|
Coase Conjecture
The Coase conjecture, developed first by Ronald Coase, is an argument in monopoly theory. The conjecture sets up a situation in which a monopolist sells a durable good to a market where resale is impossible and faces consumers who have different valuations. The conjecture proposes that a monopolist that does not know individuals' valuations will have to sell its product at a low price if the monopolist tries to separate consumers by offering different prices in different periods. This is because the monopolist is, in effect, in price competition with itself over several periods and the consumer with the highest valuation, if he is patient enough, can simply wait for the lowest price. Thus the monopolist will have to offer a competitive price in the first period which will be low. The conjecture holds only when there is an infinite time horizon, as otherwise a possible action for the monopolist would be to announce a very high price until the second to last period, and then sell a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ronald Coase
Ronald Harry Coase (; 29 December 1910 – 2 September 2013) was a British economist and author. Coase was educated at the London School of Economics, where he was a member of the faculty until 1951. He was the Clifton R. Musser Professor of Economics at the University of Chicago Law School, where he arrived in 1964 and remained for the rest of his life. He received the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences in 1991. Coase believed economists should study real-world wealth creation, in the manner of Adam Smith, stating, "It is suicidal for the field to slide into a hard science of choice, ignoring the influences of society, history, culture, and politics on the working of the economy." He believed economic study should reduce emphasis on Price Theory or theoretical markets and instead focus on real markets. He established the case for the corporation as a means to pay the costs of operating a marketplace. Coase is best known for two articles: "The Nature of the Firm" (1937), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Price Discrimination
Price discrimination (differential pricing, equity pricing, preferential pricing, dual pricing, tiered pricing, and surveillance pricing) is a Microeconomics, microeconomic Pricing strategies, pricing strategy where identical or largely similar goods or services are sold at different Price, prices by the same provider to different buyers based on which Market segmentation, market segment they are perceived to be part of. Price discrimination is distinguished from product differentiation by the difference in production cost for the differently priced products involved in the latter strategy. Price discrimination essentially relies on the variation in customers' willingness to pay and in the Demand elasticity, elasticity of their demand. For price discrimination to succeed, a seller must have market power, such as a dominant market share, product uniqueness, sole pricing power, etc. Some prices under price discrimination may be lower than the price charged by a single-price monopoli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pricing
Pricing is the Business process, process whereby a business sets and displays the price at which it will sell its products and services and may be part of the business's marketing plan. In setting prices, the business will take into account the price at which it could acquire the goods, the manufacturing cost, the marketplace, competition, market condition, brand, and quality of the product. Pricing is a fundamental aspect of product management and is one of the four Ps of the marketing mix, the other three aspects being product, promotion, and Distribution (business), place. Price is the only revenue generating element among the four Ps, the rest being cost center (business), cost centers. However, the other Ps of marketing will contribute to decreasing price elasticity and so enable price increases to drive greater revenue and profits. Pricing can be a manual or automatic process of applying prices to purchase and sales orders, based on factors such as a fixed amount, quantit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Monopoly (economics)
A monopoly (from Greek and ) is a market in which one person or company is the only supplier of a particular good or service. A monopoly is characterized by a lack of economic competition to produce a particular thing, a lack of viable substitute goods, and the possibility of a high monopoly price well above the seller's marginal cost that leads to a high monopoly profit. The verb ''monopolise'' or ''monopolize'' refers to the ''process'' by which a company gains the ability to raise prices or exclude competitors. In economics, a monopoly is a single seller. In law, a monopoly is a business entity that has significant market power, that is, the power to charge overly high prices, which is associated with unfair price raises. Although monopolies may be big businesses, size is not a characteristic of a monopoly. A small business may still have the power to raise prices in a small industry (or market). A monopoly may also have monopsony control of a sector of a market. A mono ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Durapolist
In industrial organization and in particular monopoly theory, a durapolist or durable good monopolist is a producer that manipulates the durability of its product. The term was coined by antitrust scholar Barak Orbach. The concept is used to explain how durable good manufacturers overcome the durability problem of their products and persuade consumers to purchase new goods. The concept utilizes a monopolist to simplify explanations regarding product durability. Overview Once a durable-good manufacturer sells a product to a consumer, it faces a challenge to convince this consumer to purchase another good. A consumer needs one refrigerator, one razor, a limited number of shirts, and so forth. Durability, therefore, may mean limited prospects for businesses. Ronald Coase argued that because of the durability problem a durable-good monopolist may not be able to exploit its market position and charge monopolistic prices. His thesis is known as the Coase Conjecture. The durability problem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pacman Conjecture
{{refimprove, date=May 2008 The Pacman conjecture holds that durable-goods monopolists have complete market power and so can exercise perfect price discrimination, thus extracting the total surplus.Coase versus Pacman: Who Eats Whom in the Durable Goods Monopoly? Author(s): Nils-Henrik Morch von der Fehr and Kai-Uwe Kuhn Source: The Journal of Political Economy, Vol. 103, No. 4, (Aug., 1995), pp. 785–812 Published by: The University of Chicago Press This is in contrast to the Coase conjecture which holds that a durable goods monopolist has ''no'' market power, and so price is equal to the competitive market price. In a December 1989 journal article Bagnoli, M., Salant, S.W., & Swierzbinski, J.E. "Durable-Goods Monopoly with Discrete Demand". ''The Journal of Political Economy'', 97.6 (December 1989), pp. 1459–1478.JSTOR Mark Bagnoli, Stephen W. Salant, and Joseph E. Swierzbinski theorized that if each consumer could be relied upon to buy a good as soon as its price dipped be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Profit (economics)
In economics, profit is the difference between revenue that an economic entity has received from its outputs and total costs of its inputs, also known as surplus value. It is equal to total revenue minus total cost, including both Explicit cost, explicit and implicit cost, implicit costs. It is different from accounting profit, which only relates to the explicit costs that appear on a firm's financial statements. An accountant measures the firm's accounting profit as the firm's total revenue minus only the firm's explicit costs. An Economists, economist includes all costs, both explicit and implicit costs, when analyzing a firm. Therefore, economic profit is smaller than accounting profit. ''Normal profit'' is often viewed in conjunction with economic profit. Normal profits in business refer to a situation where a company generates revenue that is equal to the total costs incurred in its operation, thus allowing it to remain operational in a competitive industry. It is the mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
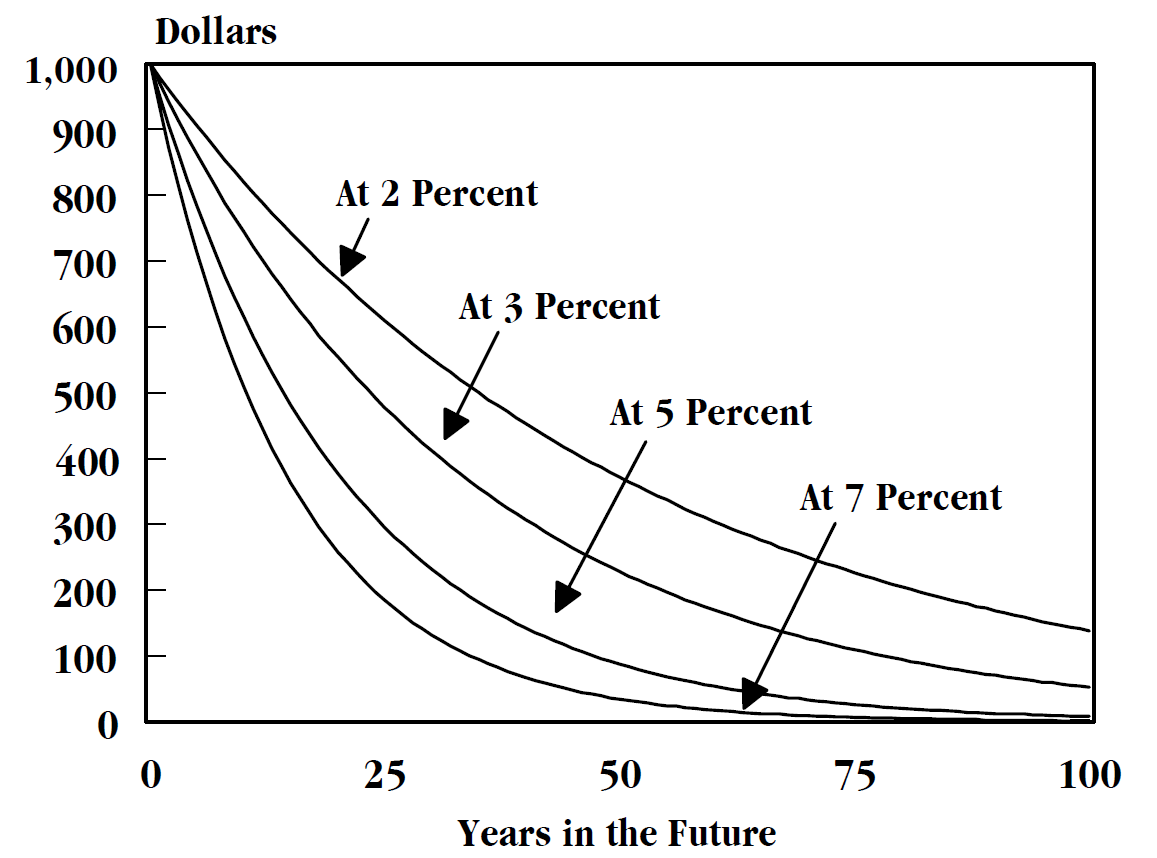
Discounting
In finance, discounting is a mechanism in which a debtor obtains the right to delay payments to a creditor, for a defined period of time, in exchange for a charge or fee.See "Time Value", "Discount", "Discount Yield", "Compound Interest", "Efficient Market", "Market Value" and "Opportunity Cost" in Downes, J. and Goodman, J. E. ''Dictionary of Finance and Investment Terms'', Baron's Financial Guides, 2003. Essentially, the party that owes money in the present purchases the right to delay the payment until some future date.See "Discount", "Compound Interest", "Efficient Markets Hypothesis", "Efficient Resource Allocation", "Pareto-Optimality", "Price", "Price Mechanism" and "Efficient Market" in Black, John, ''Oxford Dictionary of Economics'', Oxford University Press, 2002. This Financial transaction, transaction is based on the fact that most people prefer current interest to delayed interest because of Mortality salience, mortality effects, impatience effects, and Motivational sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Indifference Curve
In economics, an indifference curve connects points on a graph representing different quantities of two goods, points between which a consumer is ''indifferent''. That is, any combinations of two products indicated by the curve will provide the consumer with equal levels of utility, and the consumer has no preference for one combination or bundle of goods over a different combination on the same curve. One can also refer to each point on the indifference curve as rendering the same level of utility (satisfaction) for the consumer. In other words, an indifference curve is the locus of various points showing different combinations of two goods providing equal utility to the consumer. Utility is then a device to represent preferences rather than something from which preferences come. The main use of indifference curves is in the representation of potentially observable demand patterns for individual consumers over commodity bundles. Indifference curve analysis is a purely technol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Marginal Cost
In economics, the marginal cost is the change in the total cost that arises when the quantity produced is increased, i.e. the cost of producing additional quantity. In some contexts, it refers to an increment of one unit of output, and in others it refers to the rate of change of total cost as output is increased by an infinitesimal amount. As Figure 1 shows, the marginal cost is measured in dollars per unit, whereas total cost is in dollars, and the marginal cost is the slope of the total cost, the rate at which it increases with output. Marginal cost is different from average cost, which is the total cost divided by the number of units produced. At each level of production and time period being considered, marginal cost includes all costs that vary with the level of production, whereas costs that do not vary with production are fixed. For example, the marginal cost of producing an automobile will include the costs of labor and parts needed for the additional automobile but not t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Monopoly
A monopoly (from Greek language, Greek and ) is a market in which one person or company is the only supplier of a particular good or service. A monopoly is characterized by a lack of economic Competition (economics), competition to produce a particular thing, a lack of viable substitute goods, and the possibility of a high monopoly price well above the seller's marginal cost that leads to a high monopoly profit. The verb ''monopolise'' or ''monopolize'' refers to the ''process'' by which a company gains the ability to raise prices or exclude competitors. In economics, a monopoly is a single seller. In law, a monopoly is a business entity that has significant market power, that is, the power to charge Monopoly price, overly high prices, which is associated with unfair price raises. Although monopolies may be big businesses, size is not a characteristic of a monopoly. A small business may still have the power to raise prices in a small industry (or market). A monopoly may als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Good (economics And Accounting)
In economics, goods are anything that is good, usually in the sense that it provides well-being, welfare or utility to someone.Alan V. Deardorff, 2006. ''Terms Of Trade: Glossary of International Economics'', World Scientific. Online version: Deardorffs' Glossary of International Economics"good" an Goods can be contrasted with bads, i.e. things that provide negative value for users, like chore division, chores or waste. A bad lowers a consumer's overall welfare. Economics focuses on the study of economic goods, i.e. goods that are scarce; in other words, producing the good requires expending effort or resources. Economic goods contrast with free goods such as air, for which there is an unlimited supply.Samuelson, P. Anthony., Samuelson, W. (1980). Economics. 11th ed. / New York: McGraw-Hill. Goods are the result of the Secondary sector of the economy which involves the transformation of raw materials or intermediate goods into goods. Utility and characteristics of goods The c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |