|
Clarence Syvertson
Clarence A. "Sy" Syvertson (1926 – September 13, 2010) was the Center Director of the Ames Research Center of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration, located at Moffett Field, California. Biography Early life, education, and military service Syvertson was born in Minneapolis, Minnesota in 1926. He graduated from the University of Minnesota with a Bachelor of Aeronautical Engineering (with Distinction) in 1946 at age 20. After serving in the US Army in 1946 - 1947, he returned to the University and earned a Master of Science in the same field in 1948. He also did graduate work at Stanford University and the Harvard Business School. He is a member of the National Academy of Engineering, a Fellow of the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, of the American Astronautical Society, and of the California Council on Science and Technology (emeritus), a member of Tau Beta Pi and Tau Omega honorary societies. Aerodynamics research In 1948, Syvertson joi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minneapolis, Minnesota
Minneapolis is a city in Hennepin County, Minnesota, United States, and its county seat. With a population of 429,954 as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the state's List of cities in Minnesota, most populous city. Located in the state's center near the eastern border, it occupies both banks of the Upper Mississippi River and adjoins Saint Paul, Minnesota, Saint Paul, the state capital of Minnesota. Minneapolis, Saint Paul, and the surrounding area are collectively known as the Minneapolis–Saint Paul, Twin Cities, a metropolitan area with 3.69 million residents. Minneapolis is built on an artesian aquifer on flat terrain and is known for cold, snowy winters and hot, humid summers. Nicknamed the "City of Lakes", Minneapolis is abundant in water, with list of lakes in Minneapolis, thirteen lakes, wetlands, the Mississippi River, creeks, and waterfalls. The city's public park system is connected by the Grand Rounds National Scenic Byway. Dakota people orig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lifting Body
A lifting body is a fixed-wing aircraft or spacecraft configuration in which the body itself produces lift (force), lift. In contrast to a flying wing, which is a wing with minimal or no conventional fuselage, a lifting body can be thought of as a fuselage with little or no conventional wing. Whereas a flying wing seeks to maximize cruise efficiency at Subsonic flight, subsonic speeds by eliminating non-lifting surfaces, lifting bodies generally minimize the drag and structure of a wing for subsonic, supersonic and hypersonic flight, or spacecraft re-entry. All of these flight regimes pose challenges for proper flight safety. Lifting bodies were a major area of research in the 1960s and 1970s as a means to build a small and lightweight crewed spacecraft. The US built a number of lifting body rocket planes to test the concept, as well as several rocket-launched re-entry vehicles that were tested over the Pacific. Interest waned as the US Air Force lost interest in the crewed missio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XV-15
The Bell XV-15 is an American tiltrotor VTOL aircraft. It was the second successful experimental tiltrotor aircraft and the first to demonstrate the concept's high speed performance relative to conventional helicopters. Development Early VTOL rotor aircraft The idea of building VTOL aircraft using helicopter-like rotors at the wingtips originated in the 1930s. The first design resembling modern tiltrotors was patented by George Lehberger in May 1930, but he did not develop the concept further. In World War II, a German prototype called the Focke-Achgelis Fa 269 was developed starting in 1942, but it never flew. Two prototypes that made it to flight were the one-seat Transcendental Model 1-G and two-seat Transcendental Model 2, both powered by single reciprocating engines. Development started on the Model 1-G in 1947, and it flew in 1954. The Model 1-G flew until a crash in Chesapeake Bay on 20 July 1955, destroying the prototype aircraft but not seriously injuring the pilot. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA Exceptional Service Medal
The NASA Exceptional Service Medal is an award granted to U.S. government employees for significant sustained performance characterized by unusual initiative or creative ability that clearly demonstrates substantial improvement in engineering, aeronautics, space flight, administration, support, or space-related endeavors which contribute to NASA programs. The medal was inherited by NASA from its predecessor organization, the National Advisory Committee on Aeronautics (NACA) and featured the NACA emblem. The original NASA version featured the NASA seal. Notable recipients *Buzz Aldrin (1969) * Robert O. Aller (twice) * Aseel Anabtawi (2007) *Neil Armstrong (1966) *Brandon T. Bailey (2019) * Charles Bolden (thrice) *Frank Borman 1965 * John R. Casani (1965) * Lin Chambers (2009) * Kevin Chilton * Eileen Collins (1998) * Michael Collins (1966) * Lana Couch (1986) * Nagin Cox * William H. Dana * Jean Dickey (1998) * John H. Disher (twice, last in 1980) * Einar Enevoldson (1974 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
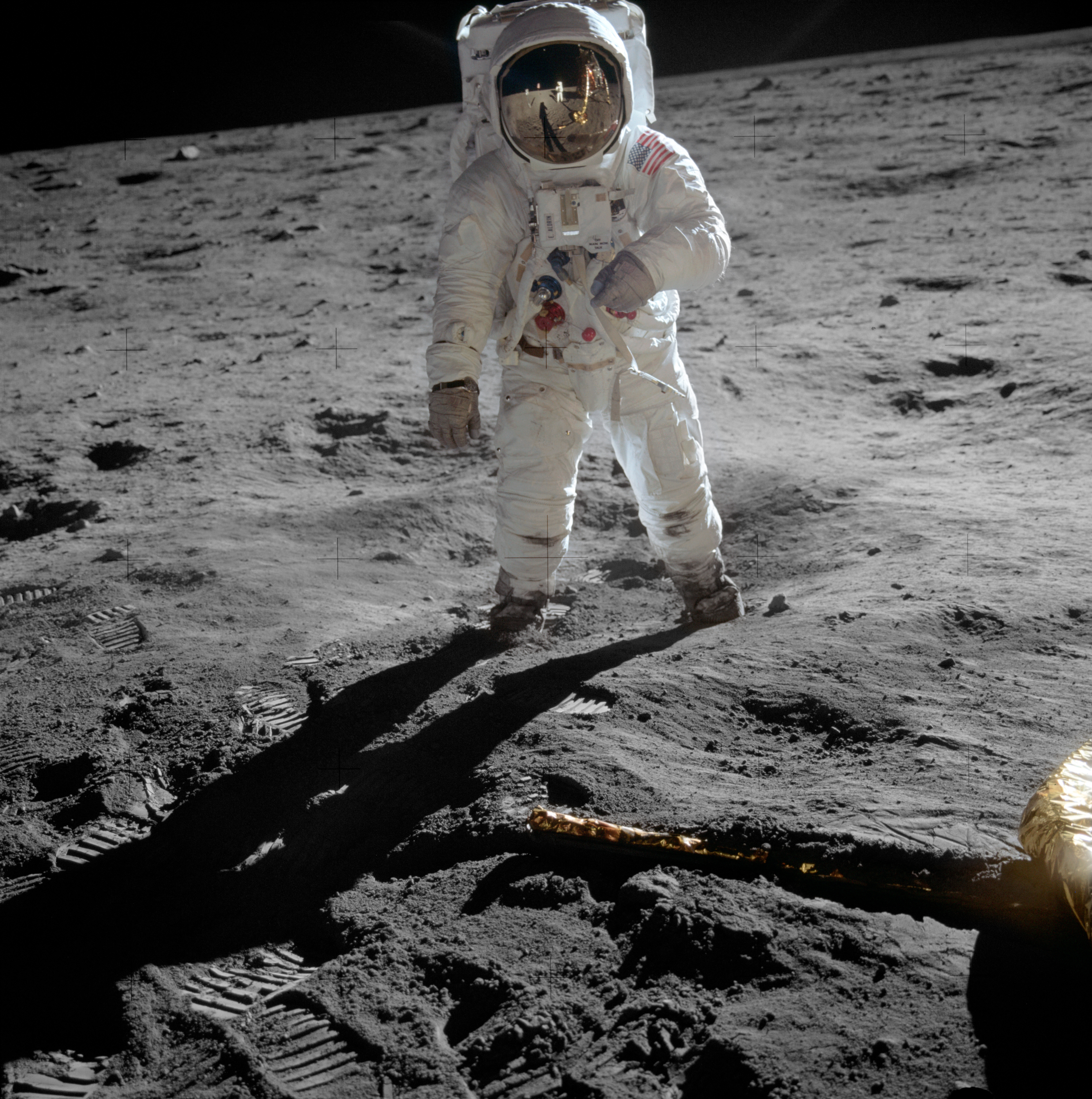
Apollo Program
The Apollo program, also known as Project Apollo, was the United States human spaceflight program led by NASA, which Moon landing, landed the first humans on the Moon in 1969. Apollo followed Project Mercury that put the first Americans in space. It was conceived in 1960 as a three-person spacecraft during President Presidency of Dwight D. Eisenhower, Dwight D. Eisenhower's administration. Apollo was later dedicated to President John F. Kennedy's national goal for the 1960s of "landing a man on the Moon and returning him safely to the Earth" in an address to United States Congress, Congress on May 25, 1961. It was the third American human spaceflight program to fly, preceded by Project Gemini conceived in 1961 to extend spaceflight capability in support of Apollo. Kennedy's goal was accomplished on the Apollo 11 mission when astronauts Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin landed their Apollo Lunar Module (LM) on July 20, 1969, and walked on the lunar surface, while Michael Collins ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetometer
A magnetometer is a device that measures magnetic field or magnetic dipole moment. Different types of magnetometers measure the direction, strength, or relative change of a magnetic field at a particular location. A compass is one such device, one that measures the direction of an ambient magnetic field, in this case, the Earth's magnetic field. Other magnetometers measure the magnetic dipole moment of a magnetic material such as a ferromagnet, for example by recording the effect of this magnetic dipole on the induced current in a coil. The invention of the magnetometer is usually credited to Carl Friedrich Gauss in 1832. Earlier, more primitive instruments were developed by Christopher Hansteen in 1819, and by William Scoresby by 1823. Magnetometers are widely used for measuring the Earth's magnetic field, in geophysical surveys, to detect magnetic anomalies of various types, and to determine the dipole moment of magnetic materials. In an aircraft's attitude and heading ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supersonic Wind Tunnel
A supersonic wind tunnel is a wind tunnel that produces supersonic speeds (1.2 Power requirements The power required to run a supersonic wind tunnel is ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Tunnels
A wind tunnel is "an apparatus for producing a controlled stream of air for conducting aerodynamic experiments". The experiment is conducted in the test section of the wind tunnel and a complete tunnel configuration includes air ducting to and from the test section and a device for keeping the air in motion, such as a fan. Wind tunnel uses include assessing the effects of air on an aircraft in flight or a ground vehicle moving on land, and measuring the effect of wind on buildings and bridges. Wind tunnel test sections range in size from less than a foot across, to over , and with air speeds from a light breeze to hypersonic. The earliest wind tunnels were invented towards the end of the 19th century, in the early days of aeronautical research, as part of the effort to develop heavier-than-air flying machines. The wind tunnel reversed the usual situation. Instead of the air standing still and an aircraft moving, an object would be held still and the air moved around it. In this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerobee
The Aerobee rocket was one of the United States' most produced and productive sounding rockets. Developed by the Aerojet Corporation, the Aerobee was designed to combine the altitude and launching capability of the V-2 with the cost effectiveness and mass production of the WAC Corporal. More than 1000 Aerobees were launched between 1947 and 1985, returning vast amounts of astronomical, physical, aeronomical, and biomedical data. Development Research using V-2 rockets after World War II produced valuable results concerning the nature of cosmic rays, the solar spectrum, and the distribution of atmospheric ozone. However, the limited supply and the expense of assembling and firing the V-2 rockets, as well as the small payload capacity of the first purpose-built sounding rocket, the WAC Corporal, created demand for a low cost sounding rocket to be used for scientific research. An Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) effort led by James Van Allen led to a contract presented 17 May 194 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviets
The Soviet people () were the citizens and nationals of the Soviet Union. This demonym was presented in the ideology of the country as the "new historical unity of peoples of different nationalities" (). Nationality policy in the Soviet Union During the history of the Soviet Union, different doctrines and practices on ethnic distinctions within the Soviet population were applied at different times. Minority national cultures were never completely abolished. Instead the Soviet definition of national cultures required them to be "socialist by content and national by form", an approach that was used to promote the official aims and values of the state. The goal was always to cement the nationalities together in a common state structure. In the 1920s and the early 1930s, the policy of national delimitation was used to demarcate separate areas of national culture into territorial-administrative units, and the policy of korenizatsiya (indigenisation) was used to promote involvement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wright-Patterson Air Force Base
Wright-Patterson Air Force Base (WPAFB) is a United States Air Force base and census-designated place just east of Dayton, Ohio, in Greene County, Ohio, Greene and Montgomery County, Ohio, Montgomery counties. It includes both Wright and Patterson Fields, which were originally Wilbur Wright Field and Fairfield Aviation General Supply Depot. Patterson Field is approximately northeast of Dayton, Ohio, Dayton; Wright Field is approximately northeast of Dayton. The host unit at Wright-Patterson AFB is the 88th Air Base Wing (88 ABW), assigned to the Air Force Life Cycle Management Center and Air Force Materiel Command. The 88 ABW operates the airfield, maintains all infrastructure and provides security, communications, medical, legal, personnel, contracting, finance, transportation, air traffic control, weather forecasting, public affairs, recreation and chaplain services for more than 60 associate units. The Air Force's National Air Intelligence Center, National Air and Space In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XB-70 Valkyrie
The North American Aviation XB-70 Valkyrie is a retired prototype version of the planned nuclear-armed, deep-penetration supersonic strategic bomber for the United States Air Force Strategic Air Command. Designed in the late 1950s by North American Aviation (NAA) to replace the B-52 Stratofortress and B-58 Hustler, the six-engine, delta-winged Valkyrie could cruise for thousands of miles at Mach 3+ while flying at . At these speeds, it was expected that the B-70 would be practically immune to interceptor aircraft, the only effective weapon against bomber aircraft at the time. The bomber would spend only a brief time over a particular radar station, flying out of its range before the controllers could position their fighters in a suitable location for an interception. Its high speed made the aircraft difficult to see on radar displays and its high-altitude and high-speed capabilities could not be matched by any contemporaneous Soviet interceptor or fighter aircraft. The int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |