|
Climate Change Acronyms
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) with the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) use tens of acronyms and initialisms in documents relating to climate change policy. A * AAU - Assigned amount unit * AGGI - Annual Greenhouse Gas Index * AMO - Atlantic multidecadal oscillation * AO - Arctic oscillation C * CDM – Clean Development Mechanism is an arrangement under the Kyoto Protocol allowing industrialised countries with a greenhouse gas reduction commitment (called Annex 1 countries) to invest in projects that reduce emissions in developing countries as an alternative to more expensive emission reductions in their own countries. * CDR - Carbon dioxide removal * CER – Certified Emission Reduction * CFC - Chlorofluorocarbon * CF4 - Carbon tetrafluoride * CH4 - Methane * COP - United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, Conference of the Parties * CO2 - Carbon dioxide * C2F6 - Hexafluoroethane D * DER – Distributed Ener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intergovernmental Panel On Climate Change
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is an intergovernmental body of the United Nations. Its job is to advance scientific knowledge about climate change caused by human activities. The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) established the IPCC in 1988. The United Nations endorsed the creation of the IPCC later that year. It has a secretariat in Geneva, Switzerland, hosted by the WMO. It has 195 member states who govern the IPCC. The member states elect a bureau of scientists to serve through an assessment cycle. A cycle is usually six to seven years. The bureau selects experts to prepare IPCC reports. It draws the experts from nominations by governments and observer organisations. The IPCC has three working groups and a task force, which carry out its scientific work. The IPCC informs governments about the state of knowledge of climate change. It does this by examining all the relevant scientific literature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Circulation Model
A general circulation model (GCM) is a type of climate model. It employs a mathematical model of the general circulation of a planetary atmosphere or ocean. It uses the Navier–Stokes equations on a rotating sphere with thermodynamic terms for various energy sources (radiation, latent heat). These equations are the basis for computer programs used to simulate the Earth's atmosphere or oceans. Atmospheric and oceanic GCMs (AGCM and OGCM) are key components along with sea ice and land-surface components. GCMs and global climate models are used for weather forecasting, understanding the climate, and forecasting climate change. Versions designed for decade to century time scale climate applications were originally created by Syukuro Manabe and Kirk Bryan at the Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory (GFDL) in Princeton, New Jersey. These models are based on the integration of a variety of fluid dynamical, chemical and sometimes biological equations. Terminology The acronym ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrous Oxide
Nitrous oxide (dinitrogen oxide or dinitrogen monoxide), commonly known as laughing gas, nitrous, or nos, is a chemical compound, an oxide of nitrogen with the formula . At room temperature, it is a colourless non-flammable gas, and has a slightly sweet scent and taste. At elevated temperatures, nitrous oxide is a powerful oxidiser similar to molecular oxygen. Nitrous oxide has significant medical uses, especially in surgery and dentistry, for its anaesthetic and pain-reducing effects. Its colloquial name, "laughing gas", coined by Humphry Davy, is due to the euphoric effects upon inhaling it, a property that has led to its recreational use as a dissociative anaesthetic. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is also used as an oxidiser in rocket propellants, and in motor racing to increase the power output of engines. Nitrous oxide's atmospheric concentration reached 333 parts per billion (ppb) in 2020, increasing at a rate of abo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
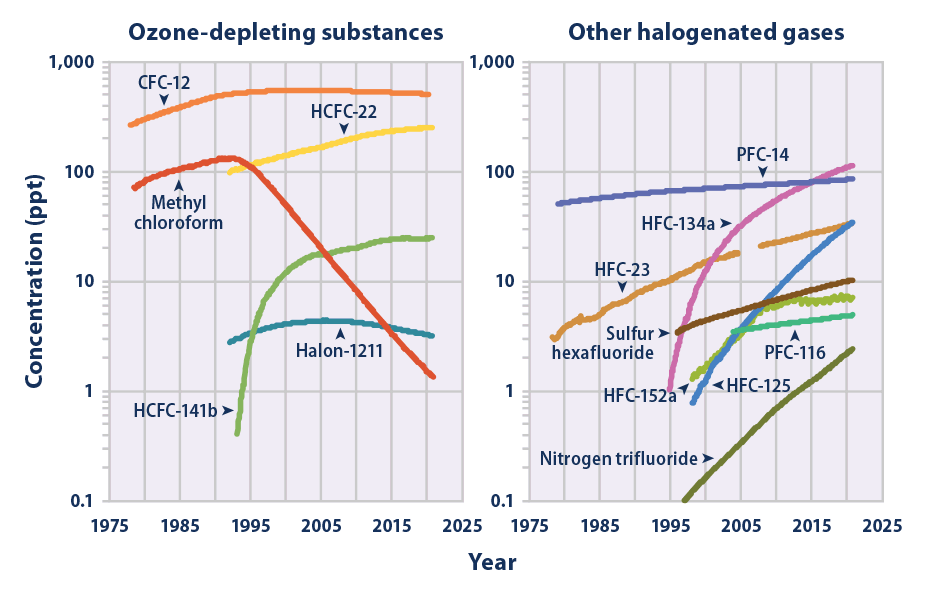
Nitrogen Trifluoride
Nitrogen trifluoride () is an inorganic, colorless, non-flammable, toxic gas with a slightly musty odor. It finds increasing use within the manufacturing of flat-panel displays, photovoltaics, LEDs and other microelectronics. Nitrogen trifluoride is also an extremely strong and long-lived greenhouse gas. Its atmospheric burden exceeded 2 parts per trillion during 2019 and has doubled every five years since the late 20th century. Synthesis and reactivity Nitrogen trifluoride did not exist in significant quantities on Earth prior to its synthesis by humans. It is a rare example of a binary fluoride that can be prepared directly from the elements only at very uncommon conditions, such as an electric discharge. After first attempting the synthesis in 1903, Otto Ruff prepared nitrogen trifluoride by the electrolysis of a molten mixture of ammonium fluoride and hydrogen fluoride. It proved to be far less reactive than the other nitrogen trihalides nitrogen trichloride, nitrogen trib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Center For Atmospheric Research
The US National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR ) is a US federally funded research and development center (FFRDC) managed by the nonprofit University Corporation for Atmospheric Research (UCAR) and funded by the National Science Foundation (NSF). NCAR has multiple facilities, including the I. M. Pei-designed Mesa Laboratory headquarters in Boulder, Colorado. Studies include meteorology, climate science, atmospheric chemistry, solar-terrestrial interactions, environmental and societal impacts. Tools and technologies NCAR was instrumental in developing lidar, light radar, now a key archaeological tool, as well as providing a broad array of tools and technologies to the scientific community for studying Earth’s atmosphere, including, * Specialized instruments to measure atmospheric processes * Research aircraft * High-performance computing and cyberinfrastructure, including supercomputers * Mauna Loa Solar Observatory * Cooperative field campaigns * Atmospheric models o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Adaptation Programme Of Action
A National Adaptation Programme of Action (NAPA) is a type of plan submitted to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) by least developed countries, to describe the country's perception of its most "urgent and immediate needs to adapt to climate change".UNFCCC: National Adaptation Programmes of Action, http://unfccc.int/national_reports/napa/items/2719.php Retrieved 16 November 2011 NAPAs are not supposed to include original research, but use existing information and include profiles of priority projects that are intended to address those needs that have been identified. The UNFCCC maintains a database of NAPAs,UNFCCC Database of NAPAs, http://unfccc.int/cooperation_support/least_developed_countries_portal/submitted_napas/items/4585.php retrieved on 16 November 2011 and of country priorities that have been identified within NAPAs. As of November 2011, it contained reports from 46 LDCs. The Least Developed Countries Fund (LDCF) was established to financ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mean Sea Level
There are several kinds of mean in mathematics Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ..., especially in statistics. Each mean serves to summarize a given group of data, often to better understand the overall value (magnitude (mathematics), magnitude and sign (mathematics), sign) of a given data set. For a data set, the ''arithmetic mean'', also known as "arithmetic average", is a measure of central tendency of a finite set of numbers: specifically, the sum of the values divided by the number of values. The arithmetic mean of a set of numbers ''x''1, ''x''2, ..., x''n'' is typically denoted using an overhead bar, \bar. If the data set were based on a series of observations obtained by sampling (statistics), sampling from a statistical population, the arithmetic mean is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interdecadal Pacific Oscillation
The Interdecadal Pacific oscillation (IPO) is an oceanographic/meteorological phenomenon similar to the Pacific decadal oscillation The Pacific decadal oscillation (PDO) is a robust, recurring pattern of ocean-atmosphere climate variability centered over the mid-latitude Pacific basin. The PDO is detected as warm or cool surface waters in the Pacific Ocean, north of 20°N. O ... (PDO), but occurring in a wider area of the Pacific. While the PDO occurs in mid-latitudes of the Pacific Ocean in the northern hemisphere, the IPO stretches from the southern hemisphere into the northern hemisphere. The period of oscillation is roughly 15–30 years. Positive phases of the IPO are characterized by a warmer than average tropical Pacific and cooler than average northern Pacific. Negative phases are characterized by an inversion of this pattern, with cool tropics and warm northern regions. The IPO had positive phases (southeastern tropical Pacific warm) from 1922 to 1946 and 1978 to 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Ocean Dipole
The Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD), also known as the Indian Niño, is an irregular oscillation of sea surface temperatures in which the western Indian Ocean becomes alternately warmer (positive phase) and then colder (negative phase) than the eastern part of the ocean. Phenomenon The IOD involves an aperiodic oscillation of sea-surface temperatures (SST), between "positive", "neutral" and "negative" phases. A positive phase sees greater-than-average sea-surface temperatures and greater precipitation in the western Indian Ocean region, with a corresponding cooling of waters in the eastern Indian Ocean—which tends to cause droughts in adjacent land areas of Indonesia and Australia. The negative phase of the IOD brings about the opposite conditions, with warmer water and greater precipitation in the eastern Indian Ocean, and cooler and drier conditions in the west. The IOD also affects the strength of monsoons over the Indian subcontinent. A significant positive IOD occurred in 1997� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Vapor
(99.9839 °C) , - , Boiling point , , - , specific gas constant , 461.5 J/( kg·K) , - , Heat of vaporization , 2.27 MJ/kg , - , Heat capacity , 1.864 kJ/(kg·K) Water vapor, water vapour or aqueous vapor is the gaseous phase of water. It is one state of water within the hydrosphere. Water vapor can be produced from the evaporation or boiling of liquid water or from the sublimation of ice. Water vapor is transparent, like most constituents of the atmosphere. Under typical atmospheric conditions, water vapor is continuously generated by evaporation and removed by condensation. It is less dense than most of the other constituents of air and triggers convection currents that can lead to clouds. Being a component of Earth's hydrosphere and hydrologic cycle, it is particularly abundant in Earth's atmosphere, where it acts as a greenhouse gas and warming feedback, contributing more to total greenhouse effect than non-condensable gases such as carbon dioxide an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrofluorocarbon
Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) are man-made organic compounds that contain fluorine and hydrogen atoms, and are the most common type of organofluorine compounds. Most are gases at room temperature and pressure. They are frequently used in air conditioning and as refrigerants; R-134a (1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane) is one of the most commonly used HFC refrigerants. In order to aid the recovery of the stratospheric ozone layer, HFCs were adopted to replace the more potent chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), which were phased out from use by the Montreal Protocol, and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) which are presently being phased out. HFCs replaced older chlorofluorocarbons such as R-12 and hydrochlorofluorocarbons such as R-21. HFCs are also used in insulating foams, aerosol propellants, as solvents and for fire protection. They do not harm the ozone layer as much as the compounds they replace, but they do contribute to global warming, with trifluoromethane having 11,700 times the warming po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrochlorofluorocarbon
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) are fully or partly halogenated hydrocarbons that contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), chlorine (Cl), and fluorine (F), produced as volatile derivatives of methane, ethane, and propane. They are also commonly known by the DuPont brand name Freon. The most common representative is dichlorodifluoromethane (R-12 or Freon-12). Many CFCs have been widely used as refrigerants, propellants (in aerosol applications), and solvents. Because CFCs contribute to ozone depletion in the upper atmosphere, the manufacture of such compounds has been phased out under the Montreal Protocol, and they are being replaced with other products such as hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) including R-410A and R-134a. Structure, properties and production As in simpler alkanes, carbon in the CFCs bond with tetrahedral symmetry. Because the fluorine and chlorine atoms differ greatly in size and effective charge from hydrogen and from each other, the metha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |