|
Chronic Eosinophilic Leukemia
Chronic eosinophilic leukemia is a form of cancer in which too many eosinophils are found in the bone marrow, blood, and other tissues. Most cases are associated with fusion genes. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms may include weight loss, fever, malaise, cough, skin and mucosal lesions, diarrhea, and peripheral neuropathy. Cardiac symptoms are also possible. In cases associated with PDGFRB and FGFR1 mutations, splenomegaly is common. Lymphadenopathy is also common with FGFR1 mutations. Infiltration of eosinophils causes organ damage. Causes Most cases of CEL are associated with rearrangements in PDGFRA, PDGFRB, or FGFR1. CEL not otherwise specified (CEL NOS) is a form in which BCR-ABL1 fusion genes and PDGFRA, PDGFRB, and FGFR1 rearrangements are not found. Diagnosis For a diagnosis of CEL, hypereosinophilia with greater than 30% eosinophils is required. Serum IgE is usually normal. In cases associated with PDGFRB, serum vitamin B12 and tryptase may be elevated. P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
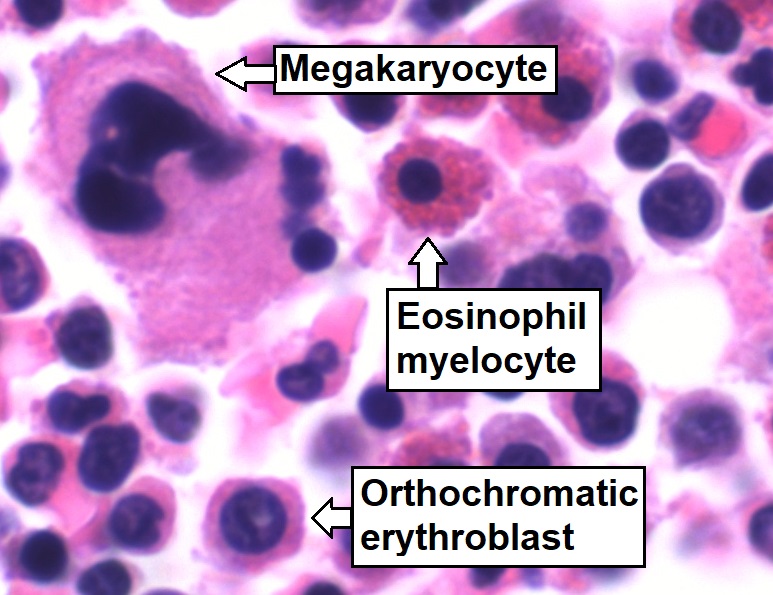
Eosinophils
Eosinophils, sometimes called eosinophiles or, less commonly, acidophils, are a variety of white blood cells (WBCs) and one of the immune system components responsible for combating multicellular parasites and certain infections in vertebrates. Along with mast cells and basophils, they also control mechanisms associated with allergy and asthma. They are granulocytes that develop during hematopoiesis in the bone marrow before migrating into blood, after which they are terminally differentiated and do not multiply. They form about 2 to 3% of WBCs. These cells are eosinophilic or "acid-loving" due to their large acidophilic cytoplasmic granules, which show their affinity for acids by their affinity to coal tar dyes: Normally transparent, it is this affinity that causes them to appear brick-red after staining with eosin, a red dye, using the Romanowsky method. The staining is concentrated in small granules within the cellular cytoplasm, which contain many chemical mediators, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PDGFRB
Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''PDGFRB'' gene. Mutations in PDGFRB are mainly associated with the clonal eosinophilia class of malignancies. Gene The ''PDGFRB'' gene is located on human chromosome 5 at position q32 (designated as 5q32) and contains 25 exons. The gene is flanked by the genes for granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and Colony stimulating factor 1 receptor (also termed macrophage-colony stimulating factor receptor), all three of which may be lost together by a single deletional mutation thereby causing development of the 5q-syndrome. Other genetic abnormalities in ''PDGFRB'' lead to various forms of potentially malignant bone marrow disorders: small deletions in and chromosome translocations causing fusions between ''PDGFRB'' and any one of at least 30 genes can cause Myeloproliferative neoplasms that commonly involve eosinophilia, eosinophil-induced organ injury, and possible progressio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer of the myeloid line of blood cells, characterized by the rapid growth of abnormal cells that build up in the bone marrow and blood and interfere with normal blood cell production. Symptoms may include feeling tired, shortness of breath, easy bruising and bleeding, and increased risk of infection. Occasionally, spread may occur to the brain, skin, or gums. As an acute leukemia, AML progresses rapidly, and is typically fatal within weeks or months if left untreated. Risk factors include smoking, previous chemotherapy or radiation therapy, myelodysplastic syndrome, and exposure to the chemical benzene. The underlying mechanism involves replacement of normal bone marrow with leukemia cells, which results in a drop in red blood cells, platelets, and normal white blood cells. Diagnosis is generally based on bone marrow aspiration and specific blood tests. AML has several subtypes for which treatments and outcomes may vary. The fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Eosinophilic Leukemia
Acute eosinophilic leukemia (AEL) is a rare subtype of acute myeloid leukemia with 50 to 80 percent of eosinophilic cells in the blood and marrow. It can arise de novo or may develop in patients having the chronic form of a hypereosinophilic syndrome. Patients with acute eosinophilic leukemia have a propensity for developing bronchospasm as well as symptoms of the acute coronary syndrome and/or heart failure due to eosinophilic myocarditis and eosinophil-based endomyocardial fibrosis. Hepatomegaly and splenomegaly Splenomegaly is an enlargement of the spleen. The spleen usually lies in the left upper quadrant (LUQ) of the human abdomen. Splenomegaly is one of the four cardinal signs of ''hypersplenism'' which include: some reduction in number of circulating ... are more common than in other variants of AML. Diagnosis A specific histochemical reaction, cyanide-resistant peroxidase, permits identification of leukemic blast cells with eosinophilic differentiation and diagnosis of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imatinib
Imatinib, sold under the brand names Gleevec and Glivec (both marketed worldwide by Novartis) among others, is an oral chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. Imatinib is a small molecule inhibitor targeting multiple receptor tyrosine kinases such as CSF1R, ABL, c-KIT, FLT3, and PDGFR-β. Specifically, it is used for chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) and acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) that are Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+), certain types of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST), hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES), chronic eosinophilic leukemia (CEL), systemic mastocytosis, and myelodysplastic syndrome. Common side effects include vomiting, diarrhea, muscle pain, headache, and rash. Severe side effects may include fluid retention, gastrointestinal bleeding, bone marrow suppression, liver problems, and heart failure. Use during pregnancy may result in harm to the baby. Imatinib works by stopping the Bcr-Abl tyrosine-kinase. This can slow growth or result in p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tryptase
Tryptase (, ) is the most abundant secretory granule-derived serine proteinase contained in mast cells and has been used as a marker for mast cell activation. Club cells contain tryptase, which is believed to be responsible for cleaving the hemagglutinin surface protein of influenza A virus, thereby activating it and causing the symptoms of flu. Nomenclature Tryptase is also known by mast cell tryptase, mast cell protease II, skin tryptase, lung tryptase, pituitary tryptase, mast cell neutral proteinase, mast cell serine proteinase II, mast cell proteinase II, mast cell serine proteinase tryptase, rat mast cell protease II, and tryptase M. Clinical use Serum levels are normally less than 11.5 ng/mL. Elevated levels of serum tryptase occur in both anaphylactic and anaphylactoid reactions, but a negative test does not exclude anaphylaxis. Tryptase is less likely to be elevated in food allergy reactions as opposed to other causes of anaphylaxis. Serum tryptase levels are a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
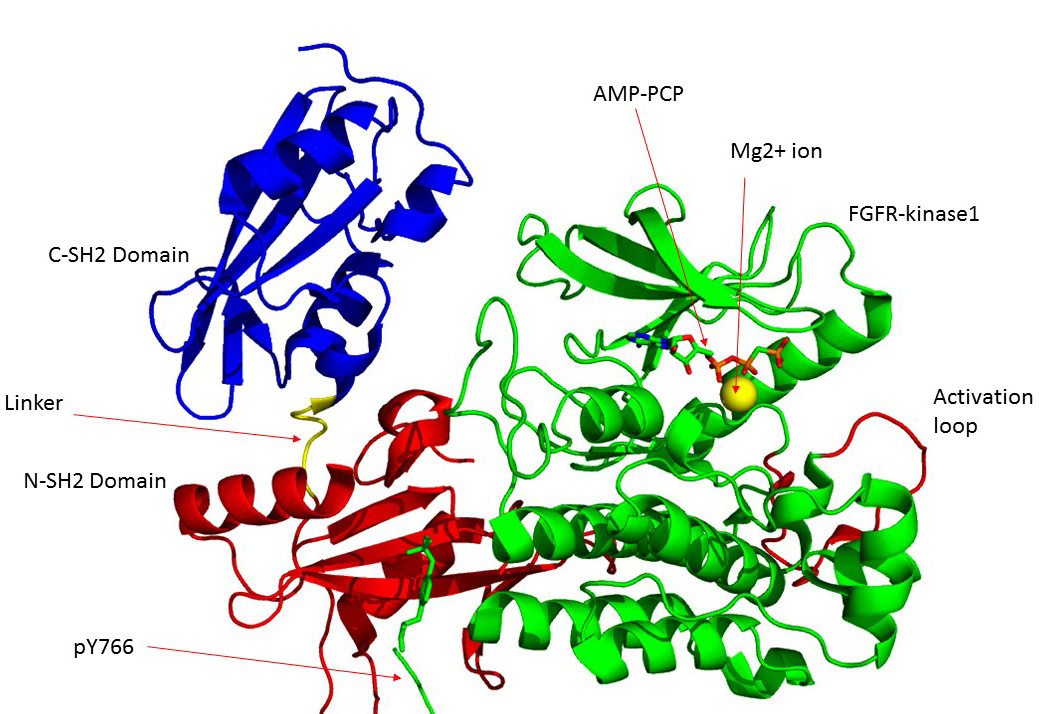
FGFR1
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1), also known as basic fibroblast growth factor receptor 1, fms-related tyrosine kinase-2 / Pfeiffer syndrome, and CD331, is a receptor tyrosine kinase whose ligands are specific members of the fibroblast growth factor family. FGFR1 has been shown to be associated with Pfeiffer syndrome, and clonal eosinophilias. Gene The ''FGFR1'' gene is located on human chromosome 8 at position p11.23 (i.e. 8p11.23), has 24 exons, and codes for a Precursor mRNA that is alternatively spliced at exons 8A or 8B thereby generating two mRNAs coding for two FGFR1 isoforms, FGFR1-IIIb (also termed FGFR1b) and FGFR1-IIIc (also termed FGFR1c), respectively. Although these two isoforms have different tissue distributions and FGF-binding affinities, FGFR1-IIIc appears responsible for most of functions of the FGFR1 gene while FGFR1-IIIb appears to have only a minor, somewhat redundant functional role. There are four other members of the ''FGFR1'' gene family: FGF ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PDGFRA
PDGFRA, i.e. platelet-derived growth factor receptor A, also termed PDGFRα, i.e. platelet-derived growth factor receptor α, or CD140a i.e. Cluster of Differentiation 140a, is a receptor located on the surface of a wide range of cell types. This receptor binds to certain isoforms of platelet-derived growth factors (PDGFs) and thereby becomes active in stimulating cell signaling pathways that elicit responses such as cellular growth and differentiation. The receptor is critical for the development of certain tissues and organs during embryogenesis and for the maintenance of these tissues and organs, particularly hematologic tissues, throughout life. Mutations in the gene which codes for PDGFRA, i.e. the ''PDGFRA'' gene, are associated with an array of clinically significant neoplasms, notably ones of the clonal hypereosinophilia class of malignancies, as well as gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs). Overall structure This gene encodes a typical receptor tyrosine kinase, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone Marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid tissue found within the spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It is composed of hematopoietic cells, marrow adipose tissue, and supportive stromal cells. In adult humans, bone marrow is primarily located in the ribs, vertebrae, sternum, and bones of the pelvis. Bone marrow comprises approximately 5% of total body mass in healthy adult humans, such that a man weighing 73 kg (161 lbs) will have around 3.7 kg (8 lbs) of bone marrow. Human marrow produces approximately 500 billion blood cells per day, which join the systemic circulation via permeable vasculature sinusoids within the medullary cavity. All types of hematopoietic cells, including both myeloid and lymphoid lineages, are created in bone marrow; however, lymphoid cells must migrate to other lymphoid organs (e.g. thymus) in order to complete maturation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Rearrangement
V(D)J recombination is the mechanism of somatic recombination that occurs only in developing lymphocytes during the early stages of T and B cell maturation. It results in the highly diverse repertoire of antibodies/immunoglobulins and T cell receptors (TCRs) found in B cells and T cells, respectively. The process is a defining feature of the adaptive immune system. V(D)J recombination in mammals occurs in the primary lymphoid organs ( bone marrow for B cells and thymus for T cells) and in a nearly random fashion rearranges variable (V), joining (J), and in some cases, diversity (D) gene segments. The process ultimately results in novel amino acid sequences in the antigen-binding regions of immunoglobulins and TCRs that allow for the recognition of antigens from nearly all pathogens including bacteria, viruses, parasites, and worms as well as "altered self cells" as seen in cancer. The recognition can also be allergic in nature (''e.g.'' to pollen or other allergens) or may match ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphadenopathy
Lymphadenopathy or adenopathy is a disease of the lymph nodes, in which they are abnormal in size or consistency. Lymphadenopathy of an inflammatory type (the most common type) is lymphadenitis, producing swollen or enlarged lymph nodes. In clinical practice, the distinction between lymphadenopathy and lymphadenitis is rarely made and the words are usually treated as synonymous. Inflammation of the lymphatic vessels is known as lymphangitis. Infectious lymphadenitis affecting lymph nodes in the neck is often called scrofula. Lymphadenopathy is a common and nonspecific sign. Common causes include infections (from minor causes such as the common cold and post-vaccination swelling to serious ones such as HIV/AIDS), autoimmune diseases, and cancer. Lymphadenopathy is frequently idiopathic and self-limiting. Causes Lymph node enlargement is recognized as a common sign of infectious, autoimmune, or malignant disease. Examples may include: * Reactive: acute infection (''e.g.,'' ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |