|
Chrysophyceae
The Chrysophyceae, usually called chrysophytes, chrysomonads, golden-brown algae, or golden algae, are a large group of algae, found mostly in freshwater. Golden algae is also commonly used to refer to a single species, '' Prymnesium parvum'', which causes fish kills. The Chrysophyceae should not be confused with the Chrysophyta, which is a more ambiguous taxon. Although "chrysophytes" is the anglicization of "Chrysophyta", it generally refers to the Chrysophyceae. Members Originally they were taken to include all such forms of the diatoms and multicellular brown algae, but since then they have been divided into several different groups (e.g., Haptophyceae, Synurophyceae) based on pigmentation and cell structure. Some heterotrophic flagellates as the bicosoecids and choanoflagellates were sometimes seen as related to golden algae too. They are now usually restricted to a core group of closely related forms, distinguished primarily by the structure of the flagella in motile cel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ochromonadales
Ochromonadales is an order of single-celled algae belonging to the class Chrysophyceae, also known as golden algae. Initially it contained numerous groups of flagellates that were not closely related. During the late 20th century, advancements in molecular and ultrastructural studies allowed the transfer of many of these groups out of Ochromonadales, and the order was reduced to a single family Ochromonadaceae. They are aquatic single-celled flagellated algae, with two heterokont flagella each, some of which have secondarily lost their chloroplasts and appear colorless. Description Species of this order are flagellates, composed of cells capable of swimming by using two flagella. Though ancestrally photosynthetic, some species have secondarily lost this ability, and appear colourless. These are heterotrophic, and can be phagotrophic. Some are mixotrophic, capable of both photosynthesis and phagotrophy, such as '' Poterioomonas'' and '' Ochromonas''. They can be found in marine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synurophyceae
The synurids (order Synurales) are a small group of heterokont algae, found mostly in freshwater environments, characterized by cells covered in silica scales. Characteristics They are covered in silicate scales and spines. In ''Synura'', these are formed on the surface of the chloroplasts, two of which are usually present, but sometimes only one divided into two lobes is seen. The cells have two heterokont flagellum, flagella, inserted parallel to one another at the anterior, whose ultrastructure is a distinguishing characteristic of the group. Both asexual and isogamy, isogamous sexual reproduction occur. Morphology File:2023 Synurophyte.svg, center, upright=2, Classification Synurales are divided into three families, each with one genus: * Family Mallomonadaceae ** ''Mallomonas'' * Family Synuraceae ** ''Synura'' * Family Neotessellaceae ** ''Neotessella'' (=''Tessella'' ) History The genus ''Synura'' was proposed in 1834 by the German microscopist Christian Gottf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
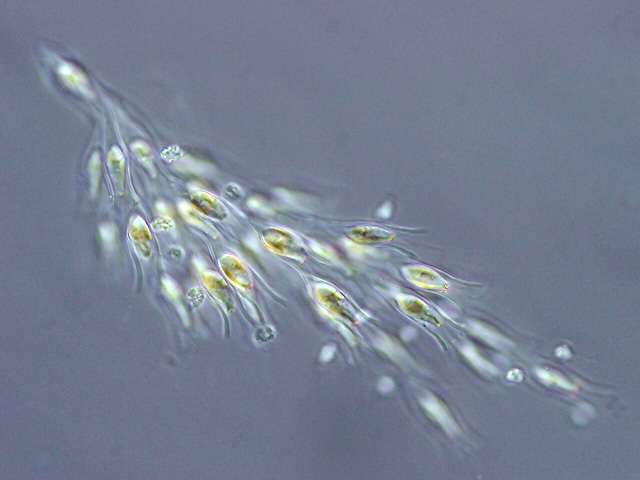
Ochromonas
''Ochromonas'' is a genus of algae belonging to the family Ochromonadaceae. The genus has cosmopolitan distribution. Chlorosulfolipids, a class of biologically active compounds, was first discovered in some ''Ochromonas'' species. Species Accepted species: *'' Ochromonas bourrellyi'' *'' Ochromonas carolina'' *'' Ochromonas cosmopoliticus'' (?) *'' Ochromonas crenata'' (?) *''Ochromonas danica ''Ochromonas'' is a genus of algae belonging to the family Ochromonadaceae. The genus has cosmopolitan distribution. Chlorosulfolipids, a class of biologically active compounds, was first discovered in some ''Ochromonas'' species. Species Acce ...'' *'' Ochromonas elegans'' *'' Ochromonas globosa'' *'' Ochromonas granularis'' *'' Ochromonas lubibunda'' *'' Ochromonas malhamensis'' (?) *'' Ochromonas minima'' *'' Ochromonas minuta'' *'' Ochromonas marina'' (?) *'' Ochromonas mutabilis'' *'' Ochromonas nana'' *'' Ochromonas oblonga'' *'' Ochromonas ostreaeformis'' *'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chrysosphaerales
Chrysosphaerales is an order of Chrysophyceae The Chrysophyceae, usually called chrysophytes, chrysomonads, golden-brown algae, or golden algae, are a large group of algae, found mostly in freshwater. Golden algae is also commonly used to refer to a single species, '' Prymnesium parvum'', wh .... References Golden algae orders Chrysophyceae {{Heterokont-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagellum
A flagellum (; : flagella) (Latin for 'whip' or 'scourge') is a hair-like appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, from fungal spores ( zoospores), and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many protists with flagella are known as flagellates. A microorganism may have from one to many flagella. A gram-negative bacterium '' Helicobacter pylori'', for example, uses its flagella to propel itself through the stomach to reach the mucous lining where it may colonise the epithelium and potentially cause gastritis, and ulcers – a risk factor for stomach cancer. In some swarming bacteria, the flagellum can also function as a sensory organelle, being sensitive to wetness outside the cell. Across the three domains of Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryota, the flagellum has a different structure, protein composition, and mechanism of propulsion but shares the same function of providing motility. The Latin word means " whip" to describe its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromista
Chromista is a proposed but polyphyletic obsolete Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom, refined from the Chromalveolata, consisting of single-celled and multicellular eukaryotic species that share similar features in their Photosynthesis, photosynthetic organelles (plastids). It includes all eukaryotes whose plastids contain chlorophyll c, chlorophyll ''c'' and are surrounded by four membranes. If the ancestor already possessed chloroplasts derived by Endosymbiont, endosymbiosis from red algae, all non-photosynthetic Chromista have secondarily lost the ability to photosynthesise. Its members might have arisen independently as separate evolutionary groups from the last eukaryotic common ancestor. Chromista as a taxon was created by the British biologist Thomas Cavalier-Smith in 1981 to distinguish the stramenopiles, haptophytes, and Cryptomonad, cryptophytes. According to Cavalier-Smith, the kingdom originally consisted mostly of photosynthetic eukaryotes (algae), but he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chrysophyta
Chrysophyta or golden algae is a term used to refer to certain heterokonts. It can be used to refer to: * Chrysophyceae (golden algae), Bacillariophyceae (diatoms), and Xanthophyceae (yellow-green algae) together. E.g., Adolf A. Pascher, Pascher (1914). * Chrysophyceae (golden algae) E.g., Lynn Margulis, Margulis et al. (1990).Lynn Margulis, Margulis, L., J.O. Corliss, M. Melkonian, D.J. Chapman. ''Handbook of Protoctista''. Jones and Bartlett Publishers, Boston, 1990. Chrysophyta has some characteristics which includes their possession of the photosynthetic pigments which are chlorophylls a and c, they also possess a yellow carotenoid called fucoxanthin, this is responsible for their unique and characteristic color. They also store food as oil and not starch, their cells contain no cellulose and are often impregnated with silicon compounds. Each species has its own special markings. References Ochrophyta {{Heterokont-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinobryon
''Dinobryon'' is a type of microscopic algae. It is one of the 22 genera Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family as used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial s ... in the family Dinobryaceae. ''Dinobryon'' are mixotrophs, capable of obtaining energy and carbon through photosynthesis and phagotrophy of bacteria. The genus comprises at least 37 described species. The best-known species are ''D. cylindricum'' and ''D. divergens'', which come to the attention of humans annually due to transient blooms in the photic zone of temperate lakes and ponds. Such blooms may produce volatile organic compounds ( VOCs) that produce odors and affect water quality. ''Dinobryon'' can exist as free-living, solitary cells or in branching colonies. Ecology Though most commonly found in freshwater lakes and ponds, ''Dinobryon'' have also b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bicosoecid
Bicosoecida ( ICZN) or Bicosoecales/Bicoecea ( ICBN) is an order of Bikosea, a small group of unicellular flagellates, included among the stramenopiles. Informally known as bicosoecids, they are free-living cells, with no chloroplasts, and in some genera are encased in a lorica. The name of the type genus '' Bicosoeca'' described by James-Clark in 1866 is derived from Greek roots (, vase, bowl, plus ''oekein'', inhabit). The philologically preferable compound would be ''Bicoeca'', as "corrected" by Stein in 1878 and followed by most subsequent authors. However, according to the ICBN and ICZN, the original spelling of the name cannot be considered incorrect and it must be used in its original form. The group was formerly considered to be related to the Chrysophyceae. Some authors use the vernacular term "bicosoecid" (or "bicoecid") in a narrower sense, only for ''Bicosoeca'', applying "bicoeceans" to ''Bicosoeca'' and related groups like '' Cafeteria''. With the advent of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagellate
A flagellate is a cell or organism with one or more whip-like appendages called flagella. The word ''flagellate'' also describes a particular construction (or level of organization) characteristic of many prokaryotes and eukaryotes and their means of motion. The term presently does not imply any specific relationship or classification of the organisms that possess flagella. However, several derivations of the term "flagellate" (such as " dinoflagellate" and " choanoflagellate") are more formally characterized. Form and behavior Flagella in eukaryotes are supported by microtubules in a characteristic arrangement, with nine fused pairs surrounding two central singlets. These arise from a basal body. In some flagellates, flagella direct food into a cytostome or mouth, where food is ingested. Flagella role in classifying eukaryotes. Among protoctists and microscopic animals, a flagellate is an organism with one or more flagella. Some cells in other animals may be flage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hibberdiales
Hibberdiales is an order of Chrysophyceae The Chrysophyceae, usually called chrysophytes, chrysomonads, golden-brown algae, or golden algae, are a large group of algae, found mostly in freshwater. Golden algae is also commonly used to refer to a single species, '' Prymnesium parvum'', wh ... (golden algae). It includes '' Chromophyton'', '' Hibberdia'', and '' Lagynion''. References Algae orders Golden algae orders Chrysophyceae {{Heterokont-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |