|
Cockpit-in-Court Plans
The Cockpit-in-Court (also known as the Royal Cockpit) was an early theatre in London, located at the Palace of Whitehall, next to St. James's Park, now the site of 70 Whitehall, in Westminster. The structure was originally built by Henry VIII, after he had acquired Cardinal Wolsey's York Place to the north of the Palace of Westminster, following the Cardinal's downfall in 1529. It was one of a number of new pleasure buildings constructed for King Henry's entertainment, including a real tennis court, a bowling alley, and a tiltyard, and was used as an actual cockpit; that is, an area for staging cockfighting. Thus enlarged, the Palace of Whitehall became the main London residence of the Tudor and Stuart Kings of England, and the Palace of Westminster was relegated to ceremonial and administrative purposes only. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
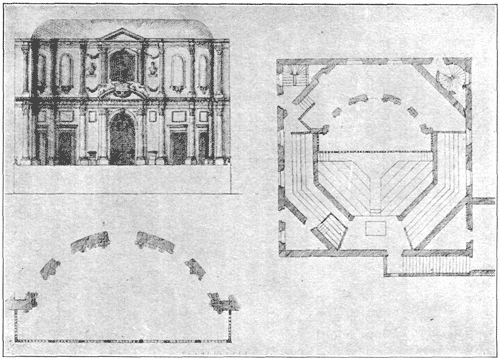
Cockpit-in-Court - Engraving By Mazell
The Cockpit-in-Court (also known as the Royal Cockpit) was an early theatre in London, located at the Palace of Whitehall, next to St. James's Park, now the site of 70 Whitehall, in Westminster. The structure was originally built by Henry VIII, after he had acquired Cardinal Wolsey's York Place to the north of the Palace of Westminster, following the Cardinal's downfall in 1529. It was one of a number of new pleasure buildings constructed for King Henry's entertainment, including a real tennis court, a bowling alley, and a tiltyard, and was used as an actual cockpit; that is, an area for staging cockfighting. Thus enlarged, the Palace of Whitehall became the main London residence of the Tudor and Stuart Kings of England, and the Palace of Westminster was relegated to ceremonial and administrative purposes only. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inigo Jones
Inigo Jones (; 15 July 1573 – 21 June 1652) was the first significant architect in England and Wales in the early modern period, and the first to employ Vitruvian rules of proportion and symmetry in his buildings. As the most notable architect in England and Wales, Jones was the first person to introduce the classical architecture of Rome and the Italian Renaissance to Britain. He left his mark on London by his design of single buildings, such as the Queen's House which is the first building in England designed in a pure classical style, and the Banqueting House, Whitehall, as well as the layout for Covent Garden square which became a model for future developments in the West End. He made major contributions to stage design by his work as theatrical designer for several dozen masques, most by royal command and many in collaboration with Ben Jonson. Early life and career Beyond the fact that he was born in Smithfield, London, as the son of clothworker Inigo Jones Snr., and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Master Of The Great Wardrobe
The King's Wardrobe, together with the Chamber, made up the personal part of medieval English government known as the King's household. Originally the room where the king's clothes, armour, and treasure were stored, the term was expanded to describe both its contents and the department of clerks who ran it. Early in the reign of Henry III the Wardrobe emerged out of the fragmentation of the '' Curia Regis'' to become the chief administrative and accounting department of the Household. The Wardrobe received regular block grants from the Exchequer for much of its history; in addition, however, the wardrobe treasure of gold and jewels enabled the king to make secret and rapid payments to fund his diplomatic and military operations, and for a time, in the 13th-14th centuries, it eclipsed the Exchequer as the chief spending department of central government. There were in fact two main Wardrobes for much of this period: around 1300 the confusingly-named Great Wardrobe, responsible only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christopher Monck, 2nd Duke Of Albemarle
Christopher Monck, 2nd Duke of Albemarle (14 August 1653 – 6 October 1688) was an English soldier and politician who sat in the House of Commons of England, House of Commons from 1667 to 1670 when he inherited the Dukedom and sat in the House of Lords. Origins Monck was the son and heir of George Monck, 1st Duke of Albemarle (1608–1670) by his wife Anne Clarges (d.1700), a daughter of John Clarges, "Farrier in the Savoy Palace, Savoy", of Drury Lane, Westminster. Anne's brother was Sir Thomas Clarges (c. 1618–1695), Member of Parliament, MP, who greatly assisted his brother-in-law, then before his elevation to the dukedom, General George Monck, in bringing about the Restoration of the English monarchy, Restoration of the Monarchy in 1660. She was the presumed widow of Thomas Radford, milliner, of New Exchange, Strand, Westminster, although it was said that her husband was still alive when her son was born. This left a question concerning Monck's legitimacy. Youth Mon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Pepys
Samuel Pepys (; 23 February 1633 – 26 May 1703) was an English diarist and naval administrator. He served as administrator of the Royal Navy and Member of Parliament and is most famous for the diary he kept for a decade. Pepys had no maritime experience, but he rose to be the Chief Secretary to the Admiralty under both King Charles II and King James II through patronage, diligence, and his talent for administration. His influence and reforms at the Admiralty were important in the early professionalisation of the Royal Navy. The detailed private diary that Pepys kept from 1660 until 1669 was first published in the 19th century and is one of the most important primary sources for the English Restoration period. It provides a combination of personal revelation and eyewitness accounts of great events, such as the Great Plague of London, the Second Dutch War, and the Great Fire of London. Early life Pepys was born in Salisbury Court, Fleet Street, London, on 23 Februar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green Room
In show business, the green room is the space in a theatre or similar venue that functions as a waiting room and lounge for performers before, during, and after a performance or show when they are not engaged on stage. Green rooms typically have seating for the performers, such as upholstered chairs and sofas. The origin of the term is often ascribed to such rooms historically being painted green. Modern green rooms need not necessarily adhere to a specifically green color scheme, though the theatrical tradition of the name remains. Some English theatres contained several green rooms, each ranked according to the status, fame, and salary of the actor: one could be fined for using a green room above one's station.The Concise Oxford Companion to the Theatre, edited by Phyllis Hartnoll, Oxford University Press, 1972, pg 220 * In 1792, Joseph Haslewood published a collection of memoirs of the actors and actresses of the London theatres entitled ''The Secret History of the Green-Room ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baize
Baize is a coarse woollen (or in cheaper variants cotton) cloth, similar in texture to felt, but more durable. History A mid-17th-century English ditty—much quoted in histories of ale and beer brewing in England—refers to 1525: Hops, heresies, bays, and beer;Came into England all in one year. ''Heresies'' refers to the Protestant Reformation, while ''bays'' is the Elizabethan spelling for ''baize''. Applications Baize is often used on billiards tables to cover the and , and is often used on other kinds of gaming tables (usually gambling) such as those for blackjack, baccarat, craps and other casino games. It is also found as a writing surface, particularly on 19th century pedestal desks. The surface finish of baize is coarse, thus increasing rolling resistance and perceptibly slowing billiard balls. Baize is available with and without a perceptible nap. Snooker, in which understanding nap effects is part of the game, uses the nappy variety, while pool and carom billia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dressing Room
A changing-room, locker-room, (usually in a sports, theater, or staff context) or changeroom (regional use) is a room or area designated for changing one's clothes. Changing-rooms are provided in a semi-public situation to enable people to change clothes with varying degrees of privacy. A fitting room, or dressing room, is a room where people try on clothes, such as in a department store. Separate changing-rooms may be provided for men and women, or there may be a non-gender-specific open space with individual cubicles or stalls, as with unisex public toilets. Many changing rooms include toilets, sinks and showers. Sometimes a changing room exists as a small portion of a restroom/washroom. For example, the men's and women's washrooms in Toronto's Dundas Square (which includes a water play area) each include a change area which is a blank counter space at the end of a row of sinks. In this case, the facility is primarily a washroom, and its use as a changing room is minimal, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles II Of England
Charles II (29 May 1630 – 6 February 1685) was King of Scotland from 1649 until 1651, and King of England, Scotland and Ireland from the 1660 Restoration of the monarchy until his death in 1685. Charles II was the eldest surviving child of Charles I of England, Scotland and Ireland and Henrietta Maria of France. After Charles I's execution at Whitehall on 30 January 1649, at the climax of the English Civil War, the Parliament of Scotland proclaimed Charles II king on 5 February 1649. But England entered the period known as the English Interregnum or the English Commonwealth, and the country was a de facto republic led by Oliver Cromwell. Cromwell defeated Charles II at the Battle of Worcester on 3 September 1651, and Charles fled to mainland Europe. Cromwell became virtual dictator of England, Scotland and Ireland. Charles spent the next nine years in exile in France, the Dutch Republic and the Spanish Netherlands. The political crisis that followed Cromwell's death in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interregnum
An interregnum (plural interregna or interregnums) is a period of discontinuity or "gap" in a government, organization, or social order. Archetypally, it was the period of time between the reign of one monarch and the next (coming from Latin ''inter-'', "between" and ''rēgnum'', "reign" rom ''rex, rēgis'', "king", and the concepts of interregnum and regency therefore overlap. Historically, longer and heavier interregna have been typically accompanied by widespread unrest, civil and succession wars between warlords, and power vacuums filled by foreign invasions or the emergence of a new power. A failed state is usually in interregnum. The term also refers to the periods between the election of a new parliament and the establishment of a new government from that parliament in parliamentary democracies, usually ones that employ some form of proportional representation that allows small parties to elect significant numbers, requiring time for negotiations to form a government. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Theatre Closure 1642
On September 2, 1642, just after the First English Civil War had begun, the Long Parliament ordered the closure of all London theatres. The order cited the current "times of humiliation" and their incompatibility with "public stage-plays", representative of "lascivious Mirth and Levity". The closure was the culmination of the rising anti-theatrical sentiment among Puritans, and along with William Prynne's ''Histriomastix'' (1633), its text was the most notorious attack on theatre in English history. The ban, which was not completely effective, was reinforced by an Act of 11 February 1648, at the beginning of the Second English Civil War, Second Civil War. It provided for the treatment of actors as rogue (vagrant), rogues, the demolition of theatre seating, and fines for spectators. On 24 January 1643, the actors pleaded with Parliament to reopen the theatres by writing a pamphlet called '''The Actors remonstrance or complaint for the silencing of their profession, and banishmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_05.jpg)


