|
Clifford Module
In mathematics, a Clifford module is a representation of a Clifford algebra. In general a Clifford algebra ''C'' is a central simple algebra over some field extension ''L'' of the field ''K'' over which the quadratic form ''Q'' defining ''C'' is defined. The abstract theory of Clifford modules was founded by a paper of M. F. Atiyah, R. Bott and Arnold S. Shapiro. A fundamental result on Clifford modules is that the Morita equivalence class of a Clifford algebra (the equivalence class of the category of Clifford modules over it) depends only on the signature . This is an algebraic form of Bott periodicity. Matrix representations of real Clifford algebras We will need to study ''anticommuting'' matrices () because in Clifford algebras orthogonal vectors anticommute : A \cdot B = \frac( AB + BA ) = 0. For the real Clifford algebra \mathbb_, we need mutually anticommuting matrices, of which ''p'' have +1 as square and ''q'' have −1 as square. : \begin \gamma_a^2 &=& +1 &\mbox &1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrix (mathematics)
In mathematics, a matrix (: matrices) is a rectangle, rectangular array or table of numbers, symbol (formal), symbols, or expression (mathematics), expressions, with elements or entries arranged in rows and columns, which is used to represent a mathematical object or property of such an object. For example, \begin1 & 9 & -13 \\20 & 5 & -6 \end is a matrix with two rows and three columns. This is often referred to as a "two-by-three matrix", a " matrix", or a matrix of dimension . Matrices are commonly used in linear algebra, where they represent linear maps. In geometry, matrices are widely used for specifying and representing geometric transformations (for example rotation (mathematics), rotations) and coordinate changes. In numerical analysis, many computational problems are solved by reducing them to a matrix computation, and this often involves computing with matrices of huge dimensions. Matrices are used in most areas of mathematics and scientific fields, either directly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clifford Module Bundle
In differential geometry, a Clifford module bundle, a bundle of Clifford modules or just Clifford module is a vector bundle whose fibers are Clifford modules, the representations of Clifford algebras. The canonical example is a spinor bundle. In fact, on a Spin manifold, every Clifford module is obtained by twisting the spinor bundle. The notion "Clifford module bundle" should not be confused with a Clifford bundle, which is a bundle of Clifford algebras. Spinor bundles Given an oriented Riemannian manifold ''M'' one can ask whether it is possible to construct a bundle of irreducible Clifford modules over ''Cℓ''(''T''*''M''). In fact, such a bundle can be constructed if and only if ''M'' is a spin manifold. Let ''M'' be an ''n''-dimensional spin manifold with spin structure ''F''Spin(''M'') → ''F''SO(''M'') on ''M''. Given any ''Cℓ''''n''R-module ''V'' one can construct the associated spinor bundle :S(M) = F_(M) \times_\sigma V\, where σ : Spin(''n'') → GL(''V'') i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Higher-dimensional Gamma Matrices
In mathematical physics, higher-dimensional gamma matrices generalize to arbitrary dimension the four-dimensional Gamma matrices of Paul Dirac, Dirac, which are a mainstay of relativistic quantum mechanics. They are utilized in relativistically invariant wave equations for fermions (such as spinors) in arbitrary space-time dimensions, notably in string theory and supergravity. The Weyl–Brauer matrices provide an explicit construction of higher-dimensional gamma matrices for Weyl spinors. Gamma matrices also appear in generic settings in Riemannian geometry, particularly when a spin structure can be defined. Introduction Consider a space-time of dimension with the flat Minkowski metric, : \eta = \, \eta_\, = \text(+1, \dots, +1, -1, \dots, -1) ~, with p positive entries, q negative entries, p + q = d and . Set . The standard Dirac matrices correspond to taking and or . In higher (and lower) dimensions, one may define a group (mathematics), group, the gamma group, be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weyl–Brauer Matrices
In mathematics, particularly in the theory of spinors, the Weyl–Brauer matrices are an explicit realization of a Clifford algebra as a matrix algebra of matrices. They generalize the Pauli matrices to dimensions, and are a specific construction of higher-dimensional gamma matrices. They are named for Richard Brauer and Hermann Weyl,. and were one of the earliest systematic constructions of spinors from a representation theoretic standpoint. The matrices are formed by taking tensor products of the Pauli matrices, and the space of spinors in dimensions may then be realized as the column vectors of size on which the Weyl–Brauer matrices act. Construction Suppose that ''V'' = Rn is a Euclidean space of dimension ''n''. There is a sharp contrast in the construction of the Weyl–Brauer matrices depending on whether the dimension ''n'' is even or odd. Let = 2 (or 2+1) and suppose that the Euclidean quadratic form on is given by :q_1^2+\dots+q_k^2+p_1^2+\dots+p_k^2 ~~ (+p_n^ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sign Convention
In physics, a sign convention is a choice of the physical significance of signs (plus or minus) for a set of quantities, in a case where the choice of sign is arbitrary. "Arbitrary" here means that the same physical system can be correctly described using different choices for the signs, as long as one set of definitions is used consistently. The choices made may differ between authors. Disagreement about sign conventions is a frequent source of confusion, frustration, misunderstandings, and even outright errors in scientific work. In general, a sign convention is a special case of a choice of coordinate system for the case of one dimension. Sometimes, the term "sign convention" is used more broadly to include factors of the imaginary unit and , rather than just choices of sign. Relativity Metric signature In relativity, the metric signature can be either or . (Throughout this article, the signs of the eigenvalues of the metric are displayed in the order that presents the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
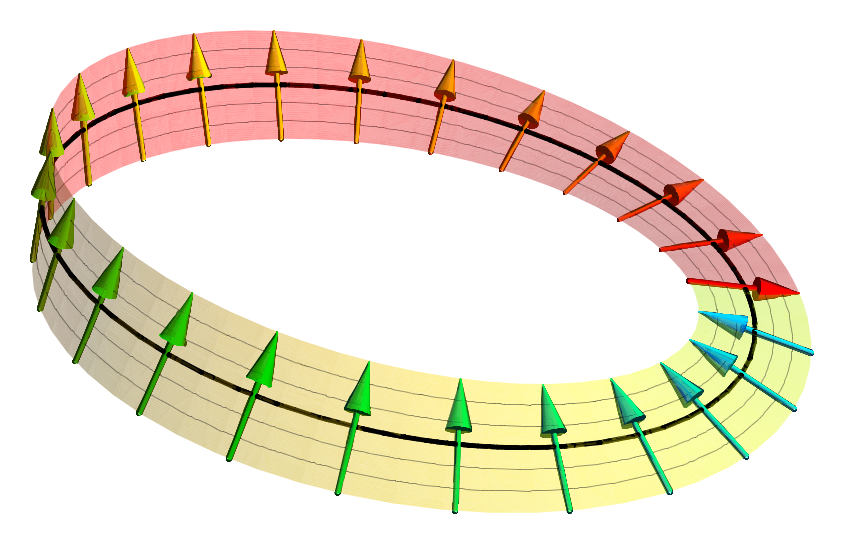
Spinors
In geometry and physics, spinors (pronounced "spinner" IPA ) are elements of a complex numbers, complex vector space that can be associated with Euclidean space. A spinor transforms linearly when the Euclidean space is subjected to a slight (infinitesimal transformation, infinitesimal) rotation, but unlike Euclidean vector, geometric vectors and tensors, a spinor transforms to its negative when the space rotates through 360° (see picture). It takes a rotation of 720° for a spinor to go back to its original state. This property characterizes spinors: spinors can be viewed as the "square roots" of vectors (although this is inaccurate and may be misleading; they are better viewed as "square roots" of Section (fiber bundle), sections of vector bundles – in the case of the exterior algebra bundle of the cotangent bundle, they thus become "square roots" of differential forms). It is also possible to associate a substantially similar notion of spinor to Minkowski space, in which cas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dirac Equation
In particle physics, the Dirac equation is a relativistic wave equation derived by British physicist Paul Dirac in 1928. In its free form, or including electromagnetic interactions, it describes all spin-1/2 massive particles, called "Dirac particles", such as electrons and quarks for which parity is a symmetry. It is consistent with both the principles of quantum mechanics and the theory of special relativity, and was the first theory to account fully for special relativity in the context of quantum mechanics. The equation is validated by its rigorous accounting of the observed fine structure of the hydrogen spectrum and has become vital in the building of the Standard Model. The equation also implied the existence of a new form of matter, '' antimatter'', previously unsuspected and unobserved and which was experimentally confirmed several years later. It also provided a ''theoretical'' justification for the introduction of several component wave functions in Pauli' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ettore Majorana
Ettore Majorana ( ,, uploaded 19 April 2013, retrieved 14 December 2019 ; 5 August 1906 – disappeared 25 March 1938) was an Italian theoretical physicist who worked on neutrino masses. Majorana was a supporter of Italian Fascism and a member of the National Fascist Party. He disappeared under mysterious circumstances after purchasing a ticket to travel by ship from Palermo to Naples. The Majorana equation, Majorana fermions, and Microsoft's device attempting to create topological qubits, Majorana 1, are named after him. In 2006, the Majorana Prize was established in his memory. In 1938, Enrico Fermi was quoted as saying about Majorana: "There are several categories of scientists in the world; those of second or third rank do their best but never get very far. Then there is the first rank, those who make important discoveries, fundamental to scientific progress. But then there are the geniuses, like Galilei and Newton. Majorana was one of these." Life and work Early and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Matrices
In mathematical physics, the gamma matrices, \ \left\\ , also called the Dirac matrices, are a set of conventional matrices with specific anticommutation relations that ensure they generate a matrix representation of the Clifford algebra \ \mathrm_(\mathbb) ~. It is also possible to define higher-dimensional gamma matrices. When interpreted as the matrices of the action of a set of orthogonal basis vectors for contravariant vectors in Minkowski space, the column vectors on which the matrices act become a space of spinors, on which the Clifford algebra of spacetime acts. This in turn makes it possible to represent infinitesimal spatial rotations and Lorentz boosts. Spinors facilitate spacetime computations in general, and in particular are fundamental to the Dirac equation for relativistic particles. Gamma matrices were introduced by Paul Dirac in 1928. In Dirac representation, the four contravariant gamma matrices are : \begin \gamma^0 &= \begin 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bott Periodicity
In mathematics, the Bott periodicity theorem describes a periodicity in the homotopy groups of classical groups, discovered by , which proved to be of foundational significance for much further research, in particular in K-theory of stable complex vector bundles, as well as the stable homotopy groups of spheres. Bott periodicity can be formulated in numerous ways, with the periodicity in question always appearing as a period-2 phenomenon, with respect to dimension, for the theory associated to the unitary group. See for example topological K-theory. There are corresponding period-8 phenomena for the matching theories, ( real) KO-theory and (quaternionic) KSp-theory, associated to the real orthogonal group and the quaternionic symplectic group, respectively. The J-homomorphism is a homomorphism from the homotopy groups of orthogonal groups to stable homotopy groups of spheres, which causes the period 8 Bott periodicity to be visible in the stable homotopy groups of spheres. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Representation Of An Algebra
Representation may refer to: Law and politics *Representation (politics), political activities undertaken by elected representatives, as well as other theories ** Representative democracy, type of democracy in which elected officials represent a group of people * Representation in contract law, a pre-contractual statement that may (if untrue) result in liability for misrepresentation * Labor representation, or worker representation, the work of a union representative who represents and defends the interests of fellow labor union members * Legal representation, provided by a barrister, lawyer, or other advocate * Lobbying or interest representation, attempts to influence the actions, policies, or decisions of officials * " No taxation without representation", a 1700s slogan that summarized one of the American colonists' 27 colonial grievances in the Thirteen Colonies, which was one of the major causes of the American Revolution * Permanent representation, a type of diplomatic missio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |