|
Coat Of Arms Of Flanders
The arms of the Flemish Community are: ''Or, a lion rampant sable, armed and langued gules''. Although the lion has been in use for almost nine hundred years as the arms of the Count of Flanders, it only became the official symbol of the Flemish Community in 1973. At present its form and use is subject to the Decree of 7 November 1990. Origin of the arms The Flemish lion derives from the arms of the Counts of Flanders. Their first appearance is on a seal of Count Philip of Alsace, dating from 1163. As such they constitute the oldest of the many territorial arms bearing a lion in the Low Countries. Still, Count Philip was not the first of his line to bear a lion, for his cousin, William of Ypres, already used a seal with a lion passant in 1158; and the shield on the enamel effigy of about 1155 from the tomb of his maternal uncle, Geoffrey Plantagenet, Count of Anjou, bears numerous lions rampant. When the county of Flanders was inherited by the Dukes of Burgundy in 1405, the Fle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vlaanderen Wapen
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, language, politics, and history, and sometimes involving neighbouring countries. The demonym associated with Flanders is Fleming, while the corresponding adjective is Flemish. The official capital of Flanders is the City of Brussels, although the Brussels-Capital Region that includes it has an independent regional government. The powers of the government of Flanders consist, among others, of economic affairs in the Flemish Region and the community aspects of Flanders life in Brussels, such as Flemish culture and education. Geographically, Flanders is mainly flat, and has a small section of coast on the North Sea. It borders the French department of Nord to the south-west near the coast, the Dutch provinces of Zeeland, North Brabant a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
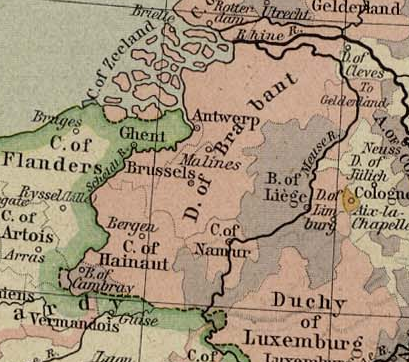
Duchy Of Brabant
The Duchy of Brabant was a State of the Holy Roman Empire established in 1183. It developed from the Landgraviate of Brabant and formed the heart of the historic Low Countries, part of the Burgundian Netherlands from 1430 and of the Habsburg Netherlands from 1482, until it was partitioned after the Dutch revolt. Present-day North Brabant (''Noord-Brabant'') was ceded to the Generality Lands of the Dutch Republic according to the 1648 Peace of Westphalia, while the reduced duchy remained part of the Habsburg Netherlands until it was conquered by French Revolutionary forces in 1794, which was recognized by treaty in 1797. Today all the duchy's former territories, apart from exclaves, are in Belgium except for the Dutch province of North Brabant. Geography The Duchy of Brabant (adjective: ''Brabantian'' or '' Brabantine'') was historically divided into four parts, each with its own capital. The four capitals were Leuven, Brussels, Antwerp and 's-Hertogenbosch. Before 's-Herto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, language, politics, and history, and sometimes involving neighbouring countries. The demonym associated with Flanders is Fleming, while the corresponding adjective is Flemish. The official capital of Flanders is the City of Brussels, although the Brussels-Capital Region that includes it has an independent regional government. The powers of the government of Flanders consist, among others, of economic affairs in the Flemish Region and the community aspects of Flanders life in Brussels, such as Flemish culture and education. Geographically, Flanders is mainly flat, and has a small section of coast on the North Sea. It borders the French department of Nord to the south-west near the coast, the Dutch provinces of Zeeland, North Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Welles, 1st Viscount Welles
John (de) Welles, 1st Viscount Welles, KG (c. 1450 – 9 February 1498) was an English Lancastrian nobleman who was made a Knight of the Garter. John was born about 1450 to Lionel de Welles, 6th Baron Welles and Margaret Beauchamp. He was a maternal half-brother of Margaret Beaufort, and thus an uncle of the half-blood of Henry VII. John died and was buried in February 1498 in Westminster, England. War of the Roses John's father, Lionel de Welles, 6th Baron Welles, was slain at the Battle of Towton in 1461, and his elder half-brother, Richard Welles, 7th Baron Welles, inherited the Welles barony. Richard Welles and his son and heir, Robert Welles, 8th Baron Willoughby de Eresby, were both beheaded in March 1470 for involvement in an uprising against Edward IV in Lincolnshire. After the death of Robert Welles, the Welles barony was inherited, in her own right, by his only sister, Joan Welles. However shortly after Joan Welles' death in about 1474/5, both her father, Richar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Jülich
The Duchy of Jülich (german: Herzogtum Jülich; nl, Hertogdom Gulik; french: Duché de Juliers) comprised a state within the Holy Roman Empire from the 11th to the 18th centuries. The duchy lay west of the Rhine river and was bordered by the Electorate of Cologne to the east and the Duchy of Limburg to the west. It had territories on both sides of the river Rur, around its capital Jülich – the former Roman ''Iuliacum'' – in the lower Rhineland. The duchy amalgamated with the County of Berg beyond the Rhine in 1423, and from then on also became known as ''Jülich-Berg''. Later it became part of the United Duchies of Jülich-Cleves-Berg. Its territory lies in present-day Germany (part of North Rhine-Westphalia) and in the present-day Netherlands (part of the Limburg province), its population sharing the same Limburgish dialect. History In the 9th century a certain Matfried was count of Jülich (pagus Juliacensis). The first count in the gau of Jülich in Lower Lor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of Flanders
The flag of Flanders, called the ''Vlaamse Leeuw'' ("Flemish Lion") or ''leeuwenvlag'' ("Lion flag"), is the flag of the Flemish Community and Flemish Region in Belgium. The flag was officially adopted by the Cultural Council for the Dutch Cultural Community (''Cultuurraad voor de Nederlandse Cultuurgemeenschap'') in 1973, and later, in 1985, by its successor, the Flemish Parliament. In 1990, the coat of arms was also adopted as an official symbol. The flag of Flanders is described as ''Or, a lion rampant armed and langued Gules.'' Variants See also * Coat of arms of Flanders * List of Belgian flags * Flag of Belgium * Flag of Wallonia * Flag of the Brussels-Capital Region References {{Flanders topics Flags of Belgium, Flanders Flanders Flags introduced in 1973, Flanders Flags displaying animals, Flanders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coat Of Arms Of The Netherlands
The coat of arms of the Kingdom of the Netherlands was originally adopted in 1815 and later modified in 1907. The arms are a composite of the arms of the former Dutch Republic and the arms of the House of Nassau, it features a checkered shield with a lion grasping a sword in one hand and a bundle of arrows in the other and is the heraldic symbol of the monarch ( King Willem-Alexander) and the country. The monarch uses a version of the arms with a mantle ( nl, Koninklijk wapen) while the government of the Netherlands uses a smaller version without the mantle (cloak) or the pavilion, sometimes only the shield and crown are used ( nl, Rijkswapen). The components of the coats of arms were regulated by Queen Wilhelmina in a royal decree of 10 July 1907, affirmed by Queen Juliana in a royal decree of 23 April 1980. Description The blazon is as follows: '' Azure, billetty Or a lion with a coronet Or armed and langued Gules holding in his dexter paw a sword Argent hilted Or and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communities, Regions And Language Areas Of Belgium
Belgium is a federal state comprising three communities and three regions that are based on four language areas. For each of these subdivision types, the subdivisions together make up the entire country; in other words, the types overlap. The language areas were established by the Second Gilson Act, which entered into force on 2 August 1963. The division into language areas was included in the Belgian Constitution in 1970. Through constitutional reforms in the 1970s and 1980s, regionalisation of the unitary state led to a three-tiered federation: federal, regional, and community governments were created, a compromise designed to minimize linguistic, cultural, social, and economic tensions. Schematic overview This is a schematic overview of the basic federal structure of Belgium as defined by Title I of the Belgian Constitution. Each of the entities either have their own parliament and government (for the federal state, the communities and the regions) or their own council a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Vlaamse Leeuw
"" (; The Flemish Lion) is the official anthem of Flanders, a region and community in Belgium. Composition The words of this anthem were written in July 1847 by Hippoliet Van Peene (1811–1864) who was clearly inspired by the song ''Sie sollen ihn nicht haben, / den freien Deutschen Rhein, / So lang sich Herzen laben / An seinem Feuerwein'' (They must never get our free German Rhine, As long as hearts relish its fiery wine) by the German author Nikolaus Becker. The music, by Karel Miry (1823–1899), is apparently influenced by Robert Schumann's ''Sonntags am Rhein.'' Like France's Marseillaise, ''De Vlaamse Leeuw'' is a nationalist battle song. Franco-Belgian political tension in the mid-19th century made the Flemish public mood ripe for such an expression of regional feeling. At the time, it was not meant as anti-Belgian (as it often came to be seen by Flemish separatists and their Belgicist opponents), for the "enemy" it refers to is Belgium's southwestern neighbour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippoliet Van Peene
Hippoliet Jan Van Peene (1 January 1811 in Kaprijke – 19 February 1864 in Ghent) was a Flemish physician and playwright. He studied medicine at the State University of Leuven and became a physician in Kaprijke and later in Ghent. In 1847 he wrote the lyrics of the Flemish anthem "De Vlaamse Leeuw "" (; The Flemish Lion) is the official anthem of Flanders, a region and community in Belgium. Composition The words of this anthem were written in July 1847 by Hippoliet Van Peene (1811–1864) who was clearly inspired by the song ''Sie s ..." of which the music was composed by Karel Miry. He was the first modern Flemish playwright and he wrote 35 theatre plays, which in his time were performed by ''Broedermin en Taelyver'' in Ghent. At the inauguration of the Minard Theatre in 1847, his ''Brigitta of de Twee Vondelingen'' was performed. Bibliography * ''Keizer Karel en de Berchemsche Boer'', comedy, 1841 * ''Jacob van Artevelde'', historical drama, 1841 * ''Willem van Dam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Golden Spurs
The Battle of the Golden Spurs ( nl, Guldensporenslag; french: Bataille des éperons d'or) was a military confrontation between the royal army of France and rebellious forces of the County of Flanders on 11 July 1302 during the Franco-Flemish War (1297–1305). It took place near the town of Kortrijk (Courtrai) in modern-day Belgium and resulted in an unexpected victory for the Flemish. It is sometimes referred to as the Battle of Courtrai. On 18 May 1302, after two years of French military occupation and several years of unrest, many cities in Flanders revolted against French rule, and the local militia massacred many Frenchmen in the city of Bruges. King Philip IV of France immediately organized an expedition of 8,000 troops, including 2,500 men-at-arms, under Count Robert II of Artois to put down the rebellion. Meanwhile, 9,400 men from the civic militias of several Flemish cities were assembled to counter the expected French attack. When the two armies met outside the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hendrik Conscience
Henri (Hendrik) Conscience (3 December 1812 – 10 September 1883) was a Belgian author. He is considered the pioneer of Dutch-language literature in Flanders, writing at a time when Belgium was dominated by the French language among the upper classes, in literature and government. Conscience fought as a Belgian revolutionary in 1830 and was a notable writer in the Romanticist style popular in the early 19th century. He is best known for his romantic nationalist novel, '' The Lion of Flanders'' (1838), inspired by the victory of a Flemish peasant militia over French knights at the 1302 Battle of the Golden Spurs during the Franco-Flemish War. Over the course of his career, he published over 100 novels and novellas and achieved considerable popularity. After his death, with the decline of romanticism, his works became less fashionable but are still considered as classics of Flemish literature. Early life Childhood Hendrik was the son of a Frenchman, Pierre Conscience, from Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |