|
Coherence (programming Language)
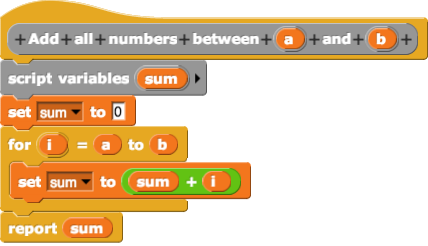
Subtext is a moderately visual programming language and environment, for writing application software. It is an experimental, research attempt to develop a new programming language, programming model, called Example Centric Programming, by treating copied blocks as first class prototypes, for program structure. It uses live text, similar to what occurs in spreadsheets as users update cells, for frequent feedback. It is intended to eventually be developed enough to become a practical language for daily use. It is planned to be open software; the license is not yet determined. Subtext was created by Jonathan Edwards who submitted a paper on the language to OOPSLA. It was accepted as part of the 2005 conference. Environment Early video previews of the Subtext environment were released circa 2006, which demonstrated the semantics of Subtext programs, and the close integration with the Subtex environment and runtime. Subtext programs are declared and manipulated (or mutated) by add ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subtext Vista
Subtext is any content of a creative work, which is not announced explicitly (by characters or author), but is implicit, or becomes something understood by the audience. Subtext has been used historically to imply controversial subjects without drawing the attention (or wrath) of censors. This has been especially true in comedy; it is also common in science fiction, where it can be easier—and/or safer—to deliver a social critique if, e.g., set in a time other than the (author's) present. Definitions Subtext is content "sub" i.e. "under" (with the sense of "hidden beneath") the verbatim wording; readers or audience must "gather" subtext "reading between the lines" or inferring meaning, a process needed for a clear and complete understanding of the text. A meaning stated explicitly is, by definition not subtext (for lack of hiding), and writers may be criticized for failure artfully to create and use subtext; such works may be faulted as too "on the nose", with the charac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Programming Language
In computing, a visual programming language (visual programming system, VPL, or, VPS) is any programming language that lets users create programs by manipulating program elements ''graphically'' rather than by specifying them ''textually''. A VPL allows programming with visual expressions, spatial arrangements of text and graphic symbols, used either as elements of syntax or secondary notation. For example, many VPLs (known as ''dataflow'' or ''diagrammatic programming'') are based on the idea of "boxes and arrows", where boxes or other screen objects are treated as entities, connected by arrows, lines or arcs which represent relations. Definition VPLs may be further classified, according to the type and extent of visual expression used, into icon-based languages, form-based languages, and diagram languages. Visual programming environments provide graphical or iconic elements which can be manipulated by users in an interactive way according to some specific spatial grammar for p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Application Software
Application may refer to: Mathematics and computing * Application software, computer software designed to help the user to perform specific tasks ** Application layer, an abstraction layer that specifies protocols and interface methods used in a communications network * Function application, in mathematics and computer science Processes and documents * Application for employment, a form or forms that an individual seeking employment must fill out * College application, the process by which prospective students apply for entry into a college or university * Patent application, a document filed at a patent office to support the grant of a patent Other uses * Application (virtue), a characteristic encapsulated in diligence * Topical application, the spreading or putting of medication to body surfaces See also * * Apply {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Programming Language
A programming language is a system of notation for writing computer programs. Most programming languages are text-based formal languages, but they may also be graphical. They are a kind of computer language. The description of a programming language is usually split into the two components of syntax (form) and semantics (meaning), which are usually defined by a formal language. Some languages are defined by a specification document (for example, the C programming language is specified by an ISO Standard) while other languages (such as Perl) have a dominant implementation that is treated as a reference. Some languages have both, with the basic language defined by a standard and extensions taken from the dominant implementation being common. Programming language theory is the subfield of computer science that studies the design, implementation, analysis, characterization, and classification of programming languages. Definitions There are many considerations when defini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spreadsheet
A spreadsheet is a computer application for computation, organization, analysis and storage of data in tabular form. Spreadsheets were developed as computerized analogs of paper accounting worksheets. The program operates on data entered in cells of a table. Each cell may contain either numeric or text data, or the results of formulas that automatically calculate and display a value based on the contents of other cells. The term ''spreadsheet'' may also refer to one such electronic document. Spreadsheet users can adjust any stored value and observe the effects on calculated values. This makes the spreadsheet useful for "what-if" analysis since many cases can be rapidly investigated without manual recalculation. Modern spreadsheet software can have multiple interacting sheets and can display data either as text and numerals or in graphical form. Besides performing basic arithmetic and mathematical functions, modern spreadsheets provide built-in functions for common financial a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OOPSLA
OOPSLA (Object-Oriented Programming, Systems, Languages & Applications) is an annual ACM research conference. OOPSLA mainly takes place in the United States, while the sister conference of OOPSLA, ECOOP, is typically held in Europe. It is operated by the Special Interest Group for Programming Languages (SIGPLAN) group of the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM). OOPSLA is an annual conference covering topics related to object-oriented programming systems, languages and applications. Like other conferences, OOPSLA offers various tracks and many simultaneous sessions, and thus has a different meaning to different people. It is an academic conference, and draws doctoral students who present peer-reviewed papers. It also draws a number of non-academic attendees, many of whom present experience reports and conduct panels, workshops and tutorials. OOPSLA has been instrumental in helping object-oriented programming develop into a mainstream programming paradigm. It has also helpe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subtext Scitest
Subtext is any content of a creative work, which is not announced explicitly (by characters or author), but is implicit, or becomes something understood by the audience. Subtext has been used historically to imply controversial subjects without drawing the attention (or wrath) of censors. This has been especially true in comedy; it is also common in science fiction, where it can be easier—and/or safer—to deliver a social critique if, e.g., set in a time other than the (author's) present. Definitions Subtext is content "sub" i.e. "under" (with the sense of "hidden beneath") the verbatim wording; readers or audience must "gather" subtext "reading between the lines" or inferring meaning, a process needed for a clear and complete understanding of the text. A meaning stated explicitly is, by definition not subtext (for lack of hiding), and writers may be criticized for failure artfully to create and use subtext; such works may be faulted as too "on the nose", with the charac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subtext Constest
Subtext is any content of a creative work, which is not announced explicitly (by characters or author), but is implicit, or becomes something understood by the audience. Subtext has been used historically to imply controversial subjects without drawing the attention (or wrath) of censors. This has been especially true in comedy; it is also common in science fiction, where it can be easier—and/or safer—to deliver a social critique if, e.g., set in a time other than the (author's) present. Definitions Subtext is content "sub" i.e. "under" (with the sense of "hidden beneath") the verbatim wording; readers or audience must "gather" subtext "reading between the lines" or inferring meaning, a process needed for a clear and complete understanding of the text. A meaning stated explicitly is, by definition not subtext (for lack of hiding), and writers may be criticized for failure artfully to create and use subtext; such works may be faulted as too "on the nose", with the charac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphical User Interface
The GUI ( "UI" by itself is still usually pronounced . or ), graphical user interface, is a form of user interface that allows users to interact with electronic devices through graphical icons and audio indicator such as primary notation, instead of text-based UIs, typed command labels or text navigation. GUIs were introduced in reaction to the perceived steep learning curve of CLIs ( command-line interfaces), which require commands to be typed on a computer keyboard. The actions in a GUI are usually performed through direct manipulation of the graphical elements. Beyond computers, GUIs are used in many handheld mobile devices such as MP3 players, portable media players, gaming devices, smartphones and smaller household, office and industrial controls. The term ''GUI'' tends not to be applied to other lower-display resolution types of interfaces, such as video games (where HUD (''head-up display'') is preferred), or not including flat screens like volumetric displays because ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Programming
In computer science, functional programming is a programming paradigm where programs are constructed by Function application, applying and Function composition (computer science), composing Function (computer science), functions. It is a declarative programming paradigm in which function definitions are Tree (data structure), trees of Expression (computer science), expressions that map Value (computer science), values to other values, rather than a sequence of Imperative programming, imperative Statement (computer science), statements which update the State (computer science), running state of the program. In functional programming, functions are treated as first-class citizens, meaning that they can be bound to names (including local Identifier (computer languages), identifiers), passed as Parameter (computer programming), arguments, and Return value, returned from other functions, just as any other data type can. This allows programs to be written in a Declarative programming, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Command-line Interface
A command-line interpreter or command-line processor uses a command-line interface (CLI) to receive commands from a user in the form of lines of text. This provides a means of setting parameters for the environment, invoking executables and providing information to them as to what actions they are to perform. In some cases the invocation is conditional based on conditions established by the user or previous executables. Such access was first provided by computer terminals starting in the mid-1960s. This provided an interactive environment not available with punched cards or other input methods. Today, many users rely upon graphical user interfaces and menu-driven interactions. However, some programming and maintenance tasks may not have a graphical user interface and use a command line. Alternatives to the command-line interface include text-based user interface menus (for example, IBM AIX SMIT), keyboard shortcuts, and various desktop metaphors centered on the pointer (usual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MIT CSAIL
Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) is a research institute at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) formed by the 2003 merger of the Laboratory for Computer Science (LCS) and the Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (AI Lab). Housed within the Ray and Maria Stata Center, CSAIL is the largest on-campus laboratory as measured by research scope and membership. It is part of the Schwarzman College of Computing but is also overseen by the MIT Vice President of Research. Research activities CSAIL's research activities are organized around a number of semi-autonomous research groups, each of which is headed by one or more professors or research scientists. These groups are divided up into seven general areas of research: * Artificial intelligence * Computational biology * Graphics and vision * Language and learning * Theory of computation * Robotics * Systems (includes computer architecture, databases, distributed systems, networks and network ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |