|
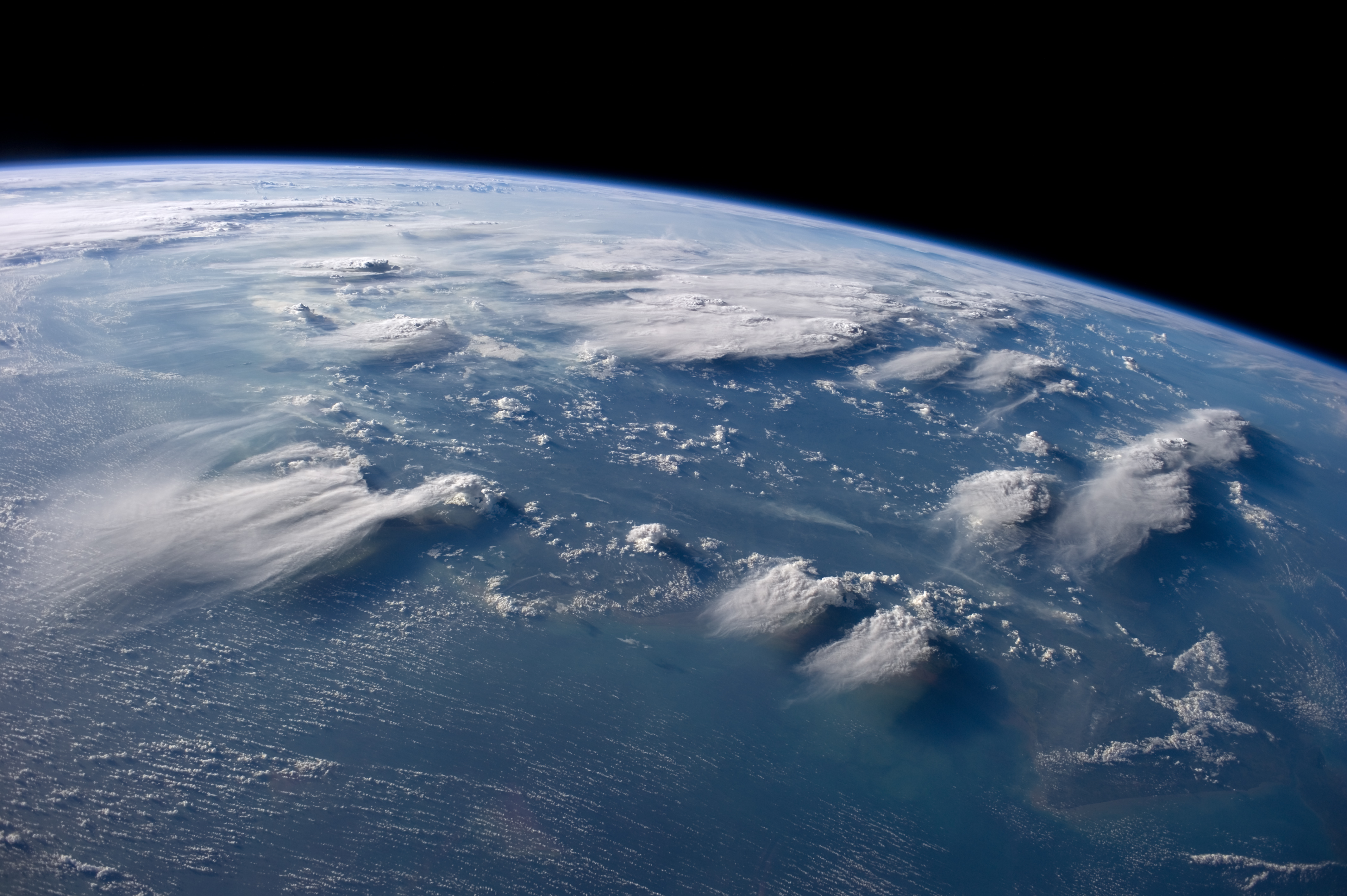
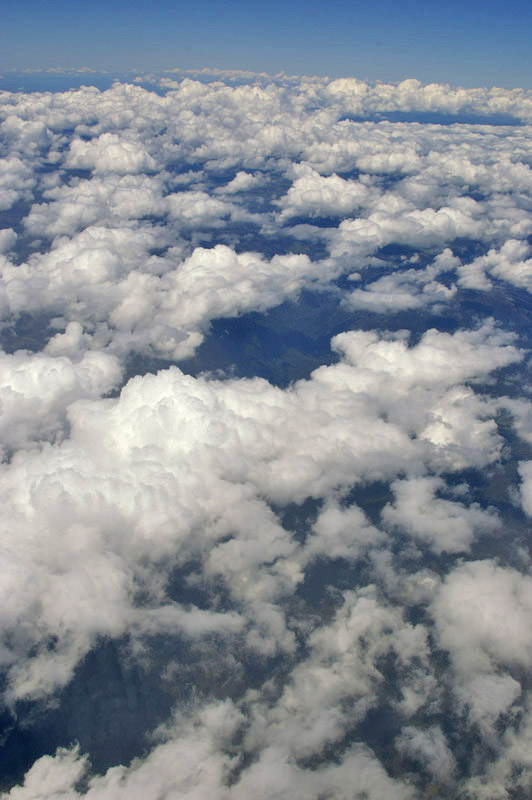
Cloud Formations
The list of cloud types groups all genera as ''high'' (cirro-, cirrus), ''middle'' (alto-), ''multi-level'' (nimbo-, cumulo-, cumulus), and ''low'' (strato-, stratus). These groupings are determined by the altitude level or levels in the troposphere at which each of the various cloud types is normally found. Small cumulus are commonly grouped with the low clouds because they do not show significant vertical extent. Of the multi-level genus-types, those with the greatest convective activity are often grouped separately as ''towering vertical''. The genus types all have Latin names. The genera are also grouped into five physical forms. These are, in approximate ascending order of instability or convective activity: ''stratiform'' sheets; ''cirriform'' wisps and patches; ''stratocumuliform'' patches, rolls, and ripples; ''cumuliform'' heaps, and ''cumulonimbiform'' towers that often have complex structures. Most genera are divided into ''species'' with Latin names, some of which are c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloud Types En
In meteorology, a cloud is an aerosol consisting of a visible mass of miniature liquid drop (liquid), droplets, ice crystals, frozen crystals, or other particulates, particles suspended in the atmosphere of a planetary body or similar space. Water or various other chemicals may compose the droplets and crystals. On Earth, clouds are formed as a result of saturation of the air when it is cooled to its dew point, or when it gains sufficient moisture (usually in the form of water vapor) from an adjacent source to raise the dew point to the ambient temperature. They are seen in the Earth's homosphere, which includes the troposphere, stratosphere, and mesosphere. Nephology is the science of clouds, which is undertaken in the cloud physics branch of meteorology. There are two methods of naming clouds in their respective layers of the homosphere, Latin and common name. Genus types in the troposphere, the atmospheric layer closest to Earth's surface, have Latin names because of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nacreous
Nacre ( , ), also known as mother of pearl, is an organicinorganic composite material produced by some molluscs as an inner shell layer; it is also the material of which pearls are composed. It is strong, resilient, and iridescent. Nacre is found in some of the most ancient lineages of bivalves, gastropods, and cephalopods. However, the inner layer in the great majority of mollusc shells is porcellaneous, not nacreous, and this usually results in a non-iridescent shine, or more rarely in non-nacreous iridescence such as ''flame structure'' as is found in conch pearls. The outer layer of cultured pearls and the inside layer of pearl oyster and freshwater pearl mussel shells are made of nacre. Other mollusc families that have a nacreous inner shell layer include marine gastropods such as the Haliotidae, the Trochidae and the Turbinidae. Physical characteristics Structure and appearance Nacre is composed of hexagonal platelets of aragonite (a form of calcium carbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fractus
Fractus clouds (''scuds'') also known as Fractostratus or Fracto-Cumulus are small, ragged cloud fragments that are usually found under an ambient cloud base. They form or have broken off from a larger cloud, and are generally sheared by strong winds, giving them a jagged, shredded appearance. Fractus have irregular patterns, appearing much like torn pieces of cotton candy. They change constantly, often forming and dissipating rapidly. They do not have clearly defined bases. Sometimes they are persistent and form very near the surface. Common kinds include ''scud'' and ''cloud tags''. Forms Fractus are accessory clouds, named for the type of cloud from which they were sheared. The two principal forms are cumulus fractus (formerly, fractocumulus) and stratus fractus (formerly, fractostratus). Fractus clouds may develop into cumulus if the ground heats enough to start convection. Stratus fractus is distinguishable from cumulus fractus by its smaller vertical extent, darker col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumulus Humilis
Cumulus humilis are cumuliform clouds with little vertical extent, common in the summer, that are often referred to as "fair weather cumulus". If they develop into cumulus mediocris or cumulus congestus, thunderstorms could form later in the day. They generally form at lower altitudes (500–3000 m (1,500–10,000 ft)), but in hot countries or over mountainous terrain these clouds can occur at an altitude of up to . They show no significant vertical development, indicating that the temperature in the atmosphere above them either drops off very slowly or not at all with altitude; that is, the environmental lapse rate is small. Cumulus humilis may be accompanied by other cloud types. Air below the cloud base can be quite turbulent due to the thermals that formed the clouds, giving occupants of light aircraft an uncomfortable ride. To avoid turbulence where such clouds are present, pilots may climb above the cloud tops. However, glider pilots actively seek out the rising air t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratocumulus
A stratocumulus cloud, occasionally called a cumulostratus, belongs to a genus-type of clouds characterized by large dark, rounded masses, usually in groups, lines, or waves, the individual elements being larger than those in altocumulus, and the whole being at a lower height, usually below . Weak convective currents create shallow cloud layers because of drier, stable air above preventing continued vertical development. Historically, in English, this type of cloud has been referred to as a twain cloud for being a combination of two types of clouds. Description Occurrence Vast areas of subtropical and polar oceans are covered with massive sheets of stratocumulus. These may organize into distinctive patterns which are currently under active study. In subtropics, they cover the edges of the horse latitude climatological highs, and reduce the amount of solar energy absorbed in the ocean. When these drift over land the summer heat or winter cold is reduced. 'Dull weather' is a common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratus Cloud
Stratus clouds are low-level clouds characterized by horizontal layering with a uniform base, as opposed to convective or cumuliform clouds that are formed by rising thermals. More specifically, the term ''stratus'' is used to describe flat, hazy, featureless clouds at low altitudes varying in color from dark gray to nearly white. The word ''stratus'' comes from the Latin prefix ''strato-'', meaning "layer". Stratus clouds may produce a light drizzle or a small amount of snow. These clouds are essentially above-ground fog formed either through the lifting of morning fog or through cold air moving at low altitudes over a region. Some call these clouds "high fog" for their fog-like form. While light rain may fall, this cloud does not indicate much meteorological precipitation. Formation Stratus clouds form when weak vertical currents lift a layer of air off the ground and it depressurizes, following the lapse rate. This causes the relative humidity to increase due to the adiabati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumulus Mediocris
Cumulus mediocris is a low to middle level cloud with some vertical extent (Family D1) of the genus cumulus, larger in vertical development than Cumulus humilis. It also may exhibit small protuberances from the top and may show the cauliflower form characteristic of cumulus clouds. Cumulus mediocris clouds do not generally produce precipitation of more than very light intensity, but can further advance into clouds such as Cumulus congestus or Cumulonimbus, which do produce precipitation and severe storms. Cumulus mediocris is also classified as a low cloud and is coded CL2 by the World Meteorological Organization. Description Cumulus mediocris is brilliantly white when sunlit, and is dark underneath. A single pattern-based variety, Cumulus radiatus, is sometime seen when the individual clouds are arranged into parallel rows. The resulting formations are known as "cloud streets" and are aligned approximately parallel to the wind. Cumulus mediocris may have precipitation-based f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nimbostratus
A nimbostratus cloud is a multi-level, amorphous, nearly uniform and often dark grey cloud that usually produces continuous rain, snow or sleet but no lightning or thunder. in the Oxford Dictionaries Online Although it is usually a low-based cloud, it actually forms most commonly in the middle level of the troposphere and then spreads vertically into the low and high levels. Nimbostratus usually produces precipitation over a wide area. ''Nimbo-'' is from the Latin word ''nimbus'', which denotes cloud or halo. Downward-growing nimbostratus can have the same vertical extent as most large upward-growing cumulus, but its horizontal extent tends to be even greater. Appearance Nimbostratus has a diffuse |
Cumulonimbus
Cumulonimbus (from Latin ''cumulus'', "heaped" and ''nimbus'', "rainstorm") is a dense, towering vertical cloud, typically forming from water vapor condensing in the lower troposphere that builds upward carried by powerful Buoyancy, buoyant air currents. Above the lower portions of the cumulonimbus the water vapor becomes ice crystals, such as snow and graupel, the interaction of which can lead to hail and to lightning formation, respectively. When occurring as a thunderstorm these clouds may be referred to as thunderheads. Cumulonimbus can form alone, in clusters, or along squall lines. These clouds are capable of producing lightning and other dangerous severe weather, such as tornadoes, hazardous winds, and large hailstones. Cumulonimbus progress from overdeveloped cumulus congestus clouds and may further develop as part of a supercell. Cumulonimbus is abbreviated Cb. Appearance Towering cumulonimbus clouds are typically accompanied by smaller Cumulus cloud, cumulus clouds. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumulus Congestus
Cumulus congestus clouds, also known as towering cumulus, are a form of cumulus that can be based in the low or middle height ranges. They achieve considerable vertical development in areas of deep, moist convection. They are an intermediate stage between cumulus mediocris and cumulonimbus, sometimes producing showers of snow, rain, or ice pellets. Precipitation that evaporates before reaching the surface is virga. Description Cumulus congestus clouds are characteristic of unstable areas of the atmosphere which are undergoing convection. They are often characterized by sharp outlines and great vertical development. Because they are produced by (and primarily composed of) strong updrafts, they are typically taller than they are wide, and cloud tops can reach , or higher in the tropics. Cumulus congestus clouds are formed by the development of cumulus mediocris generally, though they can also be formed from altocumulus castellanus or stratocumulus castellanus, which are forms of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
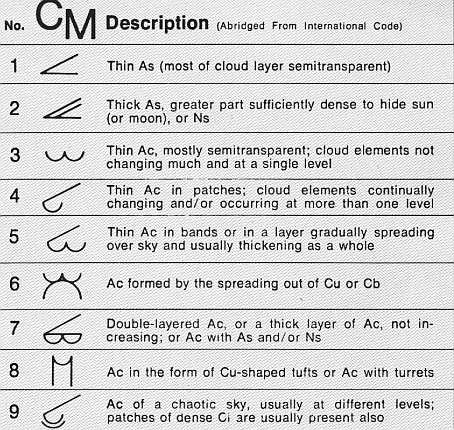
Altocumulus
Altocumulus (From Latin ''Altus'', "high", ''cumulus'', "heaped") is a middle-altitude cloud genus that belongs mainly to the ''stratocumuliform'' physical category characterized by globular masses or rolls in layers or patches, the individual elements being larger and darker than those of cirrocumulus and smaller than those of stratocumulus. However, if the layers become tufted in appearance due to increased airmass instability, then the altocumulus clouds become more purely ''cumuliform'' in structure. Like other cumuliform and stratocumuliform clouds, altocumulus signifies convection. A sheet of partially conjoined altocumulus perlucidus is sometimes found preceding a weakening warm front, where the altostratus is starting to fragment, resulting in patches of altocumulus perlucidus between the areas of altostratus. Altocumulus is also commonly found between the warm and cold fronts in a depression, although this is often hidden by lower clouds. Towering altocumulus, known as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altostratus
Altostratus is a middle-altitude cloud genus made up of water droplets, ice crystals, or a mixture of the two. Altostratus clouds are formed when large masses of warm, moist air rise, causing water vapor to condense. Altostratus clouds are usually gray or blueish featureless sheets, although some variants have wavy or banded bases. The sun can be seen through thinner altostratus clouds, but thicker layers can be quite opaque. Altostratus clouds usually predict the arrival of warm fronts. Once altostratus clouds associated with a warm front arrive, continuous rain or snow will usually follow in the next 12 to 24 hours. Although altostratus clouds predict the arrival of warmer, wetter weather, they themselves do not produce significant precipitation. Thunderstorms can be embedded in altostratus clouds; however, bringing showers. Because altostratus clouds can contain ice crystals, they can produce some optical phenomena like iridescence and coronas. Description Altostratus c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |