|
Chʼoltiʼ Language
The Chʼoltiʼ language is an extinct Mayan language which was spoken by the Manche Chʼol people of eastern Guatemala and southern Belize. The post-colonial stage of the language is only known from a single manuscript written between 1685 and 1695 which was first studied by Daniel Garrison Brinton Daniel Garrison Brinton (May 13, 1837July 31, 1899) was an American surgeon, historian, archaeologist and ethnologist. Biography Brinton was born in Thornbury Township, Chester County, Pennsylvania. After graduating from Yale University in 185 .... Chʼoltiʼ belongs to the Choʼlan branch of the Mayan languages and is closely related to Chontal and especially Chʼortiʼ. The Chʼoltiʼ language has become of particular interest for the study of Mayan Hieroglyphs since it seems that most of the glyphic texts are written in an ancient variety of Chʼoltiʼ called Classic Chʼoltiʼan or Classic Maya by epigraphers and which is thought to have been spoken as a prestige dialec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guatemala
Guatemala ( ; ), officially the Republic of Guatemala ( es, República de Guatemala, links=no), is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico; to the northeast by Belize and the Caribbean; to the east by Honduras; to the southeast by El Salvador and to the south by the Pacific Ocean. With an estimated population of around million, Guatemala is the most populous country in Central America and the 11th most populous country in the Americas. It is a representative democracy with its capital and largest city being Nueva Guatemala de la Asunción, also known as Guatemala City, the most populous city in Central America. The territory of modern Guatemala hosted the core of the Maya civilization, which extended across Mesoamerica. In the 16th century, most of this area was conquered by the Spanish and claimed as part of the viceroyalty of New Spain. Guatemala attained independence in 1821 from Spain and Mexico. In 1823, it became part of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chʼortiʼ Language
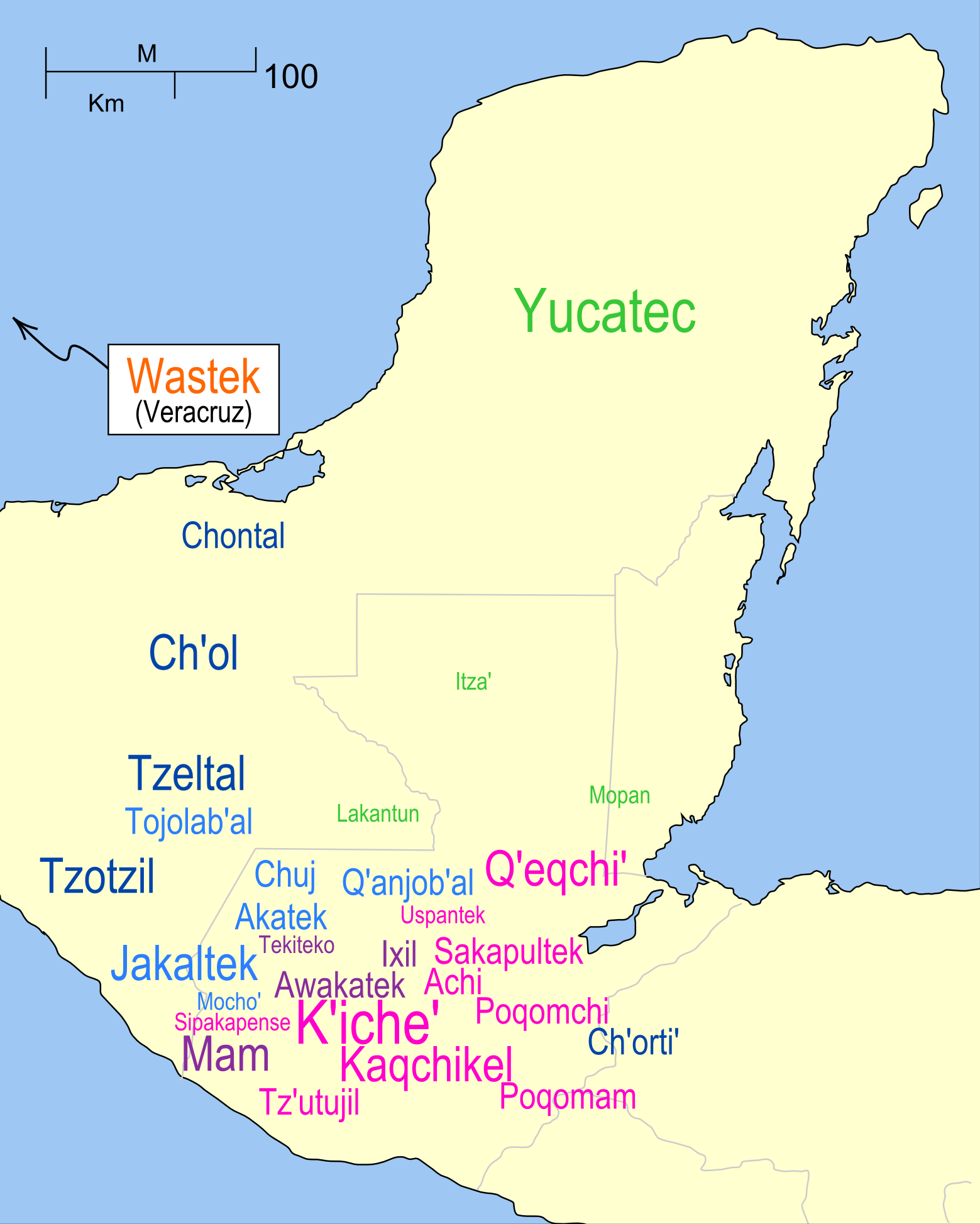
The Chʼortiʼ language (sometimes also ''Chorti'') is a Mayan language, spoken by the indigenous Maya people who are also known as the Chʼortiʼ or Chʼortiʼ Maya. Chʼortiʼ is a direct descendant of the Classic Maya language in which many of the pre-Columbian inscriptions using the Maya script were written. Chʼortiʼ is the modern version of the ancient Mayan language Chʼolan (which was actively used and most popular between the years of A.D 250 and 850).Houston, S, J Robertson, and D Stuart. "The language of Classic Maya inscriptions." Current Anthropology 41.3 (2000): 321–356. Print. Relationship to other Mayan languages Chʼortiʼ can be called a living " Rosetta Stone" of Mayan languages. The Chʼortiʼ language is an important factor to comprehend the contents of Maya glyphic writings, some of which are not yet fully understood. Over several years, many linguists and anthropologists expected to realize the Chʼortiʼ culture and language by studying its word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoamerican Languages
Mesoamerican languages are the languages indigenous to the Mesoamerican cultural area, which covers southern Mexico, all of Guatemala and Belize and parts of Honduras and El Salvador and Nicaragua. The area is characterized by extensive linguistic diversity containing several hundred different languages and seven major language families. Mesoamerica is also an area of high linguistic diffusion in that long-term interaction among speakers of different languages through several millennia has resulted in the convergence of certain linguistic traits across disparate language families. The Mesoamerican sprachbund is commonly referred to as the Mesoamerican Linguistic Area. The languages of Mesoamerica were also among the first to evolve independent traditions of writing. The oldest texts date to approximately 1000 BCE (namely olmec and zapotec), though most texts in the indigenous scripts (such as Maya) date to c. 600–900 CE. Following the arrival of the Spanish in the 16th c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Current Anthropology
''Current Anthropology'' is a peer-reviewed anthropology academic journal published by the University of Chicago Press for the Wenner-Gren Foundation for Anthropological Research. Founded in 1959 by the anthropologist Sol Tax1907-1995. ''Current Anthropology'' is one of very few journals that publishes research across all sub-disciplines of anthropology, encompassing the full range of anthropological scholarship on human cultures and on human and other primate species. Communicating across the subfields, the journal features papers in a wide variety of areas, including social, cultural, physical and linguistic anthropology as well as ethnology, ethnohistory, archaeology, prehistory and folklore. Laurence Ralph of Princeton University replaced Mark Aldenderfer ( University of California, Merced) as the editor-in-chief of the journal on January 1, 2019. Ralph is Professor of Anthropology at Princeton University. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Stuart (Mayanist)
David S. Stuart (born 1965) is an archaeologist and epigrapher specializing in the study of ancient Mesoamerica, the area now called Mexico and Central America. His work has studied all aspects of the ancient Maya civilization. He is widely recognized for his breakthroughs in deciphering Maya hieroglyphs and interpreting Maya art and iconography, starting at an early age. He is the youngest person ever to receive a MacArthur Fellowship, at age 18. He currently teaches at the University of Texas at Austin and his current research includes study of Maya, Aztec and ancient Mesoamerican images and texts. Early life He is the son of the archaeologist George E. Stuart and the writer, artist and illustrator Gene Strickland Stuart, both of whom wrote extensively for the National Geographic Society. He spent much of his childhood accompanying his parents on archaeological digs and expeditions in Mexico and Guatemala. There he developed a deep interest in Maya culture, especially their ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Texas Press
The University of Texas Press (or UT Press) is a university press that is part of the University of Texas at Austin. Established in 1950, the Press publishes scholarly books and journals in several areas, including Latin American studies, Texana, anthropology, U.S. Latino studies, Native American studies, African American studies, film & media studies, classics and the ancient Near East, Middle East studies, natural history, art, and architecture. The Press also publishes trade books and journals relating to their major subject areas. Journals * ''Asian Music (journal), Asian Music'' * ''Diálogo (journal), Diálogo'' * ''Information & Culture'' * ''Journal of Cinema and Media Studies'' (formerly known as ''Cinema Journal'') * ''Journal of the History of Sexuality'' * ''Journal of Individual Psychology'' * ''Journal of Latin American Geography'' * ''Latin American Music Review'' * ''Studies in Latin American Popular Culture'' * ''Texas Studies in Literature and Language'' * '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munro S
A Munro () is defined as a mountain in Scotland with a height over , and which is on the Scottish Mountaineering Club (SMC) official list of Munros; there is no explicit topographical prominence requirement. The best known Munro is Ben Nevis (Beinn Nibheis), the highest mountain in the British Isles at . Munros are named after Sir Hugh Munro, 4th Baronet (1856–1919), who produced the first list of such hills, known as ''Munro's Tables'', in 1891. Also included were what Munro considered lesser peaks, now known as Munro Tops, which are also over 3,000 feet but are lower than the nearby primary mountain. The publication of the original list is usually considered to be the epoch event of modern peak bagging. The list has been the subject of subsequent variation and as of 10 December 2020, the Scottish Mountaineering Club has listed 282 Munros and 226 Munro Tops. "Munro bagging" is the activity of climbing all the listed Munros. As of 31 December 2021, 7,098 people had repo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoamerican Chronology
Mesoamerican chronology divides the history of prehispanic Mesoamerica into several periods: the Paleo-Indian (first human habitation until 3500 BCE); the Archaic (before 2600 BCE), the Preclassic or Formative (2500 BCE – 250 CE), the Classic (250–900 CE), and the Postclassic (); as well as the post European contact Colonial Period (1521–1821), and Postcolonial, or the period after independence from Spain (1821–present). The periodisation of Mesoamerica by researchers is based on archaeological, ethnohistorical, and modern cultural anthropology research dating to the early twentieth century. Archaeologists, ethnohistorians, historians, and cultural anthropologists continue to work to develop cultural histories of the region. Overview Paleo-Indian period 10,000–3500 BCE The Paleo-Indian (less frequently, ''Lithic'') period or era is that which spans from the first signs of human presence in the region, to the establishment of agricult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classic Maya
A classic is an outstanding example of a particular style; something of lasting worth or with a timeless quality; of the first or highest quality, class, or rank – something that exemplifies its class. The word can be an adjective (a ''classic'' car) or a noun (a ''classic'' of English literature). It denotes a particular quality in art, architecture, literature, design, technology, or other cultural artifacts. In commerce, products are named 'classic' to denote a long-standing popular version or model, to distinguish it from a newer variety. ''Classic'' is used to describe many major, long-standing sporting events. Colloquially, an everyday occurrence (e.g. a joke or mishap) may be described in some dialects of English as 'an absolute classic'. "Classic" should not be confused with ''classical'', which refers specifically to certain cultural styles, especially in music and architecture: styles generally taking inspiration from the Classical tradition, hence classicism. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maya Script
Maya script, also known as Maya glyphs, is historically the native writing system of the Maya civilization of Mesoamerica and is the only Mesoamerican writing system that has been substantially deciphered. The earliest inscriptions found which are identifiably Maya date to the 3rd century BCE in San Bartolo, Guatemala. Maya writing was in continuous use throughout Mesoamerica until the Spanish conquest of the Maya in the 16th and 17th centuries. Maya writing used logograms complemented with a set of syllabic glyphs, somewhat similar in function to modern Japanese writing. Maya writing was called "hieroglyphics" or hieroglyphs by early European explorers of the 18th and 19th centuries who found its general appearance reminiscent of Egyptian hieroglyphs, although the two systems are unrelated. Though modern Mayan languages are almost entirely written using the Latin alphabet rather than Maya script, there have been recent developments encouraging a revival of the Maya gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chontal Maya Language
''Yokotʼan'' (self-denomination), also known as Chontal Maya, is a Maya language of the Cholan family spoken in 2020 by around 60 thousand Chontal Maya people of the Mexican state of Tabasco. According to the National Catalog of Indigenous Languages of Mexico- INALIYokotʼanhas at least four dialects: Nacajuca (Central), Centla (Northern), Macuspana (Southern) and Tamulte (Eastern). Distribution The Chontal Maya are concentrated in 159 settlements in 5 municipalities of Tabasco (Brown 2005:122). * Centla *Centro Centro may refer to: Places Brazil *Centro, Santa Maria, a neighborhood in Santa Maria, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil * Centro, Porto Alegre, a neighborhood of Porto Alegre, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil * Centro (Duque de Caxias), a neighborhood of Du ... * Jonuta * Macuspana * Nacajuca (comprising more than 50% of the Chontal Maya population) Some Chontal settlements near the town of Nacajuca include (Brown 2005:116): *El Tigre *Saloya *Guatacaloa *Olcuatitan *Tuc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mayan Languages
The Mayan languagesIn linguistics, it is conventional to use ''Mayan'' when referring to the languages, or an aspect of a language. In other academic fields, ''Maya'' is the preferred usage, serving as both a singular and plural noun, and as the adjectival form. form a language family spoken in Mesoamerica, both in the south of Mexico and northern Central America. Mayan languages are spoken by at least 6 million Maya people, primarily in Guatemala, Mexico, Belize, El Salvador and Honduras. In 1996, Guatemala formally recognized 21 Mayan languages by name,Achiʼ is counted as a variant of Kʼicheʼ by the Guatemalan government. and Mexico recognizes eight within its territory. The Mayan language family is one of the best-documented and most studied in the Americas. Modern Mayan languages descend from the Proto-Mayan language, thought to have been spoken at least 5,000 years ago; it has been partially reconstructed using the comparative method. The proto-Mayan langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)