|
Cluster State
In quantum information and quantum computing, a cluster state is a type of highly entangled state of multiple qubits. Cluster states are generated in lattices of qubits with Ising type interactions. A cluster ''C'' is a connected subset of a ''d''-dimensional lattice, and a cluster state is a pure state of the qubits located on ''C''. They are different from other types of entangled states such as GHZ states or W states in that it is more difficult to eliminate quantum entanglement (via projective measurements) in the case of cluster states. Another way of thinking of cluster states is as a particular instance of graph states, where the underlying graph is a connected subset of a ''d''-dimensional lattice. Cluster states are especially useful in the context of the one-way quantum computer. For a comprehensible introduction to the topic see. Formally, cluster states , \phi_\rangle_ are states which obey the set eigenvalue equations: : K^ =(-1)^ where K^ are the correl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Information
Quantum information is the information of the state of a quantum system. It is the basic entity of study in quantum information theory, and can be manipulated using quantum information processing techniques. Quantum information refers to both the technical definition in terms of Von Neumann entropy and the general computational term. It is an interdisciplinary field that involves quantum mechanics, computer science, information theory, philosophy and cryptography among other fields. Its study is also relevant to disciplines such as cognitive science, psychology and neuroscience. Its main focus is in extracting information from matter at the microscopic scale. Observation in science is one of the most important ways of acquiring information and measurement is required in order to quantify the observation, making this crucial to the scientific method. In quantum mechanics, due to the uncertainty principle, non-commuting observables cannot be precisely measured simultaneously ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Entanglement
Quantum entanglement is the phenomenon that occurs when a group of particles are generated, interact, or share spatial proximity in a way such that the quantum state of each particle of the group cannot be described independently of the state of the others, including when the particles are separated by a large distance. The topic of quantum entanglement is at the heart of the disparity between classical and quantum physics: entanglement is a primary feature of quantum mechanics not present in classical mechanics. Measurements of physical properties such as position, momentum, spin, and polarization performed on entangled particles can, in some cases, be found to be perfectly correlated. For example, if a pair of entangled particles is generated such that their total spin is known to be zero, and one particle is found to have clockwise spin on a first axis, then the spin of the other particle, measured on the same axis, is found to be anticlockwise. However, this behavior gives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graph State
In quantum computing, a graph state is a special type of multi-qubit state that can be represented by a graph. Each qubit is represented by a vertex of the graph, and there is an edge between every interacting pair of qubits. In particular, they are a convenient way of representing certain types of entangled states. Graph states are useful in quantum error-correcting codes, entanglement measurement and purification and for characterization of computational resources in measurement based quantum computing models. Formal definition Quantum graph states can be defined in two equivalent ways: through the notion of quantum circuits and stabilizer formalism. Quantum circuit definition Given a graph G = (V, E), with the set of vertices V and the set of edges E, the corresponding graph state is defined as : =\prod _U^ ^ where = \frac( + ) and the operator U^ is the controlled-''Z'' interaction between the two vertices (corresponding to two qubits) a and b : U^ =\left begin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultracold Atom
Ultracold atoms are atoms that are maintained at temperatures close to 0 kelvin (absolute zero), typically below several tens of microkelvin (µK). At these temperatures the atom's quantum-mechanical properties become important. To reach such low temperatures, a combination of several techniques typically has to be used. First, atoms are usually trapped and pre-cooled via laser cooling in a magneto-optical trap. To reach the lowest possible temperature, further cooling is performed using evaporative cooling in a magnetic or optical trap. Several Nobel prizes in physics are related to the development of the techniques to manipulate quantum properties of individual atoms (e.g. 1995-1997, 2001, 2005, 2012, 2017). Experiments with ultracold atoms study a variety of phenomena, including quantum phase transitions, Bose–Einstein condensation (BEC), bosonic superfluidity, quantum magnetism, many-body spin dynamics, Efimov states, Bardeen–Cooper–Schrieffer (BCS) superfluidity and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Lattice
An optical lattice is formed by the interference of counter-propagating laser beams, creating a spatially periodic polarization pattern. The resulting periodic potential may trap neutral atoms via the Stark shift. Atoms are cooled and congregate at the potential extrema (at maxima for blue-detuned lattices, and minima for red-detuned lattices). The resulting arrangement of trapped atoms resembles a crystal lattice and can be used for quantum simulation. Atoms trapped in the optical lattice may move due to quantum tunneling, even if the potential well depth of the lattice points exceeds the kinetic energy of the atoms, which is similar to the electrons in a conductor. However, a superfluid– Mott insulator transition may occur, if the interaction energy between the atoms becomes larger than the hopping energy when the well depth is very large. In the Mott insulator phase, atoms will be trapped in the potential minima and cannot move freely, which is similar to the electron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waveplate
A waveplate or retarder is an optical device that alters the polarization state of a light wave travelling through it. Two common types of waveplates are the ''half-wave plate'', which shifts the polarization direction of linearly polarized light, and the ''quarter-wave plate'', which converts linearly polarized light into circularly polarized light and vice versa. A quarter-wave plate can be used to produce elliptical polarization as well. Waveplates are constructed out of a birefringent material (such as quartz or mica, or even plastic), for which the index of refraction is different for light linearly polarized along one or the other of two certain perpendicular crystal axes. The behavior of a waveplate (that is, whether it is a half-wave plate, a quarter-wave plate, etc.) depends on the thickness of the crystal, the wavelength of light, and the variation of the index of refraction. By appropriate choice of the relationship between these parameters, it is possible to introduce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beam Splitter
A beam splitter or ''beamsplitter'' is an optical device that splits a beam of light into a transmitted and a reflected beam. It is a crucial part of many optical experimental and measurement systems, such as interferometers, also finding widespread application in fibre optic telecommunications. Beam-splitter designs In its most common form, a cube, a beam splitter is made from two triangular glass prisms which are glued together at their base using polyester, epoxy, or urethane-based adhesives. (Before these synthetic resins, natural ones were used, e.g. Canada balsam.) The thickness of the resin layer is adjusted such that (for a certain wavelength) half of the light incident through one "port" (i.e., face of the cube) is reflected and the other half is transmitted due to FTIR (Frustrated Total Internal Reflection). Polarizing beam splitters, such as the Wollaston prism, use birefringent materials to split light into two beams of orthogonal polarization states. Anoth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
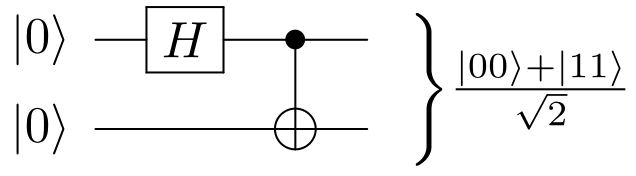
Bell State
The Bell states or EPR pairs are specific quantum states of two qubits that represent the simplest (and maximal) examples of quantum entanglement; conceptually, they fall under the study of quantum information science. The Bell states are a form of entangled and normalized basis vectors. This normalization implies that the overall probability of the particle being in one of the mentioned states is 1: \langle \Phi, \Phi \rangle = 1. Entanglement is a basis-independent result of superposition. Due to this superposition, measurement of the qubit will " collapse" it into one of its basis states with a given probability. Because of the entanglement, measurement of one qubit will "collapse" the other qubit to a state whose measurement will yield one of two possible values, where the value depends on which Bell state the two qubits are in initially. Bell states can be generalized to certain quantum states of multi-qubit systems, such as the GHZ state for 3 or more subsystems. Under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anton Zeilinger
Anton Zeilinger (; born 20 May 1945) is an Austrian quantum physicist and Nobel laureate in physics of 2022. Zeilinger is professor of physics emeritus at the University of Vienna and senior scientist at the Institute for Quantum Optics and Quantum Information of the Austrian Academy of Sciences. Most of his research concerns the fundamental aspects and applications of quantum entanglement. In 2007, Zeilinger received the first Inaugural Isaac Newton Medal of the Institute of Physics, London, for "his pioneering conceptual and experimental contributions to the foundations of quantum physics, which have become the cornerstone for the rapidly-evolving field of quantum information". In October 2022, he received the Nobel Prize in Physics, jointly with Alain Aspect and John Clauser for their outstanding work involving experiments with entangled photons, establishing the violation of Bell inequalities and pioneering quantum information science. Early life and education Anton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Markus Aspelmeyer
Markus Aspelmeyer is an Austrian quantum physicist. Aspelmeyer was born 1974 in the Bavarian town Schongau. He also attended the local school, where he received his abitur in 1993. He studied physics and philosophy at the University of Munich, receiving his BS in philosophy and his Ph.D in physics in 2002. He joined the group of Anton Zeilinger at the University of Vienna in 2002 with a Feodor Lynen PostDoctoral Fellowship of the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation. He became Universitätsassistent at the University and then, Junior, later Senior Researcher, at the Institute for Quantum Optics and Quantum Information (IQOQI) of the Austrian Academy of Sciences where he is leading a research team working on quantum effects in micro- and nanomechanical systems. His research interests are quantum entanglement and quantum optics. He was awarded the Lieben Prize in 2007 and an ERC Starting Independent Researcher Grant in 2009. He was offered chairs at the University of Oxford, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spontaneous Parametric Down-conversion
Spontaneous parametric down-conversion (also known as SPDC, parametric fluorescence or parametric scattering) is a nonlinear instant optical process that converts one photon of higher energy (namely, a pump photon), into a pair of photons (namely, a signal photon, and an idler photon) of lower energy, in accordance with the law of conservation of energy and law of conservation of momentum. It is an important process in quantum optics, for the generation of entangled photon pairs, and of single photons. Basic process A nonlinear crystal is used to produce pairs of photons from a photon beam. In accordance with the law of conservation of energy and law of conservation of momentum, the pairs have combined energies and momenta equal to the energy and momentum of the original photon. Because the index of refraction changes with frequency ( dispersion), only certain triplets of frequencies will be phase-matched so that simultaneous energy and momentum conservation can be achieve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical And Logical Qubits
In quantum computing, a '' qubit'' is a unit of information analogous to a bit (binary digit) in classical computing, but it is affected by quantum mechanical properties such as superposition and entanglement which allow qubits to be in some ways more powerful than classical bits for some tasks. Qubits are used in quantum circuits and quantum algorithms composed of quantum logic gates to solve computational problems, where they are used for input/output and intermediate computations. A physical qubit is a physical device that behaves as a two-state quantum system, used as a component of a computer system. A logical qubit is a physical or abstract qubit that performs as specified in a quantum algorithm or quantum circuit subject to unitary transformations, has a long enough coherence time to be usable by quantum logic gates (c.f. propagation delay for classical logic gates). , most technologies used to implement qubits face issues of stability, decoherence, fault tol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)