|
CoDel
CoDel (''Controlled Delay''; pronounced "wikt:coddle, coddle") is an active queue management (AQM) algorithm in network routing, developed by Van Jacobson and Kathleen Nichols and published as RFC8289. It is designed to overcome bufferbloat in networking hardware, such as router (computing), routers, by setting limits on the delay network packets experience as they pass through buffer (telecommunication), buffers in this equipment. CoDel aims to improve on the overall performance of the random early detection (RED) algorithm by addressing some of its fundamental misconceptions, as perceived by Jacobson, and by being easier to manage. In 2012, an implementation of CoDel was written by Dave Täht and Eric Dumazet for the Linux kernel and dual licensed under the GNU General Public License and the 3-clause BSD license. Dumazet's improvement on CoDel is called FQ-CoDel, standing for "Fair/Flow Queue CoDel"; it was first adopted as the standard AQM and packet scheduling solution in 2014 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bufferbloat
Bufferbloat is a cause of high latency and jitter in packet-switched networks caused by excess buffering of packets. Bufferbloat can also cause packet delay variation (also known as jitter), as well as reduce the overall network throughput. When a router or switch is configured to use excessively large buffers, even very high-speed networks can become practically unusable for many interactive applications like voice over IP (VoIP), audio streaming, online gaming, and even ordinary web browsing. Some communications equipment manufacturers designed unnecessarily large buffers into some of their network products. In such equipment, bufferbloat occurs when a network link becomes congested, causing packets to become queued for long periods in these oversized buffers. In a first-in first-out queuing system, overly large buffers result in longer queues and higher latency, and do not improve network throughput. It can also be induced by specific slow-speed connections hinderin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Queue Management
In routers and switches, active queue management (AQM) is the policy of dropping packets inside a buffer associated with a network interface controller (NIC) before that buffer becomes full, often with the goal of reducing network congestion or improving end-to-end latency. This task is performed by the network scheduler, which for this purpose uses various algorithms such as random early detection (RED), Explicit Congestion Notification (ECN), or controlled delay ( CoDel). RFC 7567 recommends active queue management as a best practice. Overview An Internet router typically maintains a set of queues, one or more per interface, that hold packets scheduled to go out on that interface. Historically, such queues use a ''drop-tail'' discipline: a packet is put onto the queue if the queue is shorter than its maximum size (measured in packets or in bytes), and dropped otherwise. Active queue disciplines drop or mark packets before the queue is full. Typically, they operate by ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OpenWrt
OpenWrt (from ''open wireless router'') is an open-source project for embedded operating systems based on Linux, primarily used on embedded devices to route network traffic. The main components are Linux, util-linux, musl, and BusyBox. All components have been optimized to be small enough to fit into the limited storage and memory available in home routers. OpenWrt is configured using a command-line interface ( ash shell) or a web interface (LuCI). There are about 8000 optional software packages available for installation via the opkg package management system. OpenWrt can run on various types of devices, including CPE routers, residential gateways, smartphones, pocket computers (e.g. Ben NanoNote). It is also possible to run OpenWrt on personal computers and laptops. History The OpenWrt project was started in 2004 after Linksys had built the firmware for their WRT54G series of wireless routers with code licensed under the GNU General Public License. Under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Buffer
In computer science, a data buffer (or just buffer) is a region of a memory used to temporarily store data while it is being moved from one place to another. Typically, the data is stored in a buffer as it is retrieved from an input device (such as a microphone) or just before it is sent to an output device (such as speakers). However, a buffer may be used when moving data between processes within a computer. This is comparable to buffers in telecommunication. Buffers can be implemented in a fixed memory location in hardware—or by using a virtual data buffer in software, pointing at a location in the physical memory. In all cases, the data stored in a data buffer are stored on a physical storage medium. A majority of buffers are implemented in software, which typically use the faster RAM to store temporary data, due to the much faster access time compared with hard disk drives. Buffers are typically used when there is a difference between the rate at which data is received and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
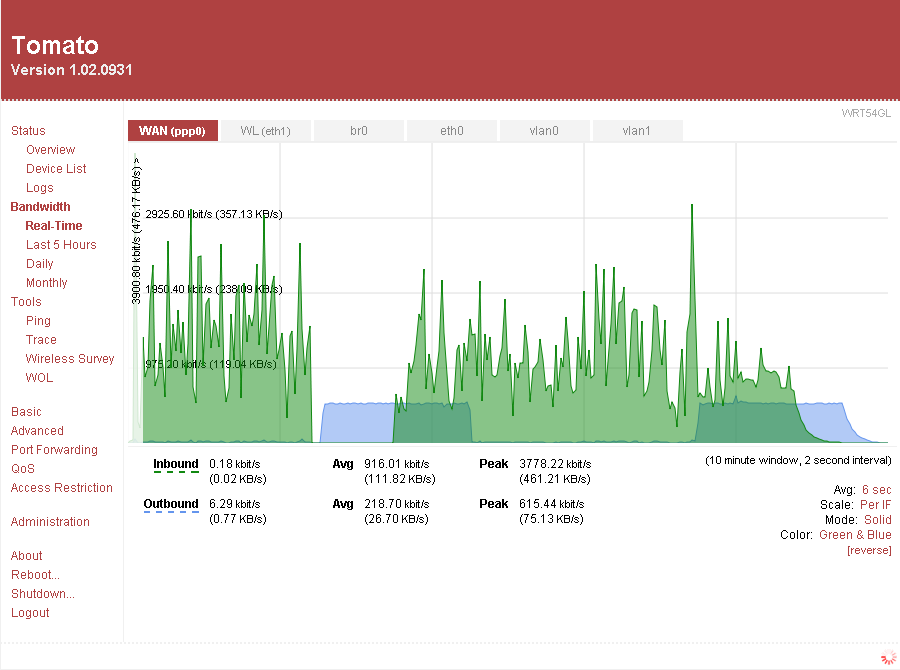
Tomato (firmware)
Tomato is a family of community-developed, custom firmware Custom firmware, also known as aftermarket firmware, is an unofficial new or modified version of firmware created by third parties on devices such as video game consoles and various embedded device types to provide new features or to unlock hidden ... for consumer-grade computer networking wireless router, routers and residential gateway, gateways powered by Broadcom chipsets. The firmware has been continually forked and modded by multiple individuals and organizations, with the most up-to-date fork provided by the FreshTomato project. History Tomato was originally released by Jonathan Zarate in 2006, using the Linux kernel and drawing extensively on the code of HyperWRT. It was targeted at many popular routers of the time, most notably the older Linksys WRT54G series, AirStation, Buffalo AirStation, Asus Routers, Asus routers and Netgear WNR3500L. His final release of the original Tomato firmware came in June 2010, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dd-wrt
DD-WRT is Linux-based firmware for wireless routers and Wireless access point, access points. Originally designed for the Linksys WRT54G series, it now runs on a wide variety of models. DD-WRT is one of a handful of List of router firmware projects, third-party firmware projects designed to replace manufacturer's original firmware with custom firmware offering additional features or functionality. Sebastian Gottschall, a.k.a. "BrainSlayer", is the founder and primary maintainer of the DD-WRT project. The letters "DD" in the project name are the Vehicle registration plates of Germany, German license-plate letters for vehicles from Dresden, where the development team lived. The remainder of the name was taken from the Linksys WRT54G model router, a home router popular in 2002–2004. WRT is assumed to be a reference to 'wireless router'. Melco, Buffalo Technology and other companies have shipped routers with factory-installed, customized versions of DD-WRT. In January 2016, Lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OPNsense
__NOTOC__ OPNsense is an open source, FreeBSD-based firewall and routing software developed by Deciso, a company in the Netherlands that makes hardware and sells support packages for OPNsense. It is a fork of pfSense, which in turn was forked from m0n0wall built on FreeBSD. It was launched in January 2015. When m0n0wall closed down in February 2015 its creator, Manuel Kasper, referred its developer community to OPNsense. OPNsense has a web-based interface and can be used on the x86-64 platform. Along with acting as a firewall, it has traffic shaping, load balancing, and virtual private network A virtual private network (VPN) extends a private network across a public network and enables users to send and receive data across shared or public networks as if their computing devices were directly connected to the private network. The be ... capabilities, and others can be added via plugins. OPNsense offers next-generation firewall capabilities utilizing Zenarmor, a NGFW ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ubiquiti
Ubiquiti Inc. (formerly Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.) is an American technology company founded in San Jose, California, in 2003. Now based in New York City, Ubiquiti manufactures and sells wireless data communication and wired products for enterprises and homes under multiple brand names. On October 13, 2011, Ubiquiti had its initial public offering (IPO) at 7.04 million shares, at $15 per share, raising $30.5 million. Products Ubiquiti's first product line was its "Super Range" mini-PCI radio card series, which was followed by other wireless products. The company's Xtreme Range (XR) cards operated on non-standard IEEE 802.11 bands, which reduced the impact of congestion in the 2.4 GHz and 5.8 GHz bands. In August 2007 a group of Italian amateur radio operators set a distance world record for point-to-point links in the 5.8 GHz spectrum. Using two XR5 cards and a pair of 35 dBi dish antennas, the Italian team was able to establish a 304 km (about 188 mi) l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Packet-switched Network
In telecommunications, packet switching is a method of grouping data into '' packets'' that are transmitted over a digital network. Packets are made of a header and a payload. Data in the header is used by networking hardware to direct the packet to its destination, where the payload is extracted and used by an operating system, application software, or higher layer protocols. Packet switching is the primary basis for data communications in computer networks worldwide. In the early 1960s, American computer scientist Paul Baran developed the concept that he called "distributed adaptive message block switching", with the goal of providing a fault-tolerant, efficient routing method for telecommunication messages as part of a research program at the RAND Corporation, funded by the United States Department of Defense. His ideas contradicted then-established principles of pre- allocation of network bandwidth, exemplified by the development of telecommunications in the Bell Syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coddle
Coddle (sometimes Dublin coddle; ) is an Irish dish which is often made to use up leftovers, and therefore without a specific recipe. However, it most commonly consists of layers of roughly sliced sausages ( pork sausages) and rashers (thinly sliced, somewhat-fatty back bacon) with chunky potatoes, sliced onion, salt, pepper, and herbs (parsley or chives). Traditionally, it can also include barley. Coddle is particularly associated with the capital of Ireland, Dublin. It was reputedly a favourite dish of the writers Seán O'Casey and Jonathan Swift, and it appears in several references to Dublin, including the works of James Joyce. The dish is braised in the stock produced by boiling the pieces of bacon and sausages. The dish is cooked in a pot with a well-fitting lid in order to steam the ingredients left uncovered by the broth. Sometimes raw sliced potato is added, but traditionally it was eaten with bread. The only seasonings are usually salt, pepper Pepper or pepp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ReadWriteWeb
ReadWrite (originally ReadWriteWeb or RWW) is a Web technology blog launched in 2003. RW covers Web 2.0 and Web technology in general, and provides industry news, reviews, and analysis. Founded by Richard MacManus, Technorati ranked ReadWriteWeb at number 12 in its list of top 100 blogs worldwide, as of October 9, 2010. MacManus is based in Lower Hutt, New Zealand, but the officers and writers of RW work from diverse locations, including Portland, Oregon. Around September or October 2008, ''The New York Times'' technology section began syndicating RW content online. RW also has many international channels such as France, Spain, Brazil and China. RW was acquired by SAY Media in 2011. On October 22, 2012, RWW redesigned its website, rebranded as ReadWrite and hired Daniel Lyons as the new editor-in-chief. Dan Lyons left ReadWrite on March 20, 2013, replaced by Owen Thomas. SAY Media sold ReadWrite to Wearable World in February 2015. In June 2015, the company announced a crowd f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buffer (telecommunication)
In computer science, a data buffer (or just buffer) is a region of a memory used to temporarily store data while it is being moved from one place to another. Typically, the data is stored in a buffer as it is retrieved from an input device (such as a microphone) or just before it is sent to an output device (such as speakers). However, a buffer may be used when moving data between processes within a computer. This is comparable to buffers in telecommunication. Buffers can be implemented in a fixed memory location in hardware—or by using a virtual data buffer in software, pointing at a location in the physical memory. In all cases, the data stored in a data buffer are stored on a physical storage medium. A majority of buffers are implemented in software, which typically use the faster RAM to store temporary data, due to the much faster access time compared with hard disk drives. Buffers are typically used when there is a difference between the rate at which data is received and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |