|
Chrony
chrony is an implementation of the Network Time Protocol (NTP). It is an alternative to ntpd, a reference implementation of NTP. It runs on Unix-like operating systems (including Linux and macOS) and is released under the GNU General Public License, GNU GPL v2. It is the default NTP Client (computing), client and Server (computing), server in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 and SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15, and available in many Linux distributions. Support for Network Time Security (NTS) was added in version 4.0. Comparison with the reference implementation In contrast to Network Time Protocol#NTPsec, NTPsec, which is a security-focused fork of , chrony was implemented from scratch. It was designed to synchronize time even in difficult conditions such as intermittent network connections (such as laptops) and congested networks. Some improvements in this regard (compared to reference ntpd) include that it never steps (abruptly adjusts) time outside of startup, can correct for as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
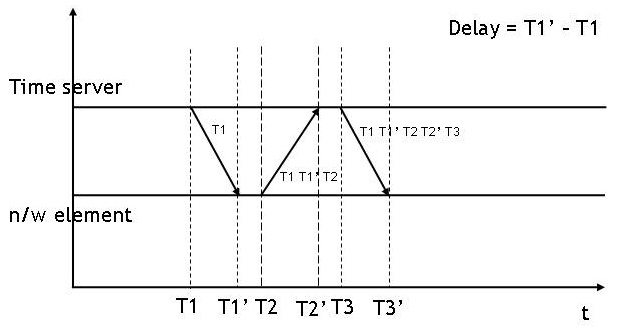
Network Time Protocol
The Network Time Protocol (NTP) is a networking protocol for clock synchronization between computer systems over packet-switched, variable-Network latency, latency data networks. In operation since before 1985, NTP is one of the oldest Internet protocols in current use. NTP was designed by David L. Mills of the University of Delaware. NTP is intended to synchronize participating computers to within a few milliseconds of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). It uses the intersection algorithm, a modified version of Marzullo's algorithm, to select accurate time servers and is designed to mitigate the effects of variable network latency. NTP can usually maintain time to within tens of milliseconds over the public Internet, and can achieve better than one millisecond accuracy in local area networks under ideal conditions. Asymmetric Routing, routes and network congestion can cause errors of 100 ms or more. The protocol is usually described in terms of a client–server model, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Hat
Red Hat, Inc. (formerly Red Hat Software, Inc.) is an American software company that provides open source software products to enterprises and is a subsidiary of IBM. Founded in 1993, Red Hat has its corporate headquarters in Raleigh, North Carolina, with other offices worldwide. Red Hat has become associated to a large extent with its enterprise operating system Red Hat Enterprise Linux. With the acquisition of open-source enterprise middleware vendor JBoss, Red Hat also offers Red Hat Virtualization (RHV), an enterprise virtualization product. Red Hat provides storage, operating system platforms, middleware, applications, management products, support, training, and consulting services. Red Hat creates, maintains, and contributes to many free software projects. It has acquired the codebases of several proprietary software products through corporate mergers and acquisitions, and has released such software under open source licenses. , Red Hat is the second largest co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server
SUSE Linux Enterprise (SLE) is a Linux-based operating system developed by SUSE. It is available in two editions, suffixed with Server (SLES) for servers and mainframes, and Desktop (SLED) for workstations and desktop computers. Its major versions are released at an interval of three–four years, while minor versions (called "Service Packs") are released about every 12 months. SUSE Linux Enterprise products receive more intense testing than the upstream openSUSE community product, with the intention that only mature, stable versions of the included components will make it through to the released enterprise product. It is developed from a common code base with other SUSE Linux Enterprise products. IBM's Watson was built on IBM's POWER7 systems using SLES. Hewlett Packard Enterprise's Frontier, world's first and fastest exascale supercomputer runs on SUSE's SLES 15 (HPE Cray OS). SUSE Linux Enterprise Server SLES was developed based on SUSE Linux by a small team led by M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Time-related Software
Network, networking and networked may refer to: Science and technology * Network theory, the study of graphs as a representation of relations between discrete objects * Network science, an academic field that studies complex networks Mathematics * Networks, a graph with attributes studied in network theory ** Scale-free network, a network whose degree distribution follows a power law ** Small-world network, a mathematical graph in which most nodes are not neighbors, but have neighbors in common * Flow network, a directed graph where each edge has a capacity and each edge receives a flow Biology * Biological network, any network that applies to biological systems * Ecological network, a representation of interacting species in an ecosystem * Neural network, a network or circuit of neurons Technology and communication * Artificial neural network, a computing system inspired by animal brains * Broadcast network, radio stations, television stations, or other electronic media outlets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timesyncd
systemd is a software suite that provides an array of system components for Linux operating systems. The main aim is to unify service configuration and behavior across Linux distributions. Its primary component is a "system and service manager" — an init system used to bootstrap user space and manage user processes. It also provides replacements for various daemons and utilities, including device management, login management, network connection management, and event logging. The name ''systemd'' adheres to the Unix convention of naming daemons by appending the letter ''d''. It also plays on the term "System D", which refers to a person's ability to adapt quickly and improvise to solve problems. Since 2015, the majority of Linux distributions have adopted systemd, having replaced other init systems such as SysV init. It has been praised by developers and users of distributions that adopted it for providing a stable, fast out-of-the-box solution for issues that had exi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OpenNTPD
OpenNTPD (also known as OpenBSD NTP Daemon) is a Unix daemon implementing the Network Time Protocol to synchronize the local clock of a computer system with remote NTP servers. It is also able to act as an NTP server to NTP-compatible clients. OpenBSD NTP Daemon was initially developed by Alexander Guy and Henning Brauer as part of the OpenBSD project, with further help by many authors. Its design goals include being secure ( non-exploitable), easy to configure, and accurate enough for most purposes. Its portable version, like that of OpenSSH, is developed as a child project which adds the portability code to the OpenBSD version and releases it separately. The portable version is developed by Brent Cook. The project developers receive some funding from the OpenBSD Foundation. History The development of OpenNTPD was motivated by a combination of issues with current NTP daemons: difficult configuration, complicated and difficult to audit code, and unsuitable licensing. Open ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anycast
Anycast is a network addressing and routing methodology in which a single IP address is shared by devices (generally servers) in multiple locations. Routers direct packets addressed to this destination to the location nearest the sender, using their normal decision-making algorithms, typically the lowest number of BGP network hops. Anycast routing is widely used by content delivery networks such as web and name servers, to bring their content closer to end users. History The first documented use of anycast routing for topological load-balancing of Internet-connected services was in 1989; the technique was first formally documented in the IETF four years later. It was first applied to critical infrastructure in 2001 with the anycasting of the I-root nameserver. Early objections Early objections to the deployment of anycast routing centered on the perceived conflict between long-lived TCP connections and the volatility of the Internet's routed topology. In concept, a long-liv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multicast
In computer networking, multicast is a type of group communication where data transmission is addressed to a group of destination computers simultaneously. Multicast can be one-to-many or many-to-many distribution. Multicast differs from physical layer point-to-multipoint communication. Group communication may either be application layer multicast or network-assisted multicast, where the latter makes it possible for the source to efficiently send to the group in a single transmission. Copies are automatically created in other network elements, such as routers, switches and cellular network base stations, but only to network segments that currently contain members of the group. Network assisted multicast may be implemented at the data link layer using one-to-many addressing and switching such as Ethernet multicast addressing, Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM), point-to-multipoint virtual circuits (P2MP) or InfiniBand multicast. Network-assisted multicast may also be im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precision Time Protocol
The Precision Time Protocol (PTP) is a protocol for clock synchronization throughout a computer network with relatively high precision and therefore ''potentially'' high accuracy. In a local area network (LAN), accuracy can be sub-microsecond making it suitable for measurement and control systems. PTP is used to synchronize financial transactions, mobile phone tower transmissions, sub-sea acoustic arrays, and networks that require precise timing but lack access to satellite navigation signals. The first version of PTP, IEEE 1588-2002, was published in 2002. IEEE 1588-2008, also known as PTP Version 2, is not backward compatible with the 2002 version. IEEE 1588-2019 was published in November 2019 and includes backward-compatible improvements to the 2008 publication. IEEE 1588-2008 includes a ''profile'' concept defining PTP operating parameters and options. Several profiles have been defined for applications including telecommunications, electric power distribution and aud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Area Network
A local area network (LAN) is a computer network that interconnects computers within a limited area such as a residence, campus, or building, and has its network equipment and interconnects locally managed. LANs facilitate the distribution of data and sharing network devices, such as printers. The LAN contrasts the wide area network (WAN), which not only covers a larger geographic distance, but also generally involves Leased line, leased telecommunication circuits or Internet links. An even greater contrast is the Internet, which is a system of globally connected business and personal computers. Ethernet and Wi-Fi are the two most common technologies used for local area networks; historical network technologies include ARCNET, Token Ring, and LocalTalk. Cabling Most wired network infrastructures utilize Category 5 cable, Category 5 or Category 6 cable, Category 6 twisted pair cabling with RJ45 (telecommunications), RJ45 compatible terminations. This medium provides physical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laptops
A laptop computer or notebook computer, also known as a laptop or notebook, is a small, portable personal computer (PC). Laptops typically have a clamshell form factor with a flat-panel screen on the inside of the upper lid and an alphanumeric keyboard and pointing device on the inside of the lower lid. Most of the computer's internal hardware is in the lower part, under the keyboard, although many modern laptops have a built-in webcam at the top of the screen, and some even feature a touchscreen display. In most cases, unlike tablet computers which run on mobile operating systems, laptops tend to run on desktop operating systems, which were originally developed for desktop computers. Laptops are used in a variety of settings, such as at work (especially on business trips), in education, for playing games, content creating, web browsing, for personal multimedia, and for general home computer use. They can run on both AC power and rechargable battery packs and can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux Distributions
A Linux distribution, often abbreviated as distro, is an operating system that includes the Linux kernel for its kernel (operating system), kernel functionality. Although the name does not imply distribution (marketing), product distribution per se, a distro—if distributed on its own—is often obtained via a website intended specifically for the purpose. Distros have been designed for a wide variety of systems ranging from personal computers (for example, Linux Mint) to Server (computing), servers (for example, Red Hat Enterprise Linux) and from embedded devices (for example, OpenWrt) to supercomputers (for example, Rocks Cluster Distribution). A distro typically includes many components in addition to the Linux kernel. Commonly, it includes a package manager, an Init, init system (such as systemd, OpenRC, or runit), GNU tools and Library (computing), libraries, documentation, Internet Protocol, IP network configuration utilities, the Getty (Unix), getty TTY setup program, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |