|
Clathria (Clathria) Elegans
''Clathria elegans'' is a species of sea sponge in the family Microcionidae Microcionidae is a family of marine demosponges. Subdivisions The following genera are recognized within the family Microcionidae: * Subfamily Microcioninae Carter 1875 ** ''Clathria'' Schmidt, 1862 ** '' Echinochalina'' Thiele, 1903 ** ''Holop .... It is found in the United States part of the North Atlantic Ocean. It was first described in 1880 by Gualtherus Carel Jacob Vosmaer. References Poecilosclerida Sponges described in 1880 Taxa named by Gualtherus Carel Jacob Vosmaer {{Demosponge-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gualtherus Carel Jacob Vosmaer
Gualtherus Carel Jacob Vosmaer (Oud-Beijerland, August 19, 1854 - Leiden, September 23, 1916 ) was a Dutch zoologist. Biography GCJ Vosmaer was born in 1854 in Oud-Beijerland, where his father, the poet and critic Carel Vosmaer was then a clerk at the subdistrict court. He studied in The Hague and subsequently at the University of Leiden, where he obtained his doctorate in 1880 with a thesis on sponges ("'' Leucandra aspera'' and the Canal System of Sponges"). In 1882 he became Anton Dohrn's assistant at his zoological station in Naples. In 1889 he returned to the Netherlands and became assistant to Professor Ambrosius Hubrecht in Utrecht. Later he became a private teacher and lecturer in Utrecht and in 1904 he became professor of zoology in Leiden. Work Vosmaer was a specialist in the field of sponges, describing many species. In Naples he examined the sponges in the Bay of Naples. issued posthumously in 1933-1935 He also described the sponges collected during the ''Willem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
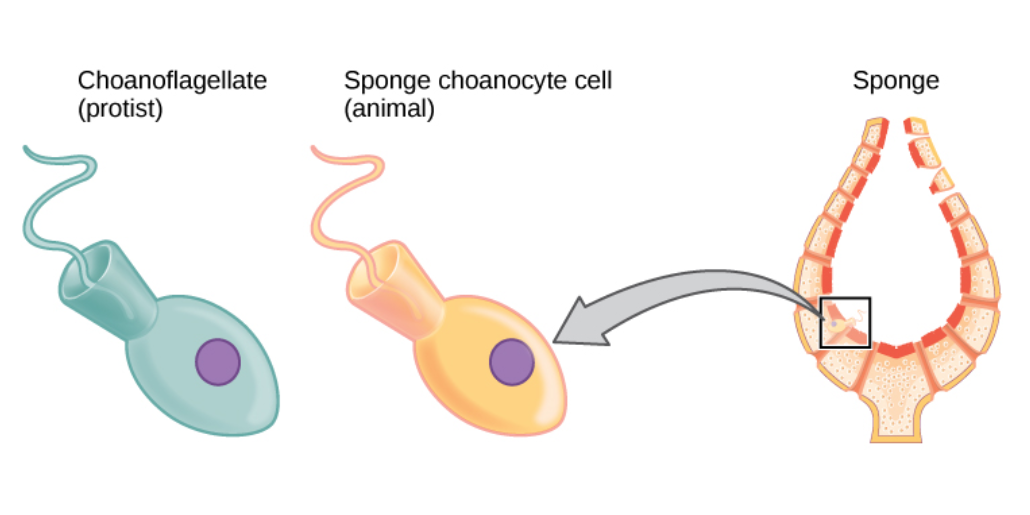
Sea Sponge
Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through them, consisting of jelly-like mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of cells. Sponges have unspecialized cells that can transform into other types and that often migrate between the main cell layers and the mesohyl in the process. Sponges do not have nervous, digestive or circulatory systems. Instead, most rely on maintaining a constant water flow through their bodies to obtain food and oxygen and to remove wastes. Sponges were first to branch off the evolutionary tree from the last common ancestor of all animals, making them the sister group of all other animals. Etymology The term ''sponge'' derives from the Ancient Greek word ( 'sponge'). Overview Sponges are similar to other animals in that they are multicellular, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcionidae
Microcionidae is a family of marine demosponges. Subdivisions The following genera are recognized within the family Microcionidae: * Subfamily Microcioninae Carter 1875 ** ''Clathria'' Schmidt, 1862 ** '' Echinochalina'' Thiele, 1903 ** ''Holopsamma'' Carter, 1885 ** ''Pandaros'' Duchassaing & Michelotti, 1864 * Subfamily Ophlitaspongiinae de Laubenfels, 1936 ** ''Antho'' Gray, 1867 ** ''Artemisina'' Vosmaer, 1885 ** ''Echinoclathria'' Carter, 1885 ** ''Ophlitaspongia ''Ophlitaspongia'' is a genus of demosponges belonging to the family Microcionidae. Many species formerly included in this genus have been moved to other genera such as ''Clathria'' and ''Echinoclathria ''Echinoclathria'' is a genus of demospo ...'' Bowerbank, 1866 ** '' Sigmeurypon'' Topsent, 1928 References Poecilosclerida Sponge families {{Demosponge-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poecilosclerida
Poecilosclerida is an order of the demosponge class. It is the most speciose demosponge order with over 2200 species (World Porifera Database). It contains about 25 recognised families. They are characterised by having chelae microscleres, that is, the minute spicules scattered through the tissues, usually in the 10-60 μm range, have a shovel-like structure on the end. Most of the families are viviparous with parenchymella larvae that are uniformly ciliated The cilium, plural cilia (), is a membrane-bound organelle found on most types of eukaryotic cell, and certain microorganisms known as ciliates. Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike projecti .... Families As of 2018, the following families are recognized: References {{demosponge-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sponges Described In 1880
Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through them, consisting of jelly-like mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of cells. Sponges have unspecialized cells that can transform into other types and that often migrate between the main cell layers and the mesohyl in the process. Sponges do not have nervous, digestive or circulatory systems. Instead, most rely on maintaining a constant water flow through their bodies to obtain food and oxygen and to remove wastes. Sponges were first to branch off the evolutionary tree from the last common ancestor of all animals, making them the sister group of all other animals. Etymology The term ''sponge'' derives from the Ancient Greek word ( 'sponge'). Overview Sponges are similar to other animals in that they are multicellular, heter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)