|
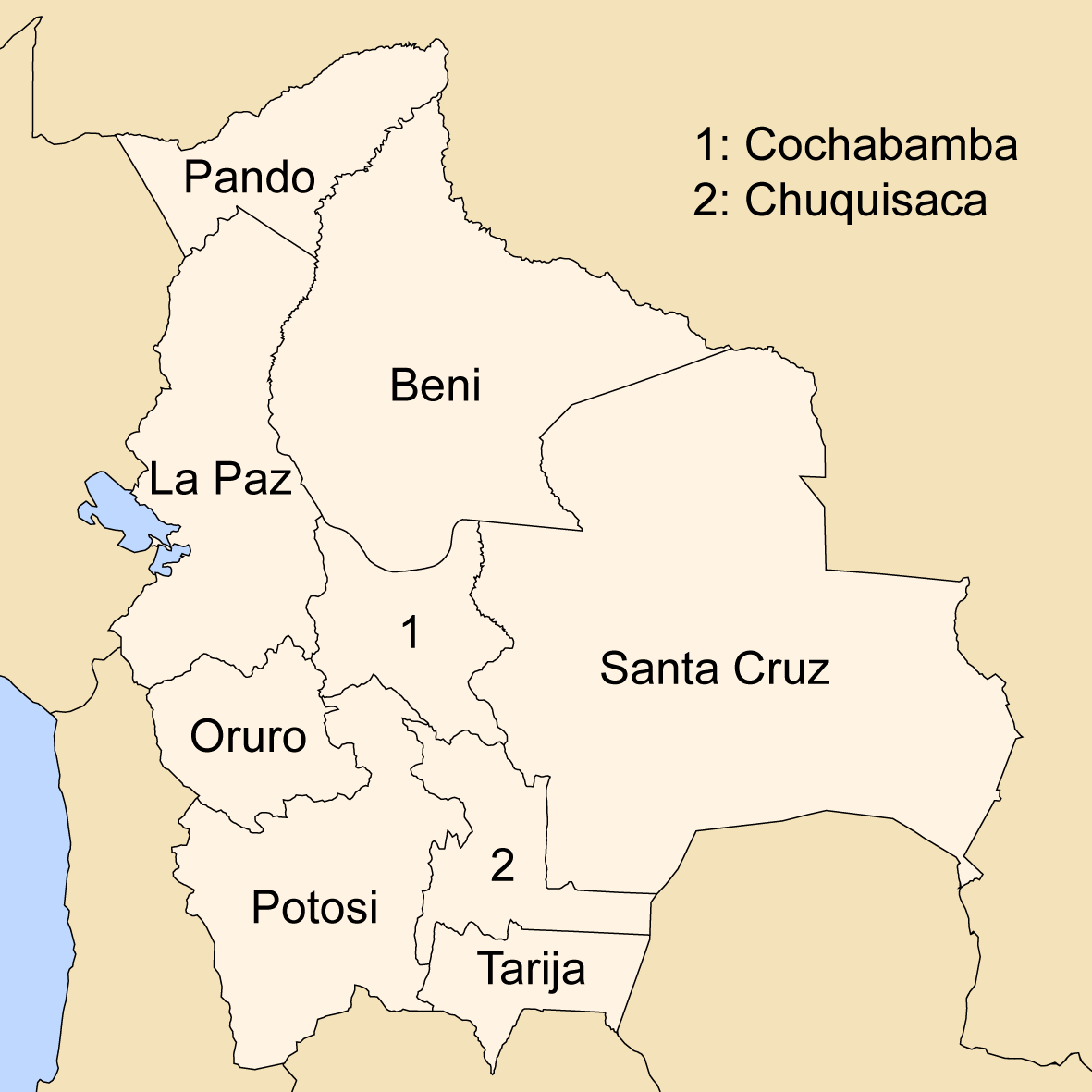
Cochabamba Department
Cochabamba ( ay, Quchapampa Jach'a Suyu, es, Departamento de Cochabamba , qu, Quchapampa Suyu), from Quechua ''qucha'' or ''qhucha'', meaning "lake", ''pampa'' meaning "plain", is one of the nine departments of Bolivia. It is known to be the "granary" of the country because of its variety of agricultural products from its geographical position. It has an area of 55,631 km2. Its population in the 2012 census was 1,758,143. Its capital is the city of Cochabamba, known as the "City of Eternal Spring" and "The Garden City" because of its spring-like temperatures all year. History The Cochabamba valley was inhabited for over a thousand years due to its fertile productive soils and climate. Archaeological evidence suggests that the initial valley inhabitants were of various ethnic indigenous groups. Tiwanaku, Tupuraya, Mojocoya, Omereque and Inca inhabited the valley at various times before the Spanish arrived. The first Spanish inhabitant of the Valley was Garci Ruiz de Orell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Departments Of Bolivia
Bolivia is a unitary state consisting of nine departments ( es, departamentos). Departments are the primary subdivisions of Bolivia, and possess certain rights under the Constitution of Bolivia. Each department is represented in the Plurinational Legislative Assembly—a bicameral legislature consisting of the Senate and the Chamber of Deputies. Each department is represented by four Senators, while Deputies are awarded to each department in proportion to their total population. Out of the nine departments, La Paz was originally the most populous, with 2,706,351 inhabitants as of 2012 but the far eastern department of Santa Cruz has since surpassed it by 2020; Santa Cruz also claims the title as the largest, encompassing . Pando is the least populated, with a population of 110,436. The smallest in area is Tarija, encompassing . Departments Former Departments By population Notes See also * ISO 3166-2:BO, the ISO codes for the departments of Bolivia. * Bolivi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Paz Department, Bolivia
The La Paz Department of Bolivia comprises with a 2012 census population of 2,706,359 inhabitants. It is situated at the western border of Bolivia, sharing Lake Titicaca with adjacent Peru. It contains the '' Cordillera Real'', which reaches altitudes of . Northeast of the Cordillera Real are the ''Yungas'', the steep eastern slopes of the Andes Mountains that make the transition to the Amazon River basin to the northeast. The capital of the department is the city of La Paz and is the administrative city and seat of government/national capital of Bolivia. Provinces The Department of La Paz is divided into 20 provinces (''provincias'') which are further subdivided into 85 municipalities (''municipios'') and - on the fourth level - into cantons. The provinces with their capitals are: Government The chief executive office of Bolivia's departments (since May 2010) is the Governor; before then, the office was called the Prefect, and until 2006 the prefect was appointed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capinota
Capinota is a small town in the Bolivian Department of Cochabamba and capital of the Capinota Province. Location ''Capinota'' is situated at an altitude of 2.380 m where the rivers Río Arque and Río Rocha meet to become the Río Caine and the Río Grande downstream. It is located 66 kilometers south of the department capital Cochabamba on the northern river bank of Río Arque, at . Climate The climate is semi-arid with a yearly rainfall average of 500 mm and a temperature average of 18 °C. The dry season lasts from May to September and has lower temperatures but no frost. The rainy season lasts from December to February and is warmer. Population The population is mainly of Quechua and mestizo of origin. The Capinota province has three sections: Capinota, Santivanes, and Sicaya and according to the 2012 census, the 29.659 population was distributed among Capinota, Santivanes, and Sicaya as 19.392, 6.527 and 3.740 inhabitants, respectively. The Capinota city is the bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arani, Bolivia
Arani, Jarani (from Quechua: ''jarani'' or ''jallmani'') is the capital of Arani Province and Arani Municipality located in Cochabamba Department in the center of Bolivia , image_flag = Bandera de Bolivia (Estado).svg , flag_alt = Horizontal tricolor (red, yellow, and green from top to bottom) with the coat of arms of Bolivia in the center , flag_alt2 = 7 × 7 square p ... at an altitude of 9,400 ft (2,865 m). At the time of census 2001 it had 3,512 inhabitants. Arani is well known for its bread due to the traditional use of multiple types of flour for making the bread. Bread is sold in various shops along the main streets leading to the main square, and along the major highway that leads to the city of Cochabamba. There is a bread festival held each year. Durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quillacollo
Quillacollo is the capital of Quillacollo Province in Cochabamba Department, Bolivia. The municipality was established on 14 September 1905 under the Presidency of Ismail Montes. Population and growth The city of Quillacollo is located westward of Cochabamba City. Quillacollo's population is 74,980 based on the 2001 census. The National Statistics Institute estimated in 2010 that the population had grown unexpectedly rapidly to approximately 142,724. The increase in population makes Quillacollo the second fastest growing city in Bolivia after El Alto in La Paz. Quillacollo City is one of the various provincial capitals around Cochabamba City, which are increasingly swallowed by the extending perimeter of "greater" Cochabamba (city). Quillacollo is linked to the city of Cochabamba through the Avenida Blanco Galindo, a particularly busy stretch on the main national highway. Quillacollo is mostly a market town with a sizable agricultural hinterland, but also hosts some relevant i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacaba
Sacaba, Sakawa is a capital city and a Municipalities of Bolivia, municipality in the Bolivian province of Chapare Province, Chapare. The city, located 13 kilometers eastward from Cochabamba, is the second largest city in the Cochabamba Department after Cochabamba city. Post-colonial architecture may be seen in the inner part of Sacaba; however, some has been destroyed due to lack of municipal care. Sacaba was the site of anti-coca eradication riots in 2002, which caused the removal of Evo Morales, leader of the ''cocalero'' movement and the Movement for Socialism (Bolivia), MAS, from his seat in the Bolivian congress. Morales opposed the closing of a coca market in Sacaba, and ensuing protests involved the death of several people on both sides. Morales served as president of Bolivia between 2006 and 2019. Demographics At the time of census 2001 Sacaba had 92,581 residents. Due to the lack of space in Cochabamba city's boundaries, several new urbanization complexes have been buil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punata
Punata is the capital of Punata Province and Punata Municipality in Cochabamba Department, Bolivia. At the time of census 2012 it had a population of 19,559 inhabitants and at the census 2012 the populations rose to 28.707 inhabitants. People from Punata and surrounding areas used to be called “Vallunos” meaning coming from the valleys of Punata and other surrounding small towns. Punata is renowned for its wonderful agricultural market held every Tuesday where people from surrounding towns and rural villages come to sell and buy. See also * Irrigation in alluvial fans {{Multiple issues, {{cleanup, date=April 2021, reason=Rephrase to remove journal-style arguments based on individual illustrations, condense excessive technical detail{{primary sources, date=April 2021{{overly detailed, date=April 2021 Water use i ... including the alluvial fan of Punata References External linksMap of Punata Province Populated places in Cochabamba Department {{CochabambaBO-ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cliza (town)
Cliza is a small town in the Cochabamba Department, Bolivia. It is the capital of the Germán Jordán Province and the Cliza Municipality. Along with Punata, Cliza is the major city in the valle alto of the Cochabamba Department. History It is believed that in the pre-columbine era, men from Cliza were known as "Sapanas" (quechua for braid), given that they wore their hair in a long braid. The Sapana men used to live in Sach'amoqo, abundant of green pastures, next to crystal clear springs, under the bluest sky. Manco Kapac's descendants farmed this land and practiced the three Inca commands: Ama quella (Do not be lazy), Ama llulla (Do not lie), and Ama sua (Do not steal), as well as the ayni. When the Spaniards arrived, the name Sach'amoqo was changed to Valle de Elisa because, it is said that when they took over the Tawantinsuyu and asked the Quechuas for the sapanas tribe's name, they answered "It's the tribe of the Lisas (Quechua for brave, surly)". The name was then chang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters (for their latitude), with a relatively narrow annual temperature range and few extremes of temperature. Oceanic climates can be found in both hemispheres generally between 45 and 63 latitude, most notably in northwestern Europe, northwestern America, as well as New Zealand. Precipitation Locations with oceanic climates tend to feature frequent cloudy conditions with precipitation, low hanging clouds, and frequent fronts and storms. Thunderstorms are normally few, since strong daytime heating and hot and cold air masses meet infrequently in the region. In most areas with an oceanic climate, precipitation comes in the form of rain for the majority of the year. However, some areas with this climate see some snowfall annually during winter. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subtropical Highland Climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters (for their latitude), with a relatively narrow annual temperature range and few extremes of temperature. Oceanic climates can be found in both hemispheres generally between 45 and 63 latitude, most notably in northwestern Europe, northwestern America, as well as New Zealand. Precipitation Locations with oceanic climates tend to feature frequent cloudy conditions with precipitation, low hanging clouds, and frequent fronts and storms. Thunderstorms are normally few, since strong daytime heating and hot and cold air masses meet infrequently in the region. In most areas with an oceanic climate, precipitation comes in the form of rain for the majority of the year. However, some areas with this climate see some snowfall annually during winter. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southwestern Amazonian Moist Forests
The Southwest Amazon moist forests (NT0166) is an ecoregion located in the Upper Amazon basin. The forest is characterized by a relatively flat landscape with alluvial plains dissected by undulating hills or high terraces. The biota of the southwest Amazon moist forest is very rich because of these dramatic edaphic and topographical variations at both the local and regional levels. This ecoregion has the highest number of both mammals and birds recorded for the Amazonian biogeographic realm: 257 with 11 endemic species for mammals and 782 and 17 endemics for birds. The inaccessibility of this region, along with few roads, has kept most of the habitat intact. Also, there are a number of protected areas, which preserve this extremely biologically rich ecoregion. Location The southwest Amazon moist forest region covers an extensive area of the Upper Amazon Basin comprising four sub-basins: (1) both the Pastaza- Marañon and (2) Ucayali River sub-basins drain into the Upper Amaz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |