|
Clotaire
Chlothar (Latin ''Chlotharius''; Greek ''Khlōthários'' Χλωθάριος; French ''Clotaire'') is a Germanic given name, attested in Old English as ''Hloþhere'', in Old High German as ''Lothari'' ( Lothair), and reconstructed in Frankish as *''Hlodhari''. It means "famous warrior", as a combination of the Germanic root ''hlut-'' (lauded, famous) and the word ''heri'' (army, warrior). It can refer to the following kings of the Franks: * Chlothar I (497–561) * Chlothar II (584–629) * Chlothar III (652–673) * Chlothar IV Chlothar IV (died 718) was the king of Austrasia from 717 until his death. He was a member of the Merovingian dynasty, and was installed by Charles Martel, a contender for the office of mayor of the palace, in opposition to Chilperic II, whose rul ... (died 719) References {{given name Given names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlothar I
Chlothar I, sometime called "the Old" ( French: le Vieux), (died December 561) also anglicised as Clotaire, was a king of the Franks of the Merovingian dynasty and one of the four sons of Clovis I. Chlothar's father, Clovis I, divided the kingdom between his four sons. In 511, Clothar I inherited two large territories on the Western coast of Francia, separated by the lands of his brother Childebert I's Kingdom of Paris. Chlothar spent most of his life in a campaign to expand his territories at the expense of his relatives and neighbouring realms in all directions. His brothers avoided outright war by cooperating with Chlothar's attacks on neighbouring lands in concert or by invading lands when their rulers died. The spoils were shared between the participating brothers. By the end of his life, Chlothar had managed to reunite Francia by surviving his brothers and seizing their territories after they died. But upon his own death, the Kingdom of the Franks was once again divided ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
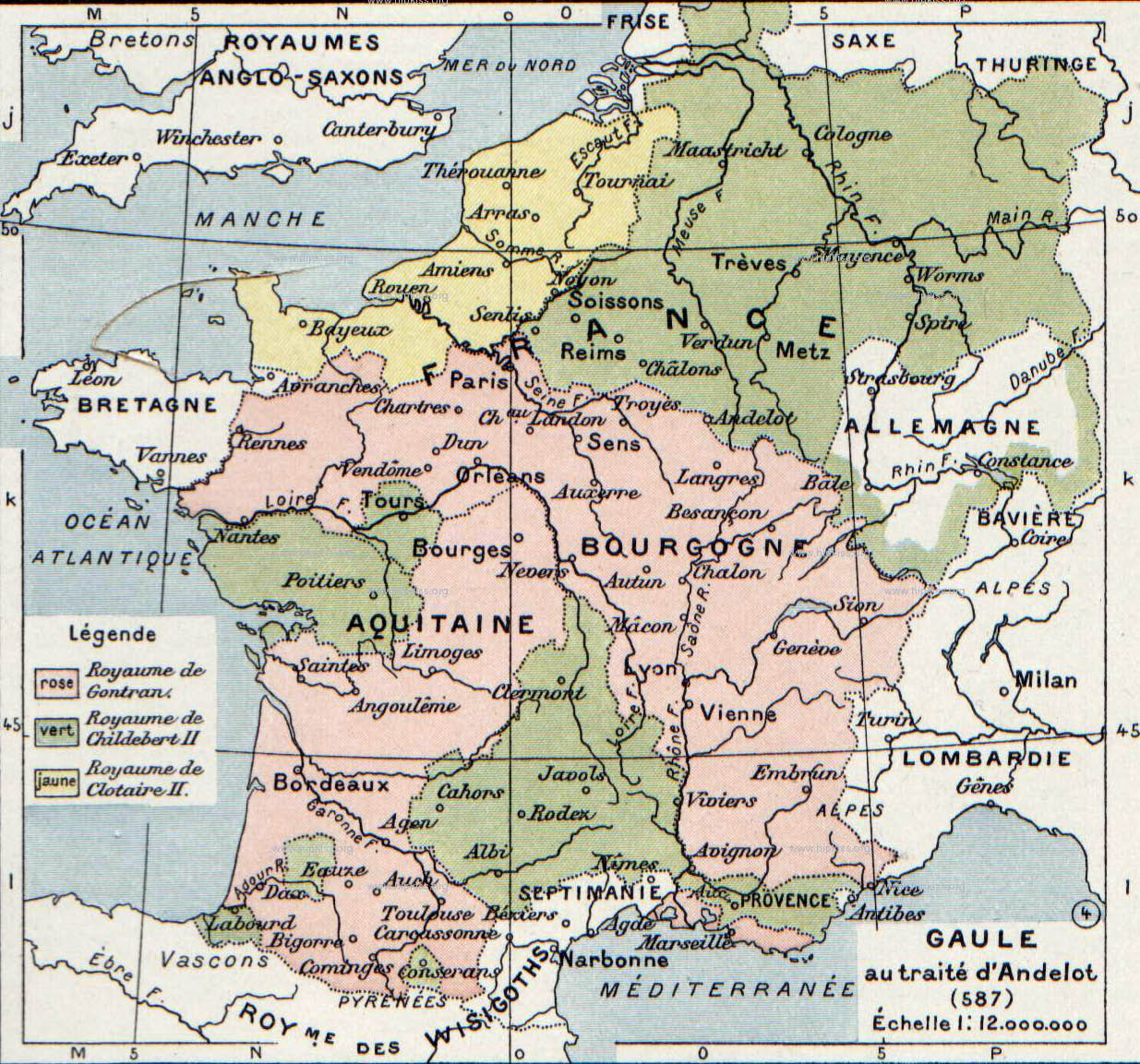
Chlothar II
Chlothar II, sometime called "the Young" (French language, French: le Jeune), (May/June 584 – 18 October 629), was king of Neustria and king of the Franks, and the son of Chilperic I and his third wife, Fredegund. He started his reign as an infant under the regency of his mother, who was in an uneasy alliance with Chlothar's uncle King Guntram of Burgundy, who died in 592. Chlothar took power upon the death of his mother in 597; though rich, Neustria was one of the smallest portions of Francia. He continued his mother's feud with Queen Brunhilda of Austrasia, Brunhilda with equal viciousness and bloodshed, finally achieving her execution in an especially brutal manner in 613, after winning the battle that enabled Chlothar to unite Francia under his rule. Like his father, he built up his territories by seizing lands after the deaths of other kings. His reign was long by contemporary standards, but saw the continuing erosion of royal power to the French nobility and the church ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlothar III
Chlothar III (or ''Chlotar'', ''Clothar'', ''Clotaire'', ''Chlotochar'', or ''Hlothar'', giving rise to the name Lothair; 652–673) was the eldest son of Clovis II, king of Neustria and Burgundy, and his queen Balthild. When Clovis died in 657, Chlothar succeeded him under the regency of his mother. Only a month beforehand, according to the near-contemporary ''Life of Eligius'' by the courtier Audoin (bishop) of Rouen, Saint Eligius had prophesied the death of Clovis, Balthild's downfall, and Chlothar's short reign. Few things are known about the time of Chlothar's reign. The ''Historia Langobardorum'' reports that in the early 660s a Frankish army invaded Provence and then Italy. This force came upon the camp of the Lombard king Grimoald I of Benevento, at Rivoli near Asta. Grimuald pretended to flee. The Franks looted the camp and celebrated. Then, after midnight, Grimuald attacked and drove them back to Neustria. After the death of Saint Eligius in 661, the ''Life of Eligius ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lothair (other)
Lothair (Latin: ''Lotharius''; German: ''Lothar''; French: ''Lothaire'') is a Germanic given name, derived from the older form Clotaire (''Chlotharius''). People *Lothair I (795–855), King of Italy and Holy Roman Emperor *Lothair I, Margrave of the Nordmark (940–1003) *Lothair II of Lotharingia (825–869), a king, son of Emperor Lothair I *Lothair II of Italy (died 950), a king *Lothair III, Holy Roman Emperor (1075–1137), also called Lothair II *Lothair of France (941–986), sometimes called Lothair II *Lothair the Lame (died 865), Abbot of Saint-Germain-des-Prés *Lothair Udo I, Count of Stade (950–994) *Lothair Udo I, Margrave of the Nordmark (994–1057) *Lothair Udo II, Margrave of the Nordmark (1025–1082) *Lothair Udo III, Margrave of the Nordmark (1070–1106) Other uses *Lothair, Georgia, in the United States * Lothair, Montana, in the United States * Lothair, Kentucky, in the United States * Lothair, South Africa, a town in Mpumalanga * ''Lothair'' (novel), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlothar IV
Chlothar IV (died 718) was the king of Austrasia from 717 until his death. He was a member of the Merovingian dynasty, and was installed by Charles Martel, a contender for the office of mayor of the palace, in opposition to Chilperic II, whose rule was thereby restricted to Neustria. This marked the first time since 679 that the Francia, kingdom of the Franks was divided. Following Chlothar's death, it was reunited under Chilperic. Chlothar's parentage and the exact dates of his reign are uncertain, since no primary source gives them explicitly. Documents from Chlothar's reign place him on the throne between 28 June 717 and 24 February 718. A Frankish king-list from the reign of Charles the Bald a century and a half later gives his reign a length of one year, which is consistent with all other evidence. His reign began no earlier than 21 March 717 and was over by 18 May 718.Richard A. Gerberding, ''The Rise of the Carolingians and the'' Liber Historiae Francorum (Oxford University ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lothar
Lothar is a Danish, Finnish, German, Norwegian, and Swedish masculine given name, while Lotár is a Hungarian masculine given name. Both names are modern forms of the Germanic Chlothar (which is a blended form of ''Hlūdaz'', meaning "fame", and ''Harjaz'', meaning "army"). Notable people with this name include: Surname * Ernst Lothar (1890–1974), Moravian-Austrian writer * Hanns Lothar or Hanns Lothar Neutze (1929–1967), German actor * Mark Lothar (1902–1985), German composer * Rudolf Lothar (1865–1943), Hungarian-born Austrian writer * Susanne Lothar (1960–2012), German actress Given name * Lothar Ahrendt (born 1936), former interior minister of the German Democratic Republic * Lothar Albrich (1905–1978), Romanian hurdler * Lothar Baumgarten (1944–2018), German artist * Lothar Berg (1930–2015), German mathematician * Lothar Bolz (1903–1986), East German politician * Lothar-Günther Buchheim (1918–2007), German author * Lothar Collatz (1910–1990), German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic Language
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania and Southern Africa. The most widely spoken Germanic language, English, is also the world's most widely spoken language with an estimated 2 billion speakers. All Germanic languages are derived from Proto-Germanic, spoken in Iron Age Scandinavia. The West Germanic languages include the three most widely spoken Germanic languages: English with around 360–400 million native speakers; German, with over 100 million native speakers; and Dutch, with 24 million native speakers. Other West Germanic languages include Afrikaans, an offshoot of Dutch, with over 7.1 million native speakers; Low German, considered a separate collection of unstandardized dialects, with roughly 4.35–7.15 million native speakers and probably 6.7–10 million people who can understand it [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Given Name
A given name (also known as a forename or first name) is the part of a personal name quoted in that identifies a person, potentially with a middle name as well, and differentiates that person from the other members of a group (typically a family or clan) who have a common surname. The term ''given name'' refers to a name usually bestowed at or close to the time of birth, usually by the parents of the newborn. A ''Christian name'' is the first name which is given at baptism, in Christian custom. In informal situations, given names are often used in a familiar and friendly manner. In more formal situations, a person's surname is more commonly used. The idioms 'on a first-name basis' and 'being on first-name terms' refer to the familiarity inherent in addressing someone by their given name. By contrast, a surname (also known as a family name, last name, or ''gentile name, gentile'' name) is normally inherited and shared with other members of one's immediate family. Regnal names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th century, and the first Old English literature, Old English literary works date from the mid-7th century. After the Norman conquest of 1066, English was replaced, for a time, by Anglo-Norman language, Anglo-Norman (a langues d'oïl, relative of French) as the language of the upper classes. This is regarded as marking the end of the Old English era, since during this period the English language was heavily influenced by Anglo-Norman, developing into a phase known now as Middle English in England and Early Scots in Scotland. Old English developed from a set of Anglo-Frisian languages, Anglo-Frisian or Ingvaeonic dialects originally spoken by Germanic peoples, Germanic tribes traditionally known as the Angles, Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old High German
Old High German (OHG; german: Althochdeutsch (Ahd.)) is the earliest stage of the German language, conventionally covering the period from around 750 to 1050. There is no standardised or supra-regional form of German at this period, and Old High German is an umbrella term for the group of continental West Germanic dialects which underwent the set of consonantal changes called the Second Sound Shift. At the start of this period, the main dialect areas belonged to largely independent tribal kingdoms, but by 788 the conquests of Charlemagne had brought all OHG dialect areas into a single polity. The period also saw the development of a stable linguistic border between German and Gallo-Romance, later French. The surviving OHG texts were all written in monastic scriptoria and, as a result, the overwhelming majority of them are religious in nature or, when secular, belong to the Latinate literary culture of Christianity. The earliest written texts in Old High German, glosses and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frankish Language
Frankish ( reconstructed endonym: *), also known as Old Franconian or Old Frankish, was the West Germanic language spoken by the Franks from the 5th to 9th century. After the Salian Franks settled in Roman Gaul, its speakers in Picardy and Île-de-France were outnumbered by the local populace who spoke Proto-Romance dialects. However, a number of modern French words and place names, including the eventual country's name of "France", have a Frankish (i.e. Germanic) origin. France itself is still known by terms literally meaning the "Frankish Realm" in languages such as German (), Yiddish ( ), Dutch (), the derived Afrikaans (), and Danish () as well as Swedish and Norwegian (). Between the 5th and 9th centuries, Frankish spoken in Northwestern France, present-day Belgium and the Netherlands is subsequently referred to as Old Dutch, whereas the Frankish varieties spoken in the Rhineland were heavily influenced by Elbe Germanic dialects and the Second Germanic consonant shi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
