|
Chytriomyces Elegans
''Chytriomyces elegans'' is a species of fungus in the genus ''Chytriomyces''. It is saprophytic on dead cells of ''Ceratium hirundinella The genus ''Ceratium'' is restricted to a small number (about 7) of freshwater dinoflagellate species. Previously the genus contained also a large number of marine dinoflagellate species. However, these marine species have now been assigned to ...'' and '' Peridinium''. (retrieved 9 April 2016) References External links * Chytridiomycota Fungi described in 1976< ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungus
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chytridiomycota
Chytridiomycota are a division of zoosporic organisms in the kingdom Fungi, informally known as chytrids. The name is derived from the Ancient Greek ('), meaning "little pot", describing the structure containing unreleased zoöspores. Chytrids are one of the early diverging fungal lineages, and their membership in kingdom Fungi is demonstrated with chitin cell walls, a posterior whiplash flagellum, absorptive nutrition, use of glycogen as an energy storage compound, and synthesis of lysine by the -amino adipic acid (AAA) pathway. Chytrids are saprobic, degrading refractory materials such as chitin and keratin, and sometimes act as parasites. There has been a significant increase in the research of chytrids since the discovery of ''Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis'', the causal agent of chytridiomycosis. Classification Species of Chytridiomycota have traditionally been delineated and classified based on development, morphology, substrate, and method of zoöspore discharge. Howeve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chytridiomycetes
Chytridiomycetes () is a class of fungi. Members are found in soil, fresh water, and saline estuaries. They are first known from the Rhynie chert. It has recently been redefined to exclude the taxa Neocallimastigomycota and Monoblepharidomycetes, which are now a phylum and a sister-class respectively. Chytridiomycetes is the major class of the phylum Chytridiomycota, which contains a number of parasitic Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has c ... species. At least two species in this class are known to infect a number of amphibian species. Phylogeny Based on the work of "The Mycota: A Comprehensive Treatise on Fungi as Experimental Systems for Basic and Applied Research", Powell and Letcher 2015 and Karpov et al. 2014. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q1137709 Chytrid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chytridiales
Fungi of the order Chytridiales, like other members of its division, may either have a monocentric thallus or a polycentric rhizomycelium. When the ribosomal genes of members classified in this order were first examined using molecular techniques, it was discovered that the order contained some species that were not related. With the culture and characterization of '' Chytridium olla'', the type species of this order, the limits of the Chytridiales were established. The Chytridiales is now monophyletic and species such as '' Polychytrium aggregatum'', '' Chytriomyces angularis'' and '' Cladochytrium replicatum'' have been transferred to other orders. Genera ''incertae sedis'' * '' Achlyella'' * '' Achlyogeton'' * '' Coralliochytrium'' * '' Delfinachytrium'' * '' Pseudorhizidium'' * '' Dermomycoides'' * '' Dictyomorpha'' * '' Ichthyochytrium'' * ''Mucophilus ''Mucophilus'' is a fungal genus in the Chytridiales of uncertain familial placement. A monotypic In biology, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chytriomycetaceae
The ''Chytriomycetaceae'' are a family of fungi in the order Chytridiales Fungi of the order Chytridiales, like other members of its division, may either have a monocentric thallus or a polycentric rhizomycelium. When the ribosomal genes of members classified in this order were first examined using molecular techniqu .... Genera *'' Chytriomyces'' *'' Rhizoclosmatium'' *'' Rhizidium'' *'' Podochytrium'' *'' Obelidium'' *'' Siphonaria'' *'' Entophlyctis'' *'' Physocladia'' *'' Asterophlyctis'' *'' Fayochytriomyces'' *'' Avachytrium'' *'' Odontochytrium'' *'' Rodmanochytrium'' References Fungus families Chytridiomycota {{Chytridiomycota-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chytriomyces
''Chytriomyces'' is the type genus of fungi in the family Chytriomycetaceae. The genus was described by mycologist John Sidney Karling in 1945. The family, created by Peter Letcher in 2011, contains species with a Group I-type zoospore, distinguishing it from Chytridiaceae members, which have a Group II-type zoospore. Taxonomy J. S. Karling circumscribed ''Chytriomyces'' in 1945 for the species ''C. hyalinus'' and ''C. aureus''. The genus was intended to include monocentric chytrids with operculate, apophysate, epibiotic zoosporangia that exhibited vesicular zoospore discharge. Another requirement was resting spores that function as prosporangia during germination. With time and the addition of species, the generic concept was altered to include species lacking one or more of these features. Karling was not clear as to which of his species was the type; ''C. hyalinus'' was later designated the type. With the use of molecular phylogenetics, it has been determined that several spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cecil Terence Ingold
Cecil Terence Ingold CMG (5 July 1905 – 31 May 2010) was "one of the most influential mycologists of the twentieth century". He was president of the British Mycological Society where he organised the first international congress of mycologists. An entire class of aquatic fungi within the Pleosporales, the Ingoldian fungi, were named after him, although recent DNA studies are changing the scientific names. Academic career Terence Ingold was born at Blackrock, Dublin and attended school in Bangor, County Down. He studied at Queen's University in Belfast, Northern Ireland, and in 1926 won a First in his bachelor's degree in botany, with emphasis on mycology. He made a short study (in the style of A.H.R. Buller) of dispersal patterns of a Podospora species before taking up a scholarship in autumn 1926 at the Royal College of Science, London. Here the teaching and practicals in higher plant physiology by V. H. Blackman and others stimulated and laid a pattern for his later expe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungus
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
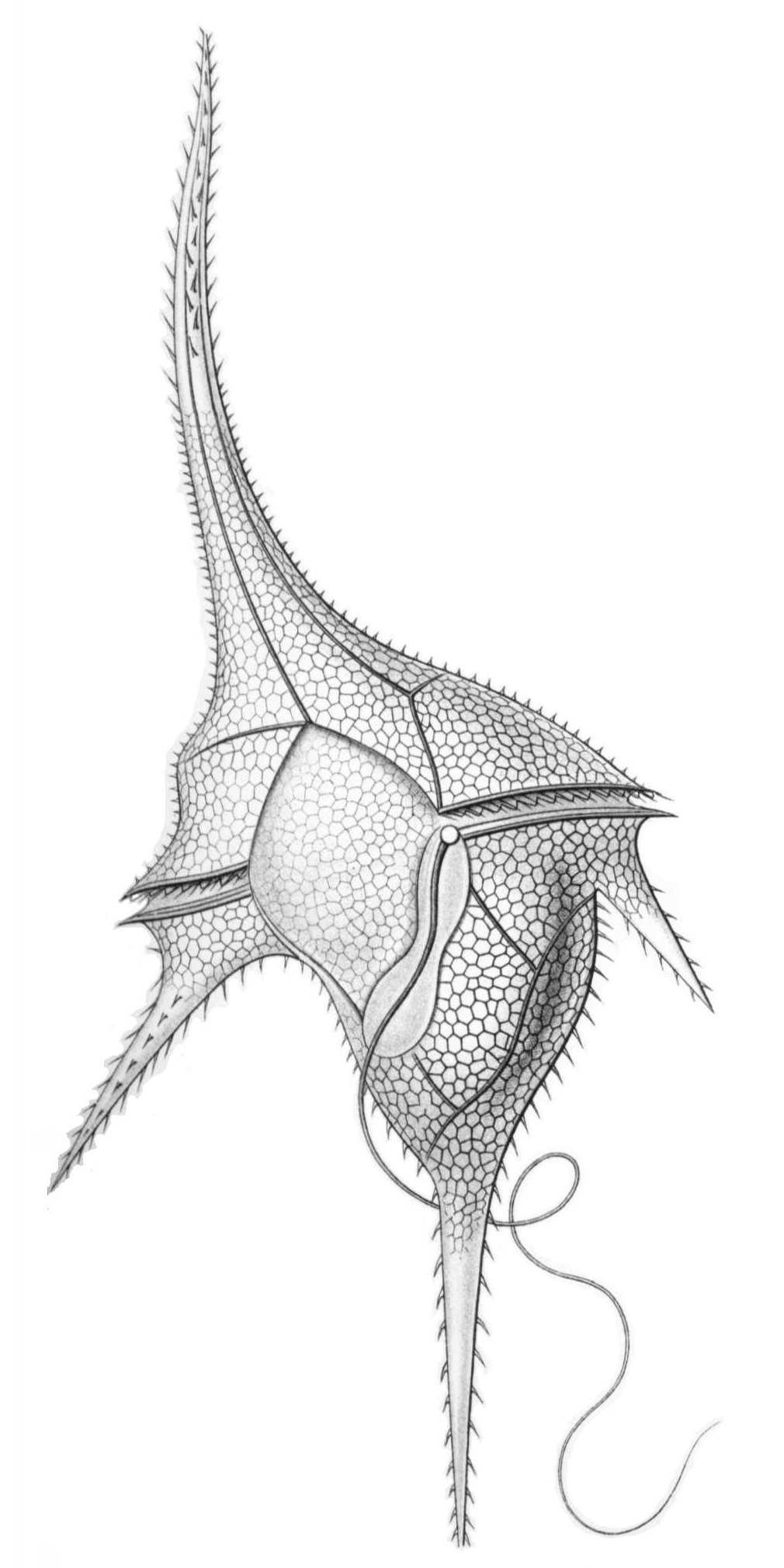
Ceratium Hirundinella
The genus ''Ceratium'' is restricted to a small number (about 7) of freshwater dinoflagellate species. Previously the genus contained also a large number of marine dinoflagellate species. However, these marine species have now been assigned to a new genus called ''Tripos''. ''Ceratium'' dinoflagellates are characterized by their armored plates, two flagella, and horns. They are found worldwide and are of concern due to their blooms. Taxonomy The genus was originally published in 1793 by Shrank, F. von Paula. The taxonomy of C''eratium'' varies among several sources. One source states the taxonomy as: Kingdom Chromista, Phylum Miozoa, Class Dinophyceae, Order Gonyaulacales, and Family Ceratiaceae. Another source lists the taxonomy as Kingdom Protozoa, Phylum Dinoflagellata, Class Dinophyceae, Order Gonyaulacales, and Family Ceratiaceae. The taxonomic information listed on the right includes Kingdom Chromalveolate. Thus, sources disagree on the higher levels of classification, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peridinium
''Peridinium'' is a genus of motile, marine and freshwater dinoflagellates. Their morphology is considered typical of the armoured dinoflagellates, and their form is commonly used in diagrams of a dinoflagellate's structure. ''Peridinium'' can range from 30 to 70 μm in diameter, and has very thick thecal plates. Morphology ''Peridinium'' is enclosed by cellulose theca and with two flagellates. The composition of the theca is laminaribiose and laminaritriose linking by ''β'' – 1, 4 and ''β'' – 1, 3 linkages. The cell body of ''Peridinium'' is highly polarized and is distinguishable from apical and antapical sides or dorsal and ventral sides. Their theca is divided into epicone and hypocone by the middle region (also called girdle or cingulum). The flagellates have two different directions, one is surrounding the middle region while the other are in the longitudinal groove of hypocone. The chloroplast in ''Peridinium'' is triple membrane, and some plastid-derived organe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |