|
Clan Boyd
Clan Boyd is a Scottish clan of the Scottish Lowlands and is recognized as such by the Lord Lyon King of Arms. History Origins of the clan The name Boyd is said to be descriptive, being derived from the Scottish Gaelic ''buidh'' which means ''fair'' or ''yellow''. It could also be the genitive of hailing from the Isle of Bute—Bhoid in Gaelic. The progenitor is said to have been Robert, son of Simon and nephew of Walter fitz Alan, the first High Steward of Scotland. This theory however is challenged by genealogist, William Anderson, who points out that most of the friends and dependents of the High Stewards were of Norman origin and it is therefore unlikely that they would use a Celtic nickname for one of their own family. Anderson believed the name to be of either Norman or Saxon origin. The historian, George Fraser Black, asserts that the first Boyds were vassals of a Norman family, the de Morvilles, for their lands around Largs and Irvine.Black, George Fraser. (19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Lowlands
The Lowlands ( sco, Lallans or ; gd, a' Ghalldachd, , place of the foreigners, ) is a cultural and historical region of Scotland. Culturally, the Lowlands and the Highlands diverged from the Late Middle Ages into the modern period, when Lowland Scots replaced Scottish Gaelic throughout most of the Lowlands. Geography The Lowlands is not an official geographical or administrative area of the country. There are two main topographic regions: the Lowlands and the Southern Uplands. The term "Lowlands" mainly refers to the Central Lowlands. However, in normal usage it refers to those parts of Scotland not in the Highlands (or Gàidhealtachd). The boundary is usually considered to be a line between Stonehaven and Helensburgh (on the Firth of Clyde). The Lowlands lie south and east of the line. Note that some parts of the Lowlands (such as the Southern Uplands) are not physically "low," Merrick for example reaching , while some areas indisputably in the Highlands (such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic ( gd, Gàidhlig ), also known as Scots Gaelic and Gaelic, is a Goidelic language (in the Celtic branch of the Indo-European language family) native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a Goidelic language, Scottish Gaelic, as well as both Irish and Manx, developed out of Old Irish. It became a distinct spoken language sometime in the 13th century in the Middle Irish period, although a common literary language was shared by the Gaels of both Ireland and Scotland until well into the 17th century. Most of modern Scotland was once Gaelic-speaking, as evidenced especially by Gaelic-language place names. In the 2011 census of Scotland, 57,375 people (1.1% of the Scottish population aged over 3 years old) reported being able to speak Gaelic, 1,275 fewer than in 2001. The highest percentages of Gaelic speakers were in the Outer Hebrides. Nevertheless, there is a language revival, and the number of speakers of the language under age 20 did not decrease between the 2001 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward I Of England
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he ruled the duchies of Duchy of Aquitaine, Aquitaine and Duchy of Gascony, Gascony as a vassal of the French king. Before his accession to the throne, he was commonly referred to as the Lord Edward. The eldest son of Henry III of England, Henry III, Edward was involved from an early age in the political intrigues of his father's reign, which included a rebellion by the English barons. In 1259, he briefly sided with a baronial reform movement, supporting the Provisions of Oxford. After reconciliation with his father, however, he remained loyal throughout the subsequent armed conflict, known as the Second Barons' War. After the Battle of Lewes, Edward was held hostage by the rebellious barons, but escaped after a few months and defeated the baronial leader Simon de Montfort at the Battle of Eve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ragman Rolls
Ragman Rolls are the collection of instruments by which the nobility and gentry of Scotland subscribed allegiance to King Edward I of England, during the time between the Conference of Norham in May 1291 and the final award in favour of Balliol in November 1292; and again in 1296. Of the former of these records two copies were preserved in the Chapter House at Westminster Abbey (now in the National Archives (United Kingdom) at Kew), and it has been printed by Thomas Rymer. Another copy, preserved originally in the Tower of London, is now also in the National Archives. The latter record, containing the various acts of homage and fealty extorted by Edward from John Balliol and others in the course of his progress through Scotland in the summer of 1296 and in August at the parliament of Berwick, was published by Prynne from the copy in the Tower and now in the National Archives. Both records were printed by the Bannatyne Club in 1834. The derivation of the word ''ragman'' is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isle Of Bute
The Isle of Bute ( sco, Buit; gd, Eilean Bhòid or '), known as Bute (), is an island in the Firth of Clyde in Scotland, United Kingdom. It is divided into highland and lowland areas by the Highland Boundary Fault. Formerly a constituent island of the larger County of Bute, it is now part of the council area of Argyll and Bute. Bute's resident population was 6,498 in 2011, a decline of just over 10% from the figure of 7,228 recorded in 2001 against a background of Scottish island populations as a whole growing by 4% to 103,702 for the same period. Name The name "Bute" is of uncertain origin. Watson and Mac an Tàilleir support a derivation from Old Irish ' ("fire"), perhaps in reference to signal fires.Watson (1926) pp 95–6Mac an Tàilleir (2003) p. 24 This reference to beacon fires may date from the Viking period, when the island was probably known to the Norse as '. Other possible derivations include Brittonic ''budh'' ("corn"), "victory", , or ', his monastic cel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irvine, North Ayrshire
Irvine ( ; sco, Irvin, gd, Irbhinn, IPA: �iɾʲivɪɲ is an ancient settlement, in medieval times a , and now a on the coast of the in , |
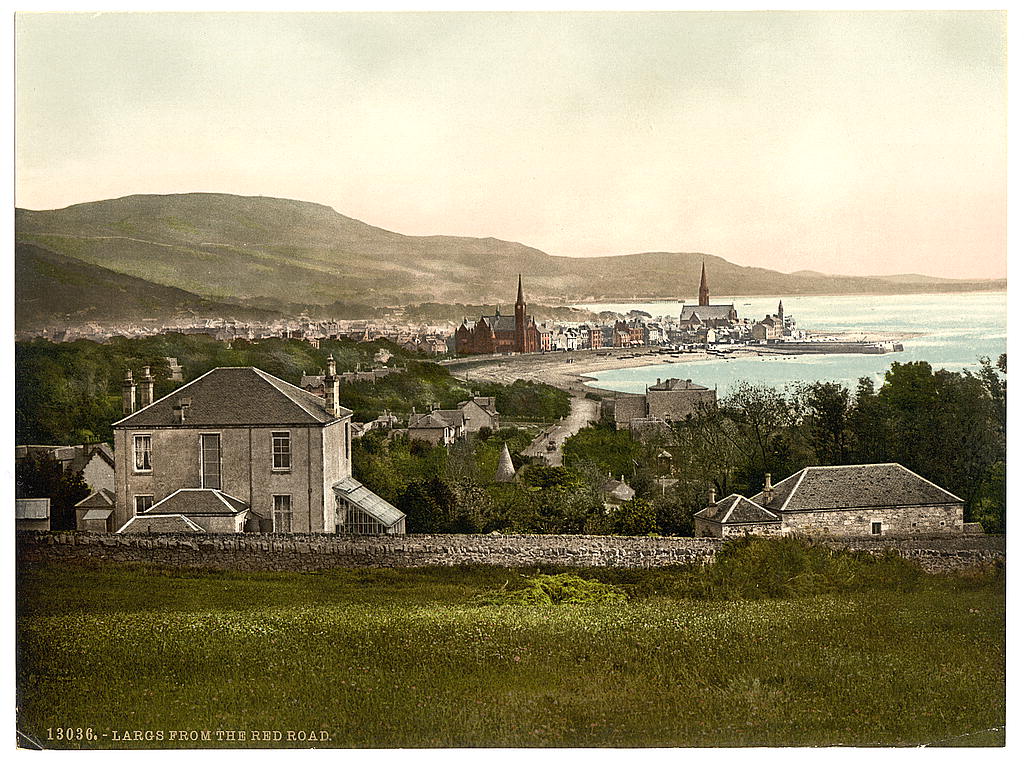
Largs
Largs ( gd, An Leargaidh Ghallda) is a town on the Firth of Clyde in North Ayrshire, Scotland, about from Glasgow. The original name means "the slopes" (''An Leargaidh'') in Scottish Gaelic. A popular seaside resort with a pier, the town markets itself on its historic links with the Vikings and an annual festival is held each year in early September. In 1263 it was the site of the Battle of Largs between the Norwegian and the Scottish armies. The National Mòd has also been held here in the past. History There is evidence of human activity in the vicinity of Largs which can be dated to the Neolithic era. The Haylie Chambered Tomb in Douglas Park dates from c. 3000 BC. Largs evolved from the estates of North Cunninghame over which the Montgomeries of Skelmorlie became temporal lords in the seventeenth century. Sir Robert Montgomerie built Skelmorlie Aisle in the ancient kirk of Largs in 1636 as a family mausoleum. Today the monument is all that remains of the old kirk. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugh De Morville, Constable Of Scotland
Hugh de Morville (died 1162) of Appleby in Westmorland, England, hereditary Constable of Scotland, was a Norman knight who made his fortune in the service of David FitzMalcolm (d.1153), Prince of the Cumbrians, later King of Scotland. Origins Hugh came from Morville in the Cotentin Peninsula, in northern France. His parentage is unclear. According to Barrow his father was probably Richard de Morville who in the early twelfth century witnessed charters made by Richard de Redvers relating to Montebourg and the church of St. Mary in the castle of Néhou, but though Keats-Rohan gives that man other possible sons, she does not similarly associate Hugh with Richard. In service of David of Scotland Prince David of Scotland held Cotentin in northern France, given to him by King Henry I of England some time after 1106. Soon after, Hugh de Morville joined David's small military retinue in France. In 1113, following his marriage, Prince David was made Earl of Huntingdon and Northam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic * * * * peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country ( Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the North Sea coast of northern Germania, in what is now Germany. In the late Roman Empire, the name was used to refer to Germanic coastal raiders, and as a name similar to the later "Viking". Their origins are believed to be in or near the German North Sea coast where they appear later, in Carolingian times. In Merovingian times, continental Saxons had been associated with the activity and settlements on the coast of what later became Normandy. Their precise origins are uncertain, and they are sometimes described as fighting inland, coming into conflict with the Franks and Thuringians. There is possibly a single classical reference to a smaller homeland of an early Saxon tribe, but its interpretation is disputed. According to this proposal, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient Indo-European people, reached the apogee of their influence and territorial expansion during the 4th century bc, extending across the length of Europe from Britain to Asia Minor."; . " e Celts, were Indo-Europeans, a fact that explains a certain compatibility between Celtic, Roman, and Germanic mythology."; . "The Celts and Germans were two Indo-European groups whose civilizations had some common characteristics."; . "Celts and Germans were of course derived from the same Indo-European stock."; . "Celt, also spelled Kelt, Latin Celta, plural Celtae, a member of an early Indo-European people who from the 2nd millennium bce to the 1st century bce spread over much of Europe."; in Europe and Anatolia, identified by their use of Celtic langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normans
The Normans ( Norman: ''Normaunds''; french: Normands; la, Nortmanni/Normanni) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norse Viking settlers and indigenous West Franks and Gallo-Romans. The term is also used to denote emigrants from the duchy who conquered other territories such as England and Sicily. The Norse settlements in West Francia followed a series of raids on the French northern coast mainly from Denmark, although some also sailed from Norway and Sweden. These settlements were finally legitimized when Rollo, a Scandinavian Viking leader, agreed to swear fealty to King Charles III of West Francia following the siege of Chartres in 911. The intermingling in Normandy produced an ethnic and cultural "Norman" identity in the first half of the 10th century, an identity which continued to evolve over the centuries. The Norman dynasty had a major political, cultural and military impact on medieval Europe and the N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Anderson (Scottish Writer)
William Anderson (1805–1866) was a Scottish miscellaneous writer in the departments of history, biography, and science. He was born at Edinburgh and educated there, and placed in a lawyer's office. As an author he published ''Poetical Aspirations''; ''Landscape Lyrics''; ''Popular Scottish Biography''; ''Treasury of Nature, Science, and Art'' and an extensive work widely known as ''The Scottish Nation''. He also assisted for some time in managing Aberdeen Journal, Witness, and Daily Mail newspapers. He died, aged 61. Biography Anderson was born in Edinburgh 10 December 1805. His father was supervisor of excise at Oban, and his mother the daughter of John Williams, author of the 'Natural History of the Mineral Kingdom.' He was thus a younger brother of John Anderson (genealogist, 1789–1832), the historian of the house of Hamilton. After receiving a good education in Edinburgh he became clerk to a Leith merchant, but subsequently entered a lawyer's office in Edinbu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |