|
Cluster Mission
Cluster II is a space mission of the European Space Agency, with NASA participation, to study the Earth's magnetosphere over the course of nearly two solar cycles. The mission is composed of four identical spacecraft flying in a tetrahedral formation. As a replacement for the original Cluster spacecraft which were lost in a launch failure in 1996, the four Cluster II spacecraft were successfully launched in pairs in July and August 2000 onboard two Soyuz-Fregat rockets from Baikonur, Kazakhstan. In February 2011, Cluster II celebrated 10 years of successful scientific operations in space. , its mission has been extended until the end of 2022. China National Space Administration/ESA Double Star mission operated alongside Cluster II from 2004 to 2007. Mission overview The four identical Cluster II satellites study the impact of the Sun's activity on the Earth's space environment by flying in formation around Earth. For the first time in space history, this mission is able to co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetosphere
In astronomy and planetary science, a magnetosphere is a region of space surrounding an astronomical object in which charged particles are affected by that object's magnetic field. It is created by a celestial body with an active interior dynamo. In the space environment close to a planetary body, the magnetic field resembles a magnetic dipole. Farther out, field lines can be significantly distorted by the flow of electrically conducting plasma, as emitted from the Sun (i.e., the solar wind) or a nearby star. Planets having active magnetospheres, like the Earth, are capable of mitigating or blocking the effects of solar radiation or cosmic radiation, that also protects all living organisms from potentially detrimental and dangerous consequences. This is studied under the specialized scientific subjects of plasma physics, space physics and aeronomy. History Study of Earth's magnetosphere began in 1600, when William Gilbert discovered that the magnetic field on the surfac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahedron
In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the ordinary convex polyhedra and the only one that has fewer than 5 faces. The tetrahedron is the three-dimensional case of the more general concept of a Euclidean simplex, and may thus also be called a 3-simplex. The tetrahedron is one kind of pyramid, which is a polyhedron with a flat polygon base and triangular faces connecting the base to a common point. In the case of a tetrahedron the base is a triangle (any of the four faces can be considered the base), so a tetrahedron is also known as a "triangular pyramid". Like all convex polyhedra, a tetrahedron can be folded from a single sheet of paper. It has two such nets. For any tetrahedron there exists a sphere (called the circumsphere) on which all four vertices lie, and another ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantify the rate of energy transfer. The watt is named after James Watt (1736–1819), an 18th-century Scottish inventor, mechanical engineer, and chemist who improved the Newcomen engine with his own steam engine in 1776. Watt's invention was fundamental for the Industrial Revolution. Overview When an object's velocity is held constant at one metre per second against a constant opposing force of one newton, the rate at which work is done is one watt. : \mathrm In terms of electromagnetism, one watt is the rate at which electrical work is performed when a current of one ampere (A) flows across an electrical potential difference of one volt (V), meaning the watt is equivalent to the volt-ampere (the latter unit, however, is used for a different quantity from the real power of an electrical circuit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Cell
A solar cell, or photovoltaic cell, is an electronic device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by the photovoltaic effect, which is a physical and chemical phenomenon.Solar Cells chemistryexplained.com It is a form of photoelectric cell, defined as a device whose electrical characteristics, such as current, voltage, or , vary when exposed to light. Individual solar cell devices are often the electrical building blocks of [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minute
The minute is a unit of time usually equal to (the first sexagesimal fraction) of an hour, or 60 seconds. In the UTC time standard, a minute on rare occasions has 61 seconds, a consequence of leap seconds (there is a provision to insert a negative leap second, which would result in a 59-second minute, but this has never happened in more than 40 years under this system). Although not an SI unit, the minute is accepted for use with SI units. The SI symbol for ''minute'' or ''minutes'' is min (without a dot). The prime symbol is also sometimes used informally to denote minutes of time. History Al-Biruni first subdivided the hour sexagesimally into minutes, seconds, thirds and fourths in 1000 CE while discussing Jewish months. Historically, the word "minute" comes from the Latin ''pars minuta prima'', meaning "first small part". This division of the hour can be further refined with a "second small part" (Latin: ''pars minuta secunda''), and this is where the word "second" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aurora (astronomy)
An aurora (plural: auroras or aurorae), also commonly known as the polar lights, is a natural light display in Earth's sky, predominantly seen in high-latitude regions (around the Arctic and Antarctic). Auroras display dynamic patterns of brilliant lights that appear as curtains, rays, spirals, or dynamic flickers covering the entire sky. Auroras are the result of disturbances in the magnetosphere caused by the solar wind. Major disturbances result from enhancements in the speed of the solar wind from coronal holes and coronal mass ejections. These disturbances alter the trajectories of charged particles in the magnetospheric plasma. These particles, mainly electrons and protons, precipitate into the upper atmosphere (thermosphere/ exosphere). The resulting ionization and excitation of atmospheric constituents emit light of varying colour and complexity. The form of the aurora, occurring within bands around both polar regions, is also dependent on the amount of accelerati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosphere is the outer region of a star, which includes the layers above the opaque photosphere; stars of low temperature might have outer atmospheres containing compound molecules. The atmosphere of Earth is composed of nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), argon (0.9%), carbon dioxide (0.04%) and trace gases. Most organisms use oxygen for respiration; lightning and bacteria perform nitrogen fixation to produce ammonia that is used to make nucleotides and amino acids; plants, algae, and cyanobacteria use carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. The layered composition of the atmosphere minimises the harmful effects of sunlight, ultraviolet radiation, the solar wind, and cosmic rays to protect organisms from genetic damage. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
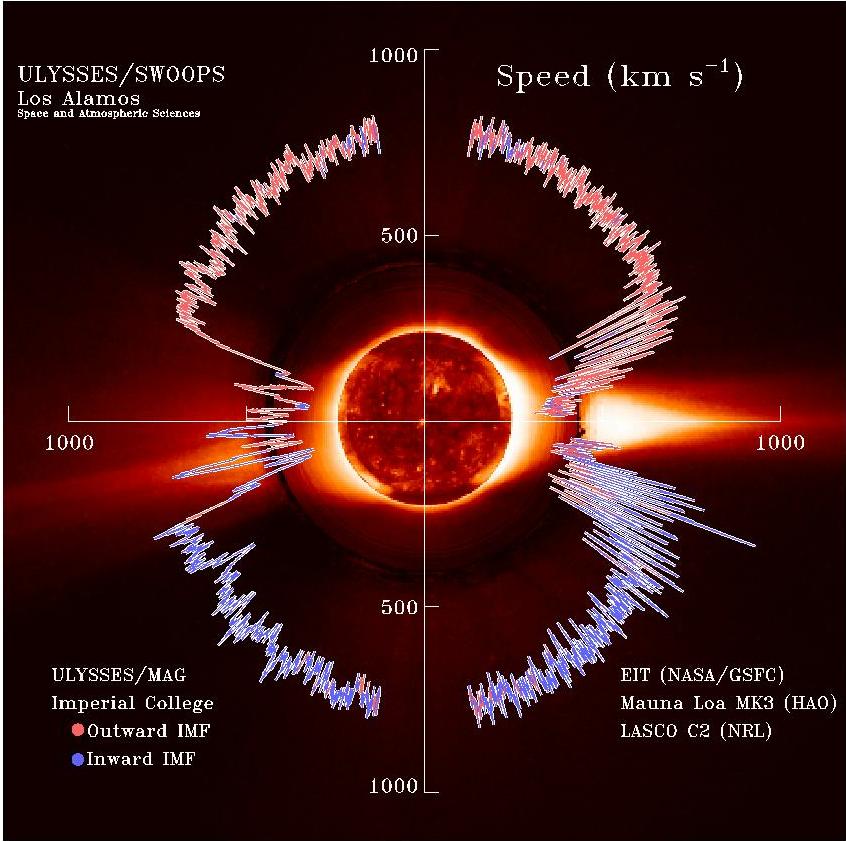
Solar Wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the upper atmosphere of the Sun, called the corona. This plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between . The composition of the solar wind plasma also includes a mixture of materials found in the solar plasma: trace amounts of heavy ions and atomic nuclei such as C, N, O, Ne, Mg, Si, S, and Fe. There are also rarer traces of some other nuclei and isotopes such as P, Ti, Cr, 54Fe and 56Fe, and 58Ni, 60Ni, and 62Ni. Superposed with the solar-wind plasma is the interplanetary magnetic field. The solar wind varies in density, temperature and speed over time and over solar latitude and longitude. Its particles can escape the Sun's gravity because of their high energy resulting from the high temperature of the corona, which in turn is a result of the coronal magnetic field. The boundary separating the corona from the solar wind is called the Alfvén surface. At a dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Star Mission
Double Star is a joint satellite based space mission by the China National Space Administration (CNSA) and the European Space Agency (ESA). It is the first space mission launched by China to investigate Earth's magnetosphere. It consists of two satellites: an Equatorial satellite (TC-1) and Polar satellite (TC-2). Double Star follows in the footsteps of ESA's Cluster mission by studying the effects of the Sun on the Earth's environment. After a nominal mission of one year (from the launch of TC-2 in July 2004), the Double Star mission was extended twice by both agencies until the end of September 2007. Overview The Double Star mission uses two satellites in Earth orbit - each designed, developed, launched, and operated by the China National Space Administration. ESA has agreed to contribute 8 million Euros to the Double Star programme. This funding will be used for refurbishment and pre-integration of the European instruments, acquisition of data for four hours per day and co-or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China National Space Administration
China National Space Administration (CNSA; ) is the government agency of the People's Republic of China that is responsible for civil space administration and international space cooperation, including organizing or leading foreign exchanges and cooperation in the aerospace field. An administrative agency under the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, its headquarters are located in Haidian, Beijing. Founded in 1993, CNSA has pioneered a number of achievements in space for China despite its relatively short history, including becoming the first space agency to land on the far side of the Moon with Chang'e 4, bringing material back from the Moon with Chang'e 5, and being the second agency who successfully landed a rover on Mars with Tianwen-1. As the governing body of civil space activities, China National Space Administration does not execute any space program. The China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation executes China's state space programs instead. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh ... to Kazakhstan–Russia border, the north and west, China to China–Kazakhstan border, the east, Kyrgyzstan to Kazakhstan–Kyrgyzstan border, the southeast, Uzbekistan to Kazakhstan–Uzbekistan border, the south, and Turkmenistan to Kazakhstan–Turkmenistan border, the southwest, with a coastline along the Caspian Sea. Its capital is Astana, known as Nur-Sultan from 2019 to 2022. Almaty, Kazakhstan's largest city, was the country's capital until 1997. Kazakhstan is the world's largest landlocked country, the largest and northernmost Muslim world, Muslim-majority cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baikonur
Baikonur ( kk, Байқоңыр, ; russian: Байконур, translit=Baykonur), formerly known as Leninsk, is a city of republic significance in Kazakhstan on the northern bank of the Syr Darya river. It is currently leased and administered by the Russian Federation as an enclave until 2050. It was constructed to service the Baikonur Cosmodrome and was officially renamed Baikonur by Russian president Boris Yeltsin on December 20, 1995. During the Soviet period, it was sometimes referred to as Zvezdograd (), Russian for ''Star City''. The rented area is an ellipse measuring east to west by north to south, with the cosmodrome situated at the area's centre. Foreign visitors need pre-approval from the Russian authorities to visit both the town of Baikonur itself and the Cosmodrome. Foreign visitors need to obtain a written approval which is completely separate from having a regular Russian visa. History The original Baikonur (Kazakh for "wealthy brown", i.e. "fertile land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

.jpg)