|
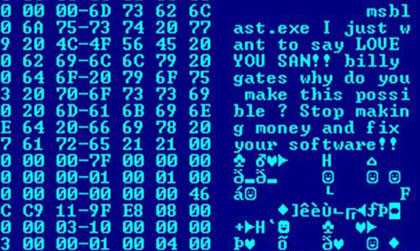
Code Injection
Code injection is the exploitation of a computer bug that is caused by processing invalid data. The injection is used by an attacker to introduce (or "inject") code into a vulnerable computer program and change the course of execution. The result of successful code injection can be disastrous, for example, by allowing computer viruses or computer worms to propagate. Code injection vulnerabilities occur when an application sends untrusted data to an interpreter. Injection flaws are most often found in SQL, LDAP, XPath, NoSQL queries, OS commands, XML parsers, SMTP headers, program arguments, etc. Injection flaws tend to be easier to discover when examining source code than via testing. Scanners and fuzzers can help find injection flaws. Injection can result in data loss or corruption, lack of accountability, or denial of access. Injection can sometimes lead to complete host takeover. Certain types of code injection are errors in interpretation, giving special meaning to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Bug
A software bug is an error, flaw or fault in the design, development, or operation of computer software that causes it to produce an incorrect or unexpected result, or to behave in unintended ways. The process of finding and correcting bugs is termed "debugging" and often uses formal techniques or tools to pinpoint bugs. Since the 1950s, some computer systems have been designed to deter, detect or auto-correct various computer bugs during operations. Bugs in software can arise from mistakes and errors made in interpreting and extracting users' requirements, planning a program's design, writing its source code, and from interaction with humans, hardware and programs, such as operating systems or libraries. A program with many, or serious, bugs is often described as ''buggy''. Bugs can trigger errors that may have ripple effects. The effects of bugs may be subtle, such as unintended text formatting, through to more obvious effects such as causing a program to crash, freezing the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Privilege Escalation
Privilege escalation is the act of exploiting a bug, a design flaw, or a configuration oversight in an operating system or software application to gain elevated access to resources that are normally protected from an application or user. The result is that an application with more privileges than intended by the application developer or system administrator can perform unauthorized actions. Background Most computer systems are designed for use with multiple user accounts, each of which has abilities known as privileges. Common privileges include viewing and editing files or modifying system files. Privilege escalation means users receive privileges they are not entitled to. These privileges can be used to delete files, view private information, or install unwanted programs such as viruses. It usually occurs when a system has a bug that allows security to be bypassed or, alternatively, has flawed design assumptions about how it will be used. Privilege escalation occurs in two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Libc
The C standard library or libc is the standard library for the C programming language, as specified in the ISO C standard.ISO/IEC (2018). '' ISO/IEC 9899:2018(E): Programming Languages - C §7'' Starting from the original ANSI C standard, it was developed at the same time as the C library POSIX specification, which is a superset of it. Since ANSI C was adopted by the International Organization for Standardization, the C standard library is also called the ISO C library. The C standard library provides macros, type definitions and functions for tasks such as string handling, mathematical computations, input/output processing, memory management, and several other operating system services. Application programming interface Header files The application programming interface (API) of the C standard library is declared in a number of header files. Each header file contains one or more function declarations, data type definitions, and macros. After a long period of stabili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dropbox (service)
Dropbox is a file hosting service operated by the American company Dropbox, Inc., headquartered in San Francisco, California, U.S. that offers cloud storage, file synchronization, personal cloud, and client software. Dropbox was founded in 2007 by MIT students Drew Houston and Arash Ferdowsi as a startup company, with initial funding from seed accelerator Y Combinator. Dropbox has experienced criticism and generated controversy for issues including security breaches and privacy concerns. Dropbox has been blocked in China since 2014. Concept Dropbox brings files together in one central place by creating a special folder on the user's computer. The contents of these folders are synchronized to Dropbox's servers and to other computers and devices where the user has installed Dropbox, keeping the same files up-to-date on all devices. Dropbox uses a freemium business model, where users are offered a free account with set storage size, with paid subscriptions available that off ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-site Scripting
Cross-site scripting (XSS) is a type of security vulnerability that can be found in some web applications. XSS attacks enable attackers to inject client-side scripts into web pages viewed by other users. A cross-site scripting vulnerability may be used by attackers to bypass access controls such as the same-origin policy. Cross-site scripting carried out on websites accounted for roughly 84% of all security vulnerabilities documented by Symantec up until 2007.During the second half of 2007, 11,253 site-specific cross-site vulnerabilities were documented by XSSed, compared to 2,134 "traditional" vulnerabilities documented by Symantec, in XSS effects vary in range from petty nuisance to significant security risk, depending on the sensitivity of the data handled by the vulnerable site and the nature of any security mitigation implemented by the site's owner network. Background Security on the web depends on a variety of mechanisms, including an underlying concept of trust know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HTML
The HyperText Markup Language or HTML is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It can be assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and scripting languages such as JavaScript. Web browsers receive HTML documents from a web server or from local storage and render the documents into multimedia web pages. HTML describes the structure of a web page semantically and originally included cues for the appearance of the document. HTML elements are the building blocks of HTML pages. With HTML constructs, images and other objects such as interactive forms may be embedded into the rendered page. HTML provides a means to create structured documents by denoting structural semantics for text such as headings, paragraphs, lists, links, quotes, and other items. HTML elements are delineated by ''tags'', written using angle brackets. Tags such as and directly introduce content into the page. Other tags such as surround ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft Windows
Windows is a group of several proprietary graphical operating system families developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. For example, Windows NT for consumers, Windows Server for servers, and Windows IoT for embedded systems. Defunct Windows families include Windows 9x, Windows Mobile, and Windows Phone. The first version of Windows was released on November 20, 1985, as a graphical operating system shell for MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces (GUIs). Windows is the most popular desktop operating system in the world, with 75% market share , according to StatCounter. However, Windows is not the most used operating system when including both mobile and desktop OSes, due to Android's massive growth. , the most recent version of Windows is Windows 11 for consumer PCs and tablets, Windows 11 Enterprise for corporations, and Windows Server 2022 for servers. Genealogy By marketing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Setuid
The Unix Unix (; trademarked as UNIX) is a family of multitasking, multiuser computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and ot ... access rights flags setuid and setgid (short for ''set user identity'' and ''set group identity'') allow users to run an executable with the file system permissions of the executable's owner or group respectively and to change behaviour in directories. They are often used to allow users on a computer system to run programs with temporarily elevated privileges in order to perform a specific task. While the assumed user id or group id privileges provided are not always elevated, at a minimum they are specific. The flags setuid and setgid are needed for tasks that require different privileges than what the user is normally granted, such as the ability to alter system files or databases to change their login password. Some of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superuser
In computing, the superuser is a special user account used for system administration. Depending on the operating system (OS), the actual name of this account might be root, administrator, admin or supervisor. In some cases, the actual name of the account is not the determining factor; on Unix-like systems, for example, the user with a user identifier (UID) of zero is the superuser, regardless of the name of that account; and in systems which implement a role based security model, any user with the role of superuser (or its synonyms) can carry out all actions of the superuser account. The principle of least privilege recommends that most users and applications run under an ordinary account to perform their work, as a superuser account is capable of making unrestricted, potentially adverse, system-wide changes. Unix and Unix-like In Unix-like computer OSes (such as Linux), ''root'' is the conventional name of the user who has all rights or permissions (to all files and programs) i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Privilege Escalation
Privilege escalation is the act of exploiting a bug, a design flaw, or a configuration oversight in an operating system or software application to gain elevated access to resources that are normally protected from an application or user. The result is that an application with more privileges than intended by the application developer or system administrator can perform unauthorized actions. Background Most computer systems are designed for use with multiple user accounts, each of which has abilities known as privileges. Common privileges include viewing and editing files or modifying system files. Privilege escalation means users receive privileges they are not entitled to. These privileges can be used to delete files, view private information, or install unwanted programs such as viruses. It usually occurs when a system has a bug that allows security to be bypassed or, alternatively, has flawed design assumptions about how it will be used. Privilege escalation occurs in two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Server Pages
Active Server Pages (ASP) is Microsoft's first server-side scripting language and engine for dynamic web pages. It was first released in December 1996, before being superseded in January 2002 by ASP.NET. History Initially released as an add-on to Internet Information Services (IIS) via the Windows NT 4.0 Option Pack (1996), it is included as a component of Windows Server (since the initial release of Windows 2000 Server). There have been three versions of ASP, each introduced with different versions of IIS: * ASP 1.0 was released in December 1996 as part of IIS 3.0 * ASP 2.0 was released in September 1997 as part of IIS 4.0 * ASP 3.0 was released in November 2000 as part of IIS 5.0 ASP 2.0 provides six built-in objects: Application, ASPError, Request, Response, Server, and Session. Session object, for example, represents a session that maintains the state of variables from page to page. The Active Scripting engine's support of the Component Object Model enables ASP webs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malware
Malware (a portmanteau for ''malicious software'') is any software intentionally designed to cause disruption to a computer, server, client, or computer network, leak private information, gain unauthorized access to information or systems, deprive access to information, or which unknowingly interferes with the user's computer security and privacy. By contrast, software that causes harm due to some deficiency is typically described as a software bug. Malware poses serious problems to individuals and businesses on the Internet. According to Symantec's 2018 Internet Security Threat Report (ISTR), malware variants number has increased to 669,947,865 in 2017, which is twice as many malware variants as in 2016. Cybercrime, which includes malware attacks as well as other crimes committed by computer, was predicted to cost the world economy $6 trillion USD in 2021, and is increasing at a rate of 15% per year. Many types of malware exist, including computer viruses, worms, Trojan horses, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)