|
Class 03 (other)
{{disambiguation ...
Class 03 may refer to: * British Rail Class 03, a class of post-war, British diesel-mechanical shunter, *DRG Class 03, a class of inter-war, German standard steam locomotive ('' Einheitslokomotive'') for express train duties on lighter main lines. *DRG Class 03.10, a streamlined, 3- cylinder development of the above DRG Class 03 built at the outset of World War II. See also *Class 3 (other) Class 3 may refer to: * BR Standard Class 3 2-6-0, British steam locomotive * BR Standard Class 3 2-6-2T, British steam locomotive * Classes of U.S. Senators * L&YR Class 3, British 4-4-0 steam locomotive * SCORE Class 3, off-road racing trucks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
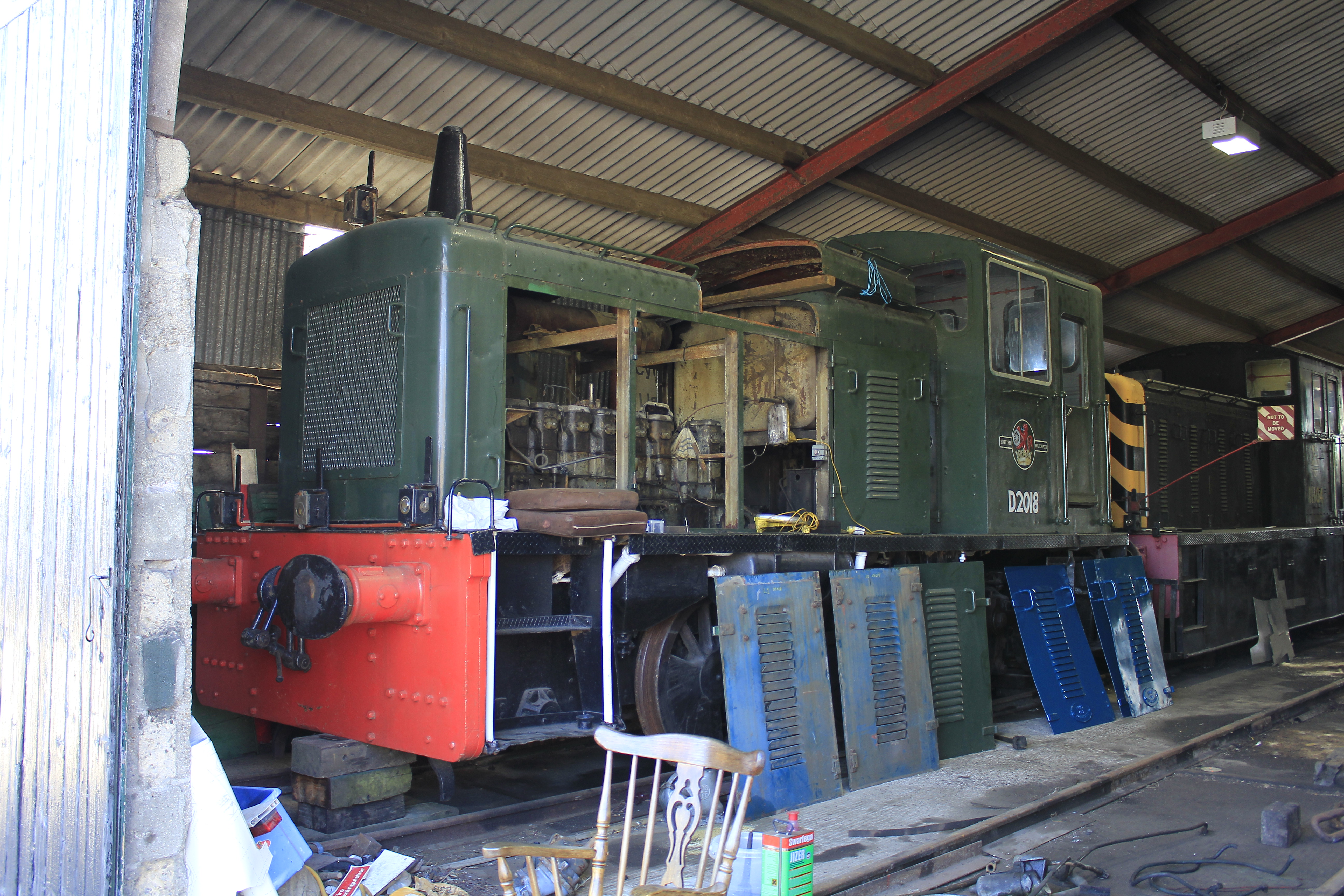
British Rail Class 03
The British Rail Class 03 locomotive was, together with the similar Class 04, one of British Railways' most successful 0-6-0 diesel-mechanical shunters. 230 were built at Doncaster and Swindon works between 1957 and 1962, and were numbered D2000-D2199 and D2370-D2399 (later 03004 to 03399). D2370 and D2371 were used as departmental locomotives and originally numbered 91 and 92 respectively. Overview Like other shunters of this size, the Class 03 was built for light duties where a larger locomotive was not needed, especially for shunting at locomotive and carriage depots and as station pilots, or where larger or heavier locomotives could not be used. The reduction over time in the demand for shunting locomotives meant that they were progressively withdrawn from 1968 onwards, many being sold to private industry, including three that were exported to Belgium. However, some remained in service much longer, with two examples on the Isle of Wight lasting until 1993 (mainland exam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diesel-mechanical
A diesel locomotive is a type of railway locomotive in which the prime mover is a diesel engine. Several types of diesel locomotives have been developed, differing mainly in the means by which mechanical power is conveyed to the driving wheels. Early internal combustion locomotives and railcars used kerosene and gasoline as their fuel. Rudolf Diesel patented his first compression-ignition engine in 1898, and steady improvements to the design of diesel engines reduced their physical size and improved their power-to-weight ratios to a point where one could be mounted in a locomotive. Internal combustion engines only operate efficiently within a limited power band, and while low power gasoline engines could be coupled to mechanical transmissions, the more powerful diesel engines required the development of new forms of transmission. This is because clutches would need to be very large at these power levels and would not fit in a standard -wide locomotive frame, or wear too quickl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shunter
A switcher, shunter, yard pilot, switch engine, yard goat, or shifter is a small Rail transport, railroad locomotive used for manoeuvring railroad cars inside a rail yard in a process known as Shunt (railway operations), ''switching'' (US) or ''shunting'' (UK). Switchers are not intended for moving trains over long distances but rather for assembling trains in order for another locomotive to take over. They do this in classification yards (Great Britain: ''marshalling yards''). Switchers may also make short transfer runs and even be the only motive power on branch lines and switching and terminal railroads. The term can also be used to describe the workers operating these engines or engaged in directing shunting operations. Switching locomotives may be purpose-built engines, but may also be downgraded main-line engines, or simply main-line engines assigned to switching. Switchers can also be used on short excursion train rides. The typical switcher is optimised for its job, be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DRG Class 03
The Class 03 steam engines were standard express train locomotives ('' Einheitslokomotiven'') in service with the Deutsche Reichsbahn. History The Class 03 engines were built between 1930 and 1938 as express train locomotives for routes that were only suitable for axle loads of up to 18 tonnes. 298 examples of this engine, whose construction was based on the Class 01, were built by the firms of Borsig, Krupp, Henschel, and Schwartzkopff. Its reduced weight was achieved by the use of a light sectional frame, smaller boiler and smaller cylinders. From engine number 03 123 onwards the pumps were located in the centre of the locomotive and from number 03 163 the locos had larger leading wheels. Locomotive number 03 154 was equipped with a parabolic smokebox door, a tapered driver's cab and driving gear cover plates. Number 03 193 was given a wine-red, streamlined, full covering and a 2′3 T 37 St tender, in order to repl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the locomotive's boiler to the point where it becomes gaseous and its volume increases 1,700 times. Functionally, it is a steam engine on wheels. In most locomotives, the steam is admitted alternately to each end of its cylinders, in which pistons are mechanically connected to the locomotive's main wheels. Fuel and water supplies are usually carried with the locomotive, either on the locomotive itself or in a tender coupled to it. Variations in this general design include electrically-powered boilers, turbines in place of pistons, and using steam generated externally. Steam locomotives were first developed in the United Kingdom during the early 19th century and used for railway transport until the middle of the 20th century. Richard Trevithick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Einheitsdampflokomotive
The Einheitsdampflokomotiven ("standard steam locomotives"), sometimes shortened to ''Einheitslokomotiven'' or ''Einheitsloks'', were the standardized steam locomotives built in Germany after 1925 under the direction of the Deutsche Reichsbahn-Gesellschaft. Their manufacture made extensive use of standard design features and components. 300px, Einheitslok of the Historic Railway, Frankfurt DRG Class 01 in 2007">DRG_Class_01.html" ;"title="Historic Railway, Frankfurt DRG Class 01">Historic Railway, Frankfurt DRG Class 01 in 2007 Development Following the merger of the state railways (''Länderbahnen'') in Germany into the Reich railway in 1920 and into the Deutsche Reichsbahn-Gesellschaft in 1924, the locomotive fleet of the new national railway administration still had 210 different types and classes of steam engine. This considerably hindered the flexible employment of locomotives within the railway network, and servicing and maintenance was very costly as a result of the large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
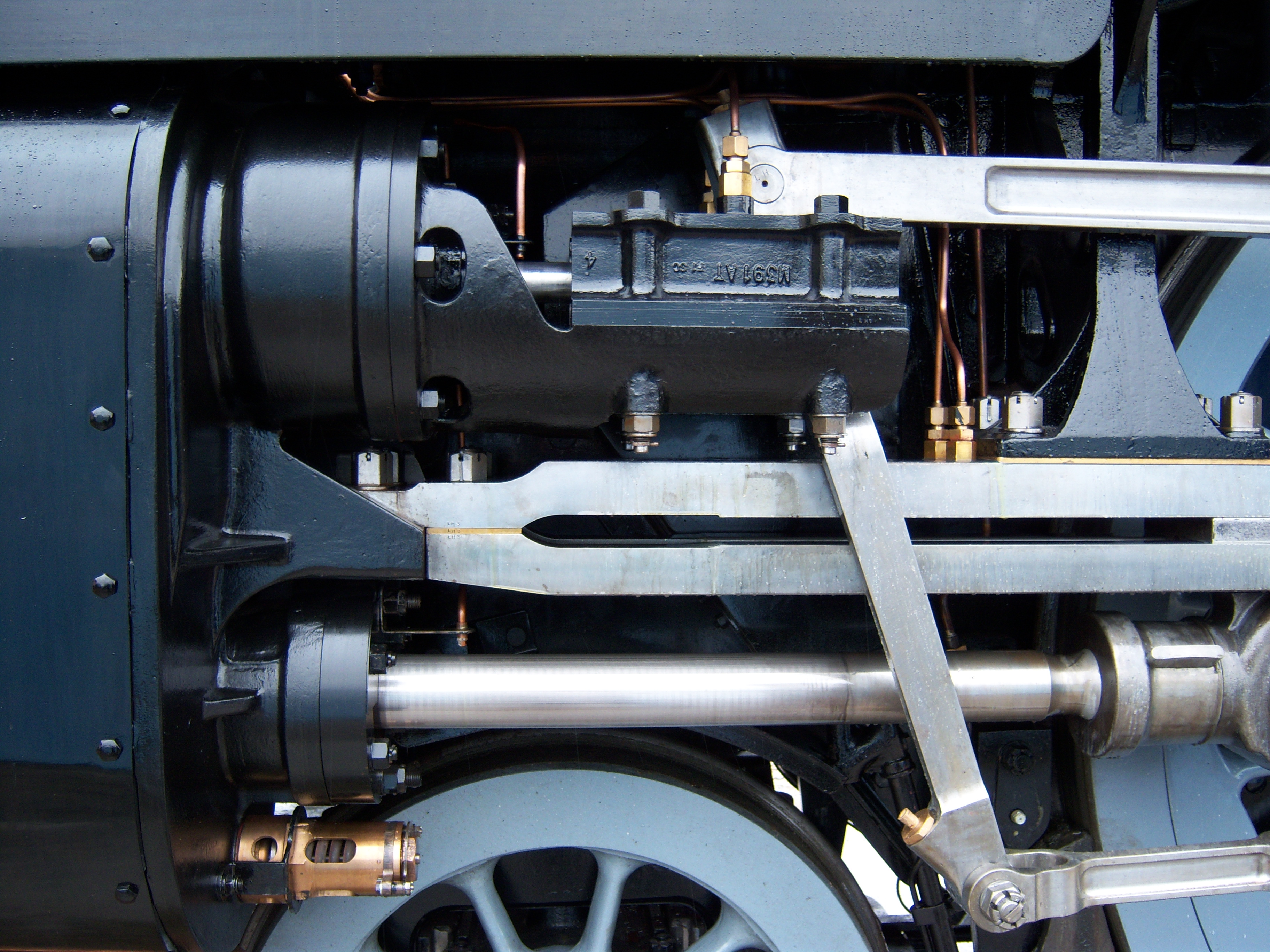
Cylinder (locomotive)
The cylinder is the power-producing element of the steam engine powering a steam locomotive. The cylinder is made pressure-tight with end covers and a piston; a valve distributes the steam to the ends of the cylinder. Cylinders were cast in iron and later made of steel. The cylinder casting includes other features such as (in the case of the early Rocket locomotive) valve ports and mounting feet. The last big American locomotives incorporated the cylinders as part of huge one-piece steel castings that were the main frame of the locomotive. Renewable wearing surfaces were needed inside the cylinders and provided by cast-iron bushings. The way the valve controlled the steam entering and leaving the cylinder was known as steam distribution and shown by the shape of the indicator diagram. What happened to the steam inside the cylinder was assessed separately from what happened in the boiler and how much friction the moving machinery had to cope with. This assessment was known as "e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |