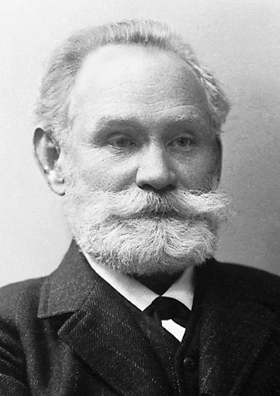|
Cognitive Revolution
The cognitive revolution was an intellectual movement that began in the 1950s as an interdisciplinary study of the mind and its processes, from which emerged a new field known as cognitive science. The preexisting relevant fields were psychology, linguistics, computer science, anthropology, neuroscience, and philosophy. The approaches used were developed within the then-nascent fields of artificial intelligence, computer science, and neuroscience. In the 1960s, the Harvard Center for Cognitive Studies and the Center for Human Information Processing at the University of California, San Diego were influential in developing the academic study of cognitive science. By the early 1970s, the cognitive movement had surpassed behaviorism as a psychological paradigm. Furthermore, by the early 1980s the cognitive approach had become the dominant line of research inquiry across most branches in the field of psychology. A key goal of early cognitive psychology was to apply the scientific metho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Science
Cognitive science is the interdisciplinary, scientific study of the mind and its processes. It examines the nature, the tasks, and the functions of cognition (in a broad sense). Mental faculties of concern to cognitive scientists include perception, memory, attention, reasoning, language, and emotion. To understand these faculties, cognitive scientists borrow from fields such as psychology, economics, artificial intelligence, neuroscience, linguistics, and anthropology.Thagard, PaulCognitive Science, ''The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy'' (Fall 2008 Edition), Edward N. Zalta (ed.). The typical analysis of cognitive science spans many levels of organization, from learning and decision-making to logic and planning; from neuron, neural circuitry to modular brain organization. One of the fundamental concepts of cognitive science is that "thinking can best be understood in terms of representational structures in the mind and computational procedures that operate on those structur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noam Chomsky
Avram Noam Chomsky (born December 7, 1928) is an American professor and public intellectual known for his work in linguistics, political activism, and social criticism. Sometimes called "the father of modern linguistics", Chomsky is also a major figure in analytic philosophy and one of the founders of the field of cognitive science. He is a laureate professor of linguistics at the University of Arizona and an institute professor emeritus at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Among the most cited living authors, Chomsky has written more than 150 books on topics such as linguistics, war, and politics. In addition to his work in linguistics, since the 1960s Chomsky has been an influential voice on the American Left, American left as a consistent critic of U.S. foreign policy, Criticism of capitalism, contemporary capitalism, and Corporate influence on politics in the United States, corporate influence on political institutions and the media. Born to Ashkenazi Jew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stimulus–response Model
The stimulus–response model is a conceptual framework in psychology that describes how individuals react to external Stimulus_(psychology), stimuli. According to this model, an external stimulus triggers a reaction in an organism, often without the need for conscious thought. This model emphasizes the mechanistic aspects of behavior, suggesting that behavior can often be predicted and controlled by understanding and manipulating the stimuli that trigger responses. Fields of application Stimulus–response models are applied in international relations, :en:Neuropsychological test, psychology, risk assessment, :en:Neuroscience, neuroscience, neurally-inspired system design, and many other fields. Pharmacological dose response relationships are an application of stimulus-response models. Another field this model can be applied to is psychological problems/disorders such as Tourette syndrome. Research shows Gilles de la Tourette syndrome (GTS) can be characterized by enhanced c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenneth Spence
Kenneth Wartinbee Spence (May 6, 1907 – January 12, 1967) was a prominent American psychologist known for both his theoretical and experimental contributions to learning theory and motivation. As one of the leading theorists of his time, Spence was the most cited psychologist in the 14 most influential psychology journals in the last six years of his life (1962 – 1967). A ''Review of General Psychology'' survey, published in 2002, ranked Spence as the 62nd most cited psychologist of the 20th century. Personal history Spence was born in Chicago on May 6, 1907. In 1911, Spence's father, an electrical engineer, moved the family to Montreal, Quebec, Canada when transferred by his employer, Western Electric. Spence spent his youth and adolescence there, attending West Hill High School in Notre Dame de Grace. While in high school, Spence was involved in basketball, tennis and track. Spence sustained a back injury during a track competition while attending McGill University. As part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clark L
Clark is an English language surname with historical links to England, Scotland, and Ireland, ultimately derived from the Latin ''clericus'' meaning "scribe", "secretary" or a scholar within a religious order, referring to someone who was educated. ''Clark'' evolved from "clerk". The first records of the name are found in 12th-century England. The name has many variants. It is often used as the Anglicized variant of Irish O'Cleary, Cleary. ''Clark'' is the twenty-seventh most common surname in the United Kingdom, including placing fourteenth in Scotland. Clark is also an occasional given name, as in the case of Clark Gable. According to the 1990 United States census, ''Clark'' was the twenty-first most frequently encountered surname, accounting for 0.23% of the population. According to the 2010 United States Census, ''Clark'' was the thirtieth most frequent surname, with a count of 562,679.United States Census Bureau (October 8, 2021) Retrieved on 2025-02-11 Disambiguation pag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John B
John Bryn Williams (born 1977), known as John B, is an English disc jockey and electronic music producer. He is widely recognised for his eccentric clothing, wild hair, and his production of several cutting edge drum and bass tracks. John B ranked number 76 in '' DJ Magazine''s 2010 Top 100 DJs annual poll, announced on 27 October 2010. Career Williams was born on 12 July 1977 in Maidenhead, Berkshire. He started producing music around the age of 14, and now is the head of drum and bass record label Beta Recordings, together with its more specialist drum and bass sub-labels Nu Electro, Tangent, and Chihuahua. He also has releases on Formation Records, Metalheadz and Planet Mu. Williams was ranked 92nd drum and bass DJ on the 2009 '' DJ Magazine'' top 100. Style While his trademark sound has evolved through the years, it generally involves female vocals and trance-like synths (a style which has been dubbed "trance and bass", "trancestep" and "futurestep" by listeners). Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 contiguous states border Canada to the north and Mexico to the south, with the semi-exclave of Alaska in the northwest and the archipelago of Hawaii in the Pacific Ocean. The United States asserts sovereignty over five Territories of the United States, major island territories and United States Minor Outlying Islands, various uninhabited islands in Oceania and the Caribbean. It is a megadiverse country, with the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest land area and List of countries and dependencies by population, third-largest population, exceeding 340 million. Its three Metropolitan statistical areas by population, largest metropolitan areas are New York metropolitan area, New York, Greater Los Angeles, Los Angel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulric Neisser
Ulric Richard Gustav Neisser (December 8, 1928 – February 17, 2012) was a German-American psychologist, Cornell University professor, and member of the US National Academy of Sciences. He has been referred to as the "father of cognitive psychology". Neisser researched and wrote about perception and memory. He posited that a person's mental processes could be measured and subsequently analyzed.Martin, D. (2012, February 25). Ulric Neisser Is Dead at 83; Reshaped Study of the Mind. The New York Times. Pp. A20. In 1967, Neisser published ''Cognitive Psychology'', which he later said was considered an attack on behaviorist psychological paradigms. ''Cognitive Psychology'' brought Neisser instant fame and recognition in the field of psychology. While ''Cognitive Psychology'' was considered unconventional, it was Neisser's ''Cognition and Reality'' that contained some of his most controversial ideas. A main theme in ''Cognition and Reality'' is Neisser's advocacy for experiments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbert A
Herbert may refer to: People * Herbert (musician), a pseudonym of Matthew Herbert * Herbert (given name) * Herbert (surname) Places Antarctica * Herbert Mountains, Coats Land * Herbert Sound, Graham Land Australia * Herbert, Northern Territory, a rural locality * Herbert, South Australia. former government town * Division of Herbert, an electoral district in Queensland * Herbert River, a river in Queensland * County of Herbert, a cadastral unit in South Australia Canada * Herbert, Saskatchewan, Canada, a town * Herbert Road, St. Albert, Canada New Zealand * Herbert, New Zealand, a town * Mount Herbert (New Zealand) United States * Herbert, Illinois, an unincorporated community * Herbert, Michigan, a former settlement * Herbert Creek, a stream in South Dakota * Herbert Island, Alaska Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities * Herbert (Disney character) * Herbert Pocket, a character in the Charles Dickens novel ''Great Expectations'' * Herbert West ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allen Newell
Allen Newell (March 19, 1927 – July 19, 1992) was an American researcher in computer science and cognitive psychology at the RAND Corporation and at Carnegie Mellon University's School of Computer Science, Tepper School of Business, and Department of Psychology. He, Herbert A. Simon, and Cliff Shaw contributed to the Information Processing Language (1956) and two of the earliest AI programs, the Logic Theorist (1956) and the General Problem Solver (1957). He and Simon were awarded the ACM's A.M. Turing Award in 1975 for their contributions to artificial intelligence and the psychology of human cognition. Early studies Newell completed his bachelor's degree in physics from Stanford in 1949. He was a graduate student at Princeton University from 1949 to 1950, where he studied mathematics. Due to his early exposure to an unknown field known as game theory and the experiences from the study of mathematics, he was convinced that he would prefer a combination of experime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marvin Minsky
Marvin Lee Minsky (August 9, 1927 – January 24, 2016) was an American cognitive scientist, cognitive and computer scientist concerned largely with research in artificial intelligence (AI). He co-founded the Massachusetts Institute of Technology's AI laboratory and wrote extensively about AI and philosophy. Minsky received many accolades and honors, including the 1969 Turing Award. Early life and education Marvin Lee Minsky was born in New York City, to Henry, an eye surgeon, and Fannie (Reiser), a Zionism, Zionist activist. His family was Jewish. He attended the Ethical Culture Fieldston School and the Bronx High School of Science. He later attended Phillips Academy in Andover, Massachusetts, Andover, Massachusetts. He then served in the United States Navy, US Navy from 1944 to 1945. He received a B.A. in mathematics from Harvard University in 1950 and a Doctor of Philosophy, Ph.D. in mathematics from Princeton University in 1954. His doctoral dissertation was titled "Theory of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John McCarthy (computer Scientist)
John McCarthy (September 4, 1927 – October 24, 2011) was an American computer scientist and cognitive scientist. He was one of the founders of the discipline of artificial intelligence. He co-authored the document that coined the term "artificial intelligence" (AI), developed the programming language family Lisp (programming language), Lisp, significantly influenced the design of the language ALGOL, popularized time-sharing, and invented Garbage collection (computer science), garbage collection. McCarthy spent most of his career at Stanford University. He received many accolades and honors, such as the 1971 Turing Award for his contributions to the topic of AI, the United States National Medal of Science, and the Kyoto Prize. Early life and education John McCarthy was born in Boston, Massachusetts, on September 4, 1927, to an Irish people, Irish immigrant father and a Lithuanian Jewish immigrant mother, John Patrick and Ida (Glatt) McCarthy. The family was obliged to relocat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |