|
Cladistic Classification Of Class Sarcopterygii
Sarcopterygii or the lobe-finned fishes ( coelacanths and lungfishes) were usually classified as either a class or a subclass of Osteichthyes based on the traditional Linnaean classification. Identification of the group is based on several characteristics, such as the presence of fleshy, lobed, paired fins, which are joined to the body by a single bone. Taxonomic and fossil history The properties defining the sarcopterygians are in contrast to the other group of bony fish, the Actinopterygii, which have ray-fins made of bony rods, called '' lepidotrichia''. These two bony fish groups were classified together as Osteichthyes at one time, the whole combined group was seen as the sister group to the tetrapods (mammals, birds, reptiles, and amphibians). The extensive fossil record and numerous morphological and molecular studies have shown, however, that lungfish and some fossil lobe-finned fish are more closely related to tetrapods than they are to coelacanths; as a result tetrapod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcopterygii
Sarcopterygii (; ) — sometimes considered synonymous with Crossopterygii () — is a taxon (traditionally a class or subclass) of the bony fishes known as the lobe-finned fishes. The group Tetrapoda, a mostly terrestrial superclass including amphibians, sauropsids (reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (with mammals being the only extant group), evolved from certain sarcopterygians; under a cladistic view, tetrapods are themselves considered a subgroup within Sarcopterygii. The known extant non-tetrapod sarcopterygians include two species of coelacanths and six species of lungfishes. Characteristics Early lobe-finned fishes are bony fish with fleshy, lobed, paired fins, which are joined to the body by a single bone. The fins of lobe-finned fishes differ from those of all other fish in that each is borne on a fleshy, lobelike, scaly stalk extending from the body. The scales of sarcopterygians are true scaloids, consisting of lamellar bone sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhipidistia
Rhipidistia, also known as Dipnotetrapodomorpha, is a clade of lobe-finned fishes which includes the tetrapods and lungfishes. Rhipidistia formerly referred to a subgroup of Sarcopterygii consisting of the Porolepiformes and Osteolepiformes, a definition that is now obsolete. However, as cladistic understanding of the vertebrates has improved over the last few decades, a monophyletic Rhipidistia is now understood to include the whole of Tetrapoda and the lungfishes. Rhipidistia includes Porolepiformes and Dipnoi. Extensive fossilization of lungfishes has contributed to many evolutionary studies of this group. Evolution of autostylic jaw suspension, in which the palatoquadrate bone fuses to the cranium, and the lymph pumping "lymph heart" (later lost in mammals and flying birds), are unique to this group. The precise time at which the choana The choanae (singular choana), posterior nasal apertures or internal nostrils are two openings found at the back of the nasal passage b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
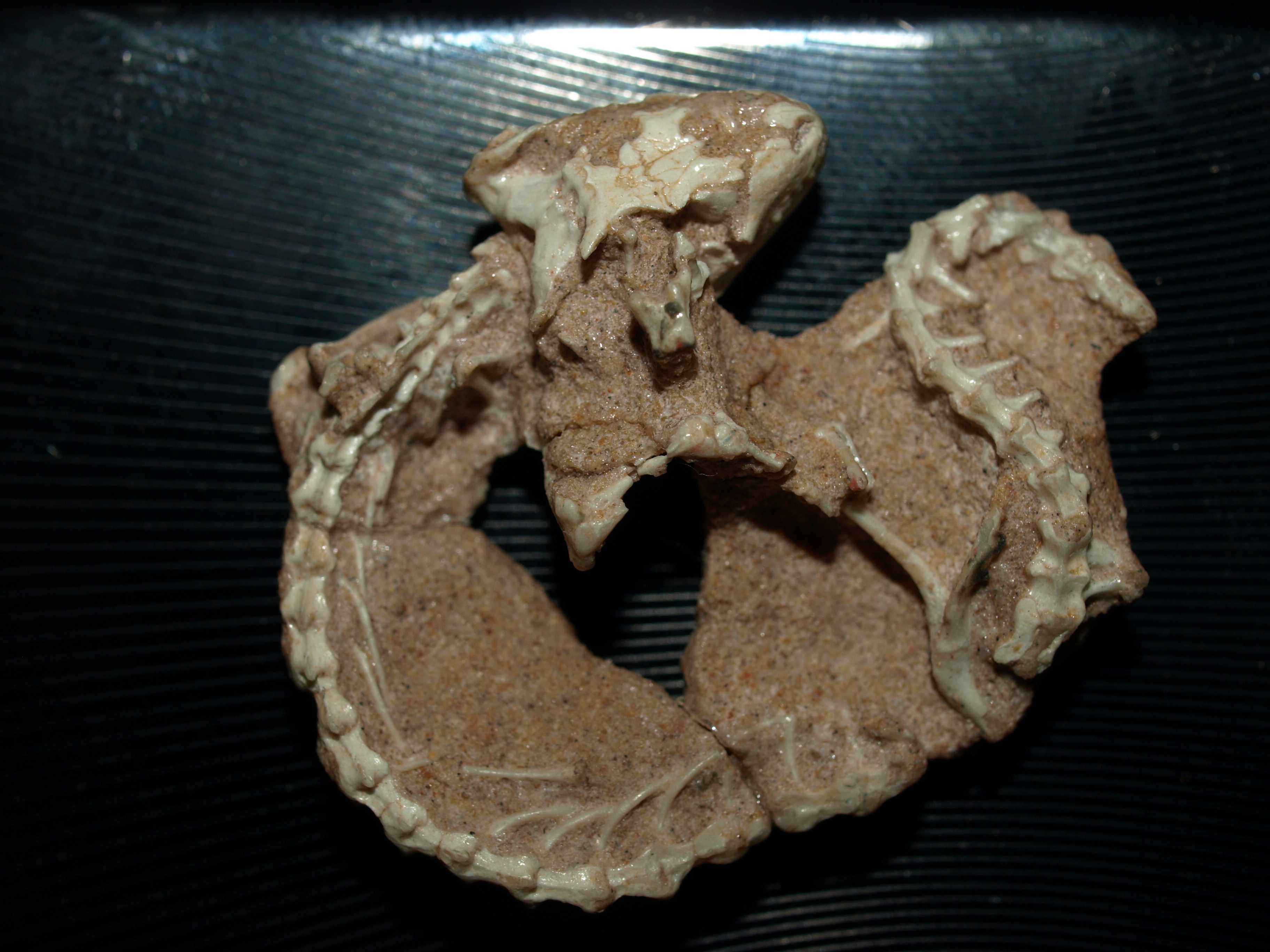
Testudinata
Testudinata is the group of all tetrapods with a true turtle shell. It includes both modern turtles (Testudines) and many of their extinct, shelled relatives (stem-turtles). Though it was first coined as the group containing turtles by Jacob Theodor Klein in 1760, it was first defined in the modern sense by Joyce and colleagues in 2004. Testudinata does not include the primitive stem-turtle ''Odontochelys'', which only had the bottom half of a shell. A recent phylogenetic tree of Testudinata included Angolachelonia and Testudines Turtles are an order of reptiles known as Testudines, characterized by a special shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Cryptodira (hidden necked t ... as sister-taxa and subgroups of Testudinata. Classification The cladogram below follows an analysis by Jérémy Anquetin in 2012. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q16114972 Reptile taxonomy Norian f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squamata
Squamata (, Latin ''squamatus'', 'scaly, having scales') is the largest order of reptiles, comprising lizards, snakes, and amphisbaenians (worm lizards), which are collectively known as squamates or scaled reptiles. With over 10,900 species, it is also the second-largest order of extant (living) vertebrates, after the perciform fish. Members of the order are distinguished by their skins, which bear horny scales or shields, and must periodically engage in molting. They also possess movable quadrate bones, making possible movement of the upper jaw relative to the neurocranium. This is particularly visible in snakes, which are able to open their mouths very wide to accommodate comparatively large prey. Squamata is the most variably sized order of reptiles, ranging from the dwarf gecko (''Sphaerodactylus ariasae'') to the Reticulated python (''Malayopython reticulatus'') and the now-extinct mosasaurs, which reached lengths over . Among other reptiles, squamates are most close ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhynchocephalia
Rhynchocephalia (; ) is an order of lizard-like reptiles that includes only one living species, the tuatara (''Sphenodon punctatus'') of New Zealand. Despite its current lack of diversity, during the Mesozoic rhynchocephalians were a diverse group including a wide array of morphologically distinct forms. The oldest record of the group is dated to the Middle Triassic around 238 to 240 million years ago, and they had achieved a worldwide distribution by the Early Jurassic. Most rhynchocephalians belong to the group Sphenodontia ('wedge-teeth'). Their closest living relatives are lizards and snakes in the order Squamata, with the two orders being grouped together in the superorder Lepidosauria. Many of the niches occupied by lizards today were held by sphenodontians during the Triassic and Jurassic, although lizard diversity began to overtake sphenodontian diversity in the Cretaceous, and they had disappeared almost entirely by the beginning of the Cenozoic. While the modern tuat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lepidosauria
The Lepidosauria (, from Greek meaning ''scaled lizards'') is a subclass or superorder of reptiles, containing the orders Squamata and Rhynchocephalia. Squamata includes snakes, lizards, and amphisbaenians. Squamata contains over 9,000 species, making it by far the most species-rich and diverse order of reptiles in the present day. Rhynchocephalia was a formerly widespread and diverse group of reptiles in the Mesozoic Era. However, it is represented by only one living species: the tuatara (''Sphenodon punctatus),'' a superficially lizard-like reptile native to New Zealand. Lepidosauria is a monophyletic group (i.e. a clade), containing all descendants of the last common ancestor of squamates and rhynchocephalians. Lepidosaurs can be distinguished from other reptiles via several traits, such as large keratinous scales which may overlap one another. Purely in the context of modern taxa, Lepidosauria can be considered the sister taxon to Archosauria, which includes Aves (birds) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sauria
Sauria is the clade containing the most recent common ancestor of archosaurs (such as crocodilians, dinosaurs, etc.) and lepidosaurs ( lizards and kin), and all its descendants. Since most molecular phylogenies recover turtles as more closely related to archosaurs than to lepidosaurs as part of Archelosauria, Sauria can be considered the crown group of diapsids, or reptiles in general. Depending on the systematics, Sauria includes all modern reptiles or most of them (including birds, a type of archosaur) as well as various extinct groups. Sauria lies within the larger total group Sauropsida, which also contains various stem-reptiles which are more closely related to reptiles than to mammals. Prior to its modern usage, "Sauria" was used as a name for the suborder occupied by lizards, which before 1800 were considered crocodilians. Systematics Recent genomic studiesCrawford, Nicholas G., et al. "More than 1000 ultraconserved elements provide evidence that turtles are the sister g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frog
A frog is any member of a diverse and largely Carnivore, carnivorous group of short-bodied, tailless amphibians composing the order (biology), order Anura (ανοὐρά, literally ''without tail'' in Ancient Greek). The oldest fossil "proto-frog" ''Triadobatrachus'' is known from the Early Triassic of Madagascar, but molecular clock, molecular clock dating suggests their split from other amphibians may extend further back to the Permian, 265 Myr, million years ago. Frogs are widely distributed, ranging from the tropics to subarctic regions, but the greatest concentration of species diversity is in tropical rainforest. Frogs account for around 88% of extant amphibian species. They are also one of the five most diverse vertebrate orders. Warty frog species tend to be called toads, but the distinction between frogs and toads is informal, not from Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy or evolutionary history. An adult frog has a stout body, protruding eyes, anteriorly-attached tongue, limb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urodela
Salamanders are a group of amphibians typically characterized by their lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults. All ten extant salamander families are grouped together under the order Urodela. Salamander diversity is highest in eastern North America, especially in the Appalachian Mountains; most species are found in the Holarctic realm, with some species present in the Neotropical realm. Salamanders rarely have more than four toes on their front legs and five on their rear legs, but some species have fewer digits and others lack hind limbs. Their permeable skin usually makes them reliant on habitats in or near water or other cool, damp places. Some salamander species are fully aquatic throughout their lives, some take to the water intermittently, and others are entirely terrestrial as adults. This group of amphibians is capable of regenerating lost lim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
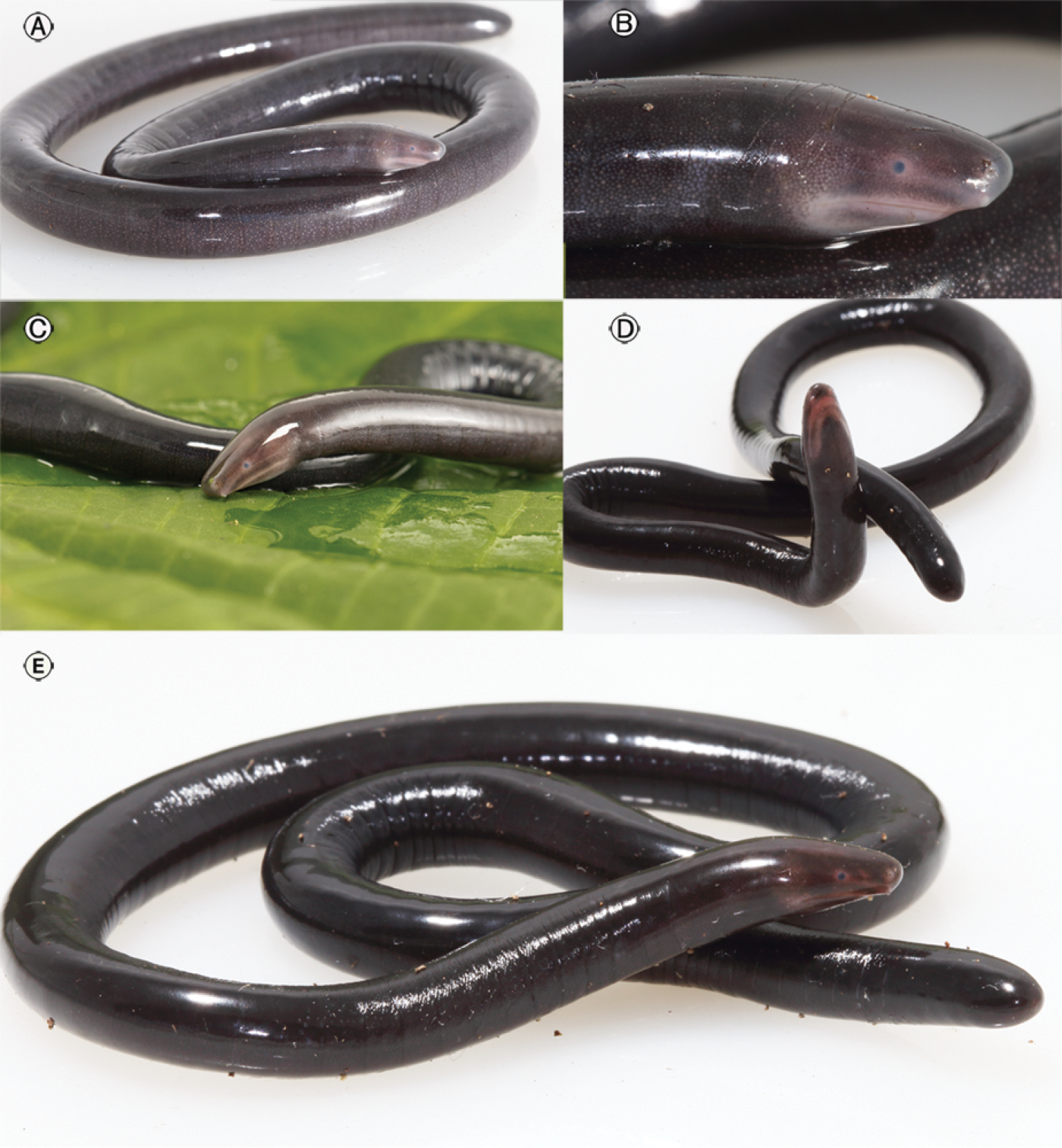
Caecilian
Caecilians (; ) are a group of limbless, vermiform or serpentine amphibians. They mostly live hidden in the ground and in stream substrates, making them the least familiar order of amphibians. Caecilians are mostly distributed in the tropics of South and Central America, Africa, and southern Asia. Their diet consists of small subterranean creatures such as earthworms. All modern caecilians and their closest fossil relatives are grouped as a clade, Apoda , within the larger group Gymnophiona , which also includes more primitive extinct caecilian-like amphibians. The name derives from the Greek words γυμνος (''gymnos'', naked) and οφις (''ophis'', snake), as the caecilians were originally thought to be related to snakes. The body is cylindrical dark brown or bluish black in colour. The skin is slimy and bears grooves or ringlike markings. Description Caecilians completely lack limbs, making the smaller species resemble worms, while the larger species, with lengths up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lissamphibia
The Lissamphibia is a group of tetrapods that includes all modern amphibians. Lissamphibians consist of three living groups: the Salientia (frogs, toads, and their extinct relatives), the Caudata (salamanders, newts, and their extinct relatives), and the Gymnophiona (the limbless caecilians and their extinct relatives). A fourth group, the Allocaudata, was moderately successful, spanning 160 million years from the Middle Jurassic to the Early Pleistocene, but became extinct two million years ago. For several decades, this name has been used for a group that includes all living amphibians, but excludes all the main groups of Paleozoic tetrapods, such as Temnospondyli, Lepospondyli, Embolomeri, and Seymouriamorpha. Some scientists have concluded that all of the primary groups of modern amphibians—frogs, salamanders and caecilians—are closely related. Some writers have argued that the early Permian dissorophoid ''Gerobatrachus hottoni'' is a lissamphibian. If it is not, the earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_601758.jpg)

_Ranomafana.jpg)