|
Clayton-Marsh Creek-Greenville Fault
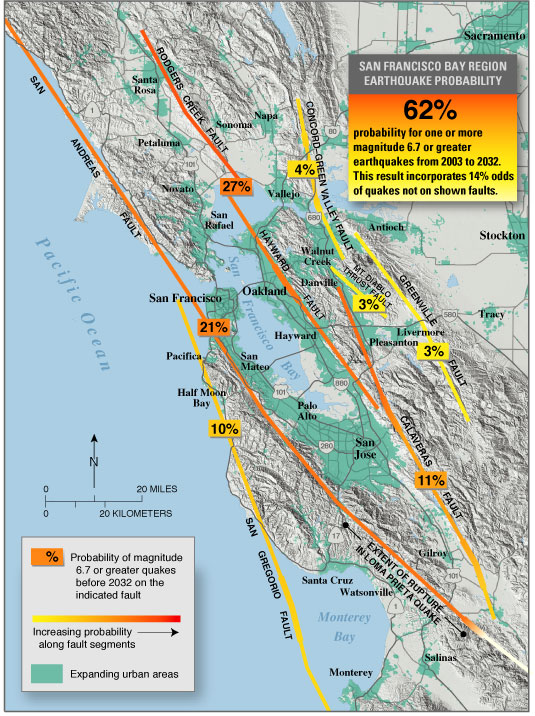
The Clayton-Marsh Creek-Greenville Fault is a fault located in the eastern San Francisco Bay Area of California, in Alameda County and Contra Costa County. It is part of the somewhat parallel system of faults that are secondary to the San Andreas Fault. Seismic activity The 5.8 magnitude 1980 Livermore earthquake occurred on this fault. The fault creeps at a rate of at 2 mm/year. The predicted probability of a major earthquake on this fault within the next 30 years is relatively low, at 3%, compared to nearby faults such as the Hayward Fault. See also * Calaveras Fault * Concord Fault The Concord Fault is a geologic fault in the San Francisco Bay Area. The reason it is called that is because it is located under the city of Concord. It is connected to, and considered to be part of, the same fault zone as the Green Valley fault, ... References Seismic faults of California Geography of Alameda County, California Natural history of Contra Costa County, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fault (geology)
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic forces, with the largest forming the boundaries between the plates, such as the megathrust faults of subduction zones or transform faults. Energy release associated with rapid movement on active faults is the cause of most earthquakes. Faults may also displace slowly, by aseismic creep. A ''fault plane'' is the plane that represents the fracture surface of a fault. A ''fault trace'' or ''fault line'' is a place where the fault can be seen or mapped on the surface. A fault trace is also the line commonly plotted on geologic maps to represent a fault. A ''fault zone'' is a cluster of parallel faults. However, the term is also used for the zone of crushed rock along a single fault. Prolonged motion along closely spaced faults can blur the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Francisco Bay Area
The San Francisco Bay Area, often referred to as simply the Bay Area, is a populous region surrounding the San Francisco, San Pablo, and Suisun Bay estuaries in Northern California. The Bay Area is defined by the Association of Bay Area Governments to include the nine counties that border the aforementioned estuaries: Alameda, Contra Costa, Marin, Napa, San Mateo, Santa Clara, Solano, Sonoma, and San Francisco. Other definitions may be either smaller or larger, and may include neighboring counties that do not border the bay such as Santa Cruz and San Benito (more often included in the Central Coast regions); or San Joaquin, Merced, and Stanislaus (more often included in the Central Valley). The core cities of the Bay Area are San Francisco, San Jose, and Oakland. Home to approximately 7.76 million people, Northern California's nine-county Bay Area contains many cities, towns, airports, and associated regional, state, and national parks, connected by a comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territories of the United States by population, most populous U.S. state and the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 3rd largest by area. It is also the most populated Administrative division, subnational entity in North America and the 34th most populous in the world. The Greater Los Angeles area and the San Francisco Bay Area are the nation's second and fifth most populous Statistical area (United States), urban regions respectively, with the former having more than 18.7million residents and the latter having over 9.6million. Sacramento, California, Sacramento is the state's capital, while Los Angeles is the List of largest California cities by population, most populous city in the state and the List of United States cities by population, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alameda County, California
Alameda County ( ) is a county located in the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 census, the population was 1,682,353, making it the 7th-most populous county in the state and 21st most populous nationally. The county seat is Oakland. Alameda County is in the San Francisco Bay Area, occupying much of the East Bay region. The Spanish word ''alameda'' means either "a grove of poplars...or a tree lined street." The name was originally used to describe the Arroyo de la Alameda. The willow and sycamore trees along the banks of the river reminded the early Spanish explorers of a road lined with trees. Although a strict translation to English might be "Poplar Grove Creek," the name of the principal stream that flows through the county is now simply " Alameda Creek." Alameda County is part of the San Francisco–Oakland–Berkeley, CA Metropolitan Statistical Area, and the San Jose–San Francisco–Oakland, CA Combined Statistical Area. History The county was formed on Mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contra Costa County, California
) of the San Francisco Bay , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = United States , subdivision_type1 = State , subdivision_name1 = California , subdivision_type2 = Region , subdivision_name2 = San Francisco Bay Area , seat_type = County seat , seat = Martinez , parts_type = Largest city , parts = Concord (population and land area)Richmond (total area) , unit_pref = US , area_total_sq_mi = 804 , area_land_sq_mi = 715.94 , area_water_sq_mi = 81 , elevation_max_footnotes = , elevation_max_ft = 3852 , population_as_of = 2020 , population_footnotes = , population_total = 1,165,927 , population_density_sq_mi = 1629 , established_title ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Andreas Fault
The San Andreas Fault is a continental transform fault that extends roughly through California. It forms the tectonics, tectonic boundary between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate, and its motion is Fault (geology)#Strike-slip faults, right-lateral strike-slip (horizontal). The fault divides into three segments, each with different characteristics and a different degree of earthquake risk. The slip rate along the fault ranges from /yr. It was formed by a transform boundary. The fault was identified in 1895 by Professor Andrew Lawson of University of California, Berkeley, UC Berkeley, who discovered the northern zone. It is often described as having been named after San Andreas Lake, a small body of water that was formed in a valley between the two plates. However, according to some of his reports from 1895 and 1908, Lawson actually named it after the surrounding San Andreas Valley. Following the 1906 San Francisco earthquake, Lawson concluded that the fault extende ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1980 Livermore Earthquake
The 1980 Livermore earthquake occurred on January 24 at 11:00 PST in California. The epicenter of the 5.8 earthquake was a hilly area southeast of Mount Diablo and north of Livermore Valley. The earthquake had a maximum Modified Mercalli intensity scale, Modified Mercalli intensity of VII (''Very strong''). Forty four people were injured and damage across the San Francisco Bay Area totaled $11.5 million, with the majority inflicted at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. Earthquake The mainshock was preceded by a 2.7 foreshock 1.5 minutes prior. In the first six says after the mainshock, 59 aftershocks were recorded measuring ≥ 2.5 . On January 26, a 5.3 aftershock occurred with an epicenter southeast of the mainshock. Six hundred aftershocks were recorded in the 33 days after the mainshock. An analysis of P wave indicate the fault plane solution was right-lateral strike-slip faulting. Faulting Surface faulting consisting of discontinued and small offsets occurred a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fault (geology)
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic forces, with the largest forming the boundaries between the plates, such as the megathrust faults of subduction zones or transform faults. Energy release associated with rapid movement on active faults is the cause of most earthquakes. Faults may also displace slowly, by aseismic creep. A ''fault plane'' is the plane that represents the fracture surface of a fault. A ''fault trace'' or ''fault line'' is a place where the fault can be seen or mapped on the surface. A fault trace is also the line commonly plotted on geologic maps to represent a fault. A ''fault zone'' is a cluster of parallel faults. However, the term is also used for the zone of crushed rock along a single fault. Prolonged motion along closely spaced faults can blur the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aseismic Creep
In geology, aseismic creep or fault creep is measurable surface displacement along a fault in the absence of notable earthquakes. Aseismic creep may also occur as "after-slip" days to years after an earthquake. Notable examples of aseismic slip include faults in California (e.g. Calaveras Fault, Hayward Fault, and San Andreas Fault). Causes Aseismic creep accommodates far-field motions on localized zones of deformation at tectonic plate boundaries. The underlying causes of aseismic creep are primarily attributed to poor frictional strength of the fault, low normal stress acting on the fault in the shallow crust, and excessive pore-fluid pressures, which limit the viable amount of normal stress on a fault. The frictional reaction of geologic materials can explain the transition from seismic to aseismic deformation with depth. Friction along faults can cause sudden slips with associated stress drops (earthquakes), along with phases of no motion as stress recharges. Measurements ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hayward Fault
The Hayward Fault Zone is a right-lateral strike-slip geologic fault zone capable of generating destructive earthquakes. This fault is about long, situated mainly along the western base of the hills on the east side of San Francisco Bay. It runs through densely populated areas, including Richmond, El Cerrito, Berkeley, Oakland, San Leandro, Castro Valley, Hayward, Union City, Fremont, and San Jose. The Hayward Fault is parallel to the San Andreas Fault, which lies offshore and through the San Francisco Peninsula. To the east of the Hayward Fault lies the Calaveras Fault. In 2007, the Hayward Fault was discovered to have merged with the Calaveras Fault east of San Jose at a depth of , with the potential of creating earthquakes much larger than previously anticipated. Some geologists have suggested that the Southern Calaveras should be renamed as the Southern Hayward. North of San Pablo Bay is the Rodgers Creek Fault, which was shown in 2016 to be linked with the Hayward Faul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calaveras Fault
The Calaveras Fault is a major branch of the San Andreas Fault System that is located in northern California in the San Francisco Bay Area. Activity on the different segments of the fault includes moderate and large earthquakes as well as aseismic creep. The last large event was the magnitude 6.2 1984 Morgan Hill event. The most recent moderate earthquakes were the magnitude 5.1 event on 25 October 2022, and the magnitude 5.6 2007 Alum Rock event. It is believed to link with the Hayward fault, as well as the West Napa Fault, north of the Carquinez Strait. It passes through or near the cities of Alamo, Danville, San Ramon, Dublin, Pleasanton, Sunol, Milpitas, San Jose, Gilroy, and Hollister. Location To the east of the Hayward-Rodgers Creek fault, the Calaveras fault extends , splaying from the San Andreas fault near Hollister and terminating at Danville at its northern end. It runs east of the San Andreas, diverging from it in the vicinity of Hollister, California, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |