color of cyan. Reds range from the brilliant yellow-tinged scarlet and vermillion to bluish-red crimson, and vary in shade from the pale red pink to the dark red burgundy. Red pigment made from ochre was one of the first colors used in prehistoric art. The Ancient Egyptians and Mayans colored their faces red in ceremonies; Roman generals had their bodies colored red to celebrate victories. It was also an important color in China, where it was used to color early pottery and later the gates and walls of palaces. In the Renaissance, the brilliant red costumes for the nobility and wealthy were dyed with kermes and cochineal. The 19th century brought the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |