|
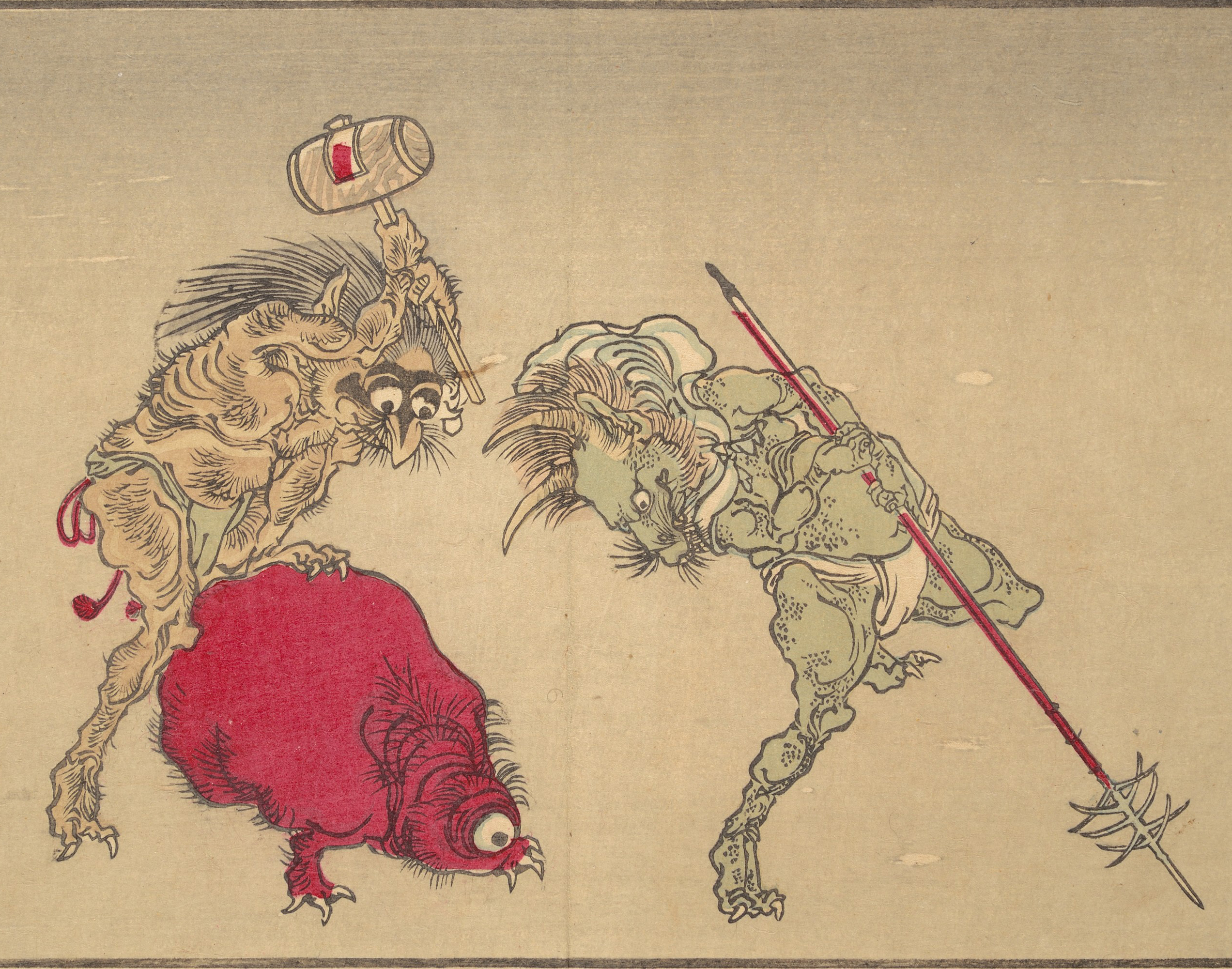
ChŇćchin-obake
' is a Japanese ''yŇćkai'' of ''chŇćchin'' (a type of lantern), ''"[the] lantern-spook (chochinobake) ... a stock character in the pantheon of ghouls and earned mention in the definitive demonology of 1784."'' They can also be called simply ''chŇćchin'', ''bake-chŇćchin'', ''obake-chŇćchin'', and ''chŇćchin-kozŇć''. They appear in the ''kusazŇćshi'', ''omocha-e'', and ''karuta'' card games like ''obake karuta'' starting from the Edo period to the early 20th century (and still in use today), as well as in Meiji and TaishŇć toys, children's books, and haunted house attractions. Description An old ''chŇćchin'' would split upwards and downwards, and the part that got split would become a mouth and stick out a long tongue, and the ''chŇćchin obake'' is commonly considered not to have one eye in its upper half, but two. Sometimes, the ''chŇćchin'' would also grow a face, hands, a torso, and wings. In pictures from the Edo Period, both bucket-shaped and cylindrical ''chŇćchin'' were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
YŇćkai
are a class of supernatural entities and spirits in Japanese folklore. The word is composed of the kanji for "attractive; calamity" and "apparition; mystery; suspicious." are also referred to as , or . Despite often being translated as such, are not literally demons in the Western sense of the word, but are instead spirits and entities. Their behavior can range from malevolent or mischievous to benevolent to humans. often have animal features (such as the , depicted as appearing similar to a turtle, and the , commonly depicted with wings), but may also appear humanoid in appearance, such as the . Some resemble inanimate objects (such as the ), while others have no discernible shape. are typically described as having spiritual or supernatural abilities, with shapeshifting being the most common trait associated with them. that shapeshift are known as or . Japanese folklorists and historians explain as personifications of "supernatural or unaccountable phenomena to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
One Hundred Ghost Stories
''One Hundred Ghost Stories'' (, ''Hyaku monogatari'') is a series of ukiyo-e woodblock prints made by Katsushika Hokusai (1760-1849) in the YŇęrei-zu genre circa 1830. He created this series around the same time he was creating his most famous works, the '' Thirty-six Views of Mount Fuji'' series. There are only five prints in this series, though as its title suggests, the publisher, Tsuruya Kiemon, and Hokusai wanted to make a series of one hundred prints. Material was copied from this source, which is available under Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0/ref> Hokusai was in his seventies when he worked on this series, and though his most famous impressions are landscape and wild-life works, he was attuned to the superstitions of the Edo period. This culminated in him creating these yokai prints of popular ghost stories being told at the time. The prints show scenes from such stories, that could be recited during the game of Hyakumonogatari Kaidankai. ''The One Hundred Gh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tbs Chochinobake
TBS may stand for: Entertainment * Taipei Broadcasting Station, a radio station in Taipei, Taiwan * Tokyo Broadcasting System, a stock holding company in Tokyo, Japan ** TBS Television (Japan), a television station ** TBS Radio, a radio station ** BS-TBS, a satellite broadcasting station in Tokyo, Japan * Turner Broadcasting System, media company in the United States ** TBS (American TV channel), a cable television channel in the United States ** TBS (Latin American TV channel), the Latin American channel * Traffic Broadcasting System, a radio and television broadcaster in Seoul, South Korea * Taking Back Sunday, an American rock band from Long Island, New York Education * TBS Education, France. The ''Grande école'' formerly known as: Toulouse Business School * Tau Beta Sigma, an honorary band sorority * The Basic School, US Marine Corps * Therapeutic boarding school Transport * Tbilisi International Airport, an airport in Georgia, IATA code * Terminal Bersepad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
śĮéśó•śĖįŤĀěÁ§ĺ
The is one of the major newspapers in Japan, published by In addition to the ''Mainichi Shimbun'', which is printed twice a day in several local editions, Mainichi also operates an English language news website called ''The Mainichi'' (previously ''Mainichi Daily News''), and publishes a bilingual news magazine, ''Mainichi Weekly''. It also publishes paperbacks, books and other magazines, including a weekly news magazine, ''Sunday Mainichi''. It is one of the four national newspapers in Japan; the other three are the ''Asahi Shimbun'', the ''Yomiuri Shimbun'' and the ''Nihon Keizai Shimbun''. The Sankei Shimbun and The ''Chunichi Shimbun'' are not currently in the position of a national newspaper despite a large circulation for the both respectively. History The history of the ''Mainichi Shinbun'' began with the founding of two papers during the Meiji period. The ''Tokyo Nichi Nichi Shimbun'' was founded first, in 1872. The ''Mainichi'' claims that it is the oldest existing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Lantern
are a type of traditional East Asian lantern made of stone, wood, or metal. Originating in China, stone lanterns spread to Japan, Korea and Vietnam, though they are most commonly found in both China ‚Äď extant in Buddhist temples and traditional Chinese gardens ‚Äď and Japan. In Japan, were originally used only in Buddhist temples, where they lined and illuminated paths. Lit lanterns were then considered an offering to Buddha. Their use in Shinto shrines and also private homes started during the Heian period (794‚Äď1185). Stone lanterns have been known in China as early as the Han dynasty (202 BCE‚Äď220 CE), and prevailed from the Wei, Jin, Southern and Northern Dynasties all the way up to the Tang Dynasty, when they were introduced to Japan. The oldest extant bronze and stone lanterns in Japan can be found in Nara. Taima-dera has a stone lantern built during the Nara period, while Kasuga-taisha has one of the following Heian period. During the Azuchi-Momoyama period (1568 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ŚįŹŚ≠¶ť§®
is a Japanese publisher of dictionaries, literature, comics (manga), non-fiction, DVDs, and other media in Japan. Shogakukan founded Shueisha, which also founded Hakusensha. These are three separate companies, but are together called the Hitotsubashi Group, one of the largest publishing groups in Japan. Shogakukan is headquartered in the Shogakukan Building in Hitotsubashi, part of Kanda, Chiyoda, Tokyo, near the Jimbocho book district. The corporation also has the other two companies located in the same ward. International operations In the United States Shogakukan, along with Shueisha, owns Viz Media, which publishes manga from both companies in the United States. Shogakukan's licensing arm in North America was ShoPro Entertainment; it was merged into Viz Media in 2005. Shogakukan's production arm is Shogakukan-Shueisha Productions (previously Shogakukan Productions Co., Ltd.) In March 2010 it was announced that Shogakukan would partner with the American comics publisher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |