|
Chromatosome
In molecular biology, a chromatosome is a result of histone H1 binding to a nucleosome, which contains a histone octamer and DNA. The chromatosome contains 166 base pair A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA ...s of DNA. 146 base pairs are from the DNA wrapped around the histone core of the nucleosome. The remaining 20 base pairs are from the DNA of histone H1 binding to the nucleosome. Histone H1, and its other variants, are referred to as linker histones. Protruding from the linker histone are linker DNA. Chromatosomes are connected to each other when the linker DNA of one chromatosome binds to the linker histone of another chromatosome.{{Cite journal, last=Widom, first=J., date=1998, title=Structure, dynamics, and function of chromatin in vitro, journal=Annual Revie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basic Units Of Chromatin Structure
Basic or BASIC may refer to: Science and technology * BASIC, a computer programming language * Basic (chemistry), having the properties of a base * Basic access authentication, in HTTP Entertainment * ''Basic'' (film), a 2003 film * Basic, one of the languages in ''Star Wars'' Music * ''Basic'' (Glen Campbell album), 1978 * ''Basic'' (Robert Quine and Fred Maher album), 1984 * ''B.A.S.I.C.'' (Alpinestars album), 2000 * ''Basic'' (Brown Eyed Girls album), 2015 * ''B.A.S.I.C.'' (The Basics album), 2019 Places * Basic, Mississippi, a community in the US * BASIC countries, Brazil, South Africa, India and China in climate change negotiations Organizations * BASIC Bank Limited, government owned bank in Bangladesh * Basic Books, an American publisher Other uses * Basic (cigarette), a brand of cigarettes manufactured by the Altria Group (Philip Morris Company) * Basic (dance move), the dance move that defines the character of a particular dance * Basic (slang), a pejorative t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Biology
Molecular biology is a branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecule, molecular basis of biological activity in and between Cell (biology), cells, including biomolecule, biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions. Though cells and other microscopic structures had been observed in living organisms as early as the 18th century, a detailed understanding of the mechanisms and interactions governing their behavior did not emerge until the 20th century, when technologies used in physics and chemistry had advanced sufficiently to permit their application in the biological sciences. The term 'molecular biology' was first used in 1945 by the English physicist William Astbury, who described it as an approach focused on discerning the underpinnings of biological phenomena—i.e. uncovering the physical and chemical structures and properties of biological molecules, as well as their interactions with other molecules and how these interactions explain observ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histone H1
Histone H1 is one of the five main histone protein families which are components of chromatin in eukaryotic cells. Though highly conserved, it is nevertheless the most variable histone in sequence across species. Structure Metazoan H1 proteins feature a central globular "winged helix" domain and long C- and short N-terminal tails. H1 is involved with the packing of the "beads on a string" sub-structures into a high order structure, whose details have not yet been solved. H1 found in protists and bacteria, otherwise known as nucleoproteins HC1 and HC2 (, ), lack the central domain and the N-terminal tail. H1 is less conserved than core histones. The globular domain is the most conserved part of H1. Function Unlike the other histones, H1 does not make up the nucleosome "bead". Instead, it sits on top of the structure, keeping in place the DNA that has wrapped around the nucleosome. H1 is present in half the amount of the other four histones, which contribute two molecule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleosome
A nucleosome is the basic structural unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes. The structure of a nucleosome consists of a segment of DNA wound around eight histone, histone proteins and resembles thread wrapped around a bobbin, spool. The nucleosome is the fundamental subunit of chromatin. Each nucleosome is composed of a little less than two turns of DNA wrapped around a set of eight proteins called histones, which are known as a histone octamer. Each histone octamer is composed of two copies each of the histone proteins Histone H2A, H2A, Histone H2B, H2B, Histone H3, H3, and Histone H4, H4. DNA must be compacted into nucleosomes to fit within the cell nucleus. In addition to nucleosome wrapping, eukaryotic chromatin is further compacted by being folded into a series of more complex structures, eventually forming a chromosome. Each human cell contains about 30 million nucleosomes. Nucleosomes are thought to carry Epigenetics, epigenetically inherited information in the form of coval ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histone Octamer
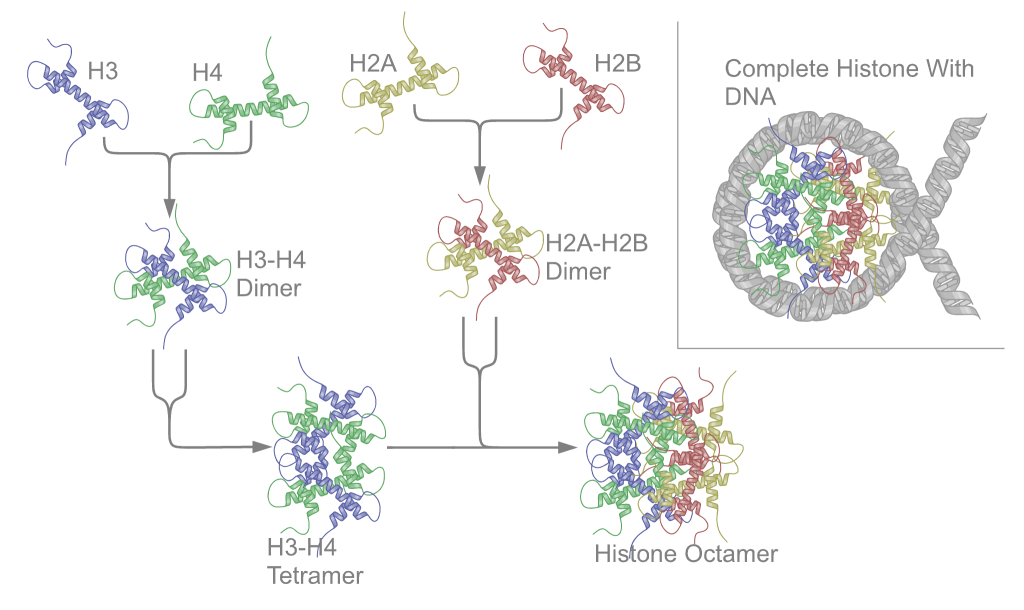
In molecular biology, a histone octamer is the eight-protein complex found at the center of a nucleosome core particle. It consists of two copies of each of the four core histone proteins ( H2A, H2B, H3, and H4). The octamer assembles when a tetramer, containing two copies of H3 and two of H4, complexes with two H2A/H2B dimers. Each histone has both an N-terminal tail and a C-terminal histone-fold. Each of these key components interacts with DNA in its own way through a series of weak interactions, including hydrogen bonds and salt bridges. These interactions keep the DNA and the histone octamer loosely associated, and ultimately allow the two to re-position or to separate entirely. History of research Histone post-translational modifications were first identified and listed as having a potential regulatory role on the synthesis of RNA in 1964. Since then, over several decades, chromatin theory has evolved. Chromatin subunit models as well as the notion of the nucleosome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base Pair
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA and RNA. Dictated by specific hydrogen bonding patterns, "Watson–Crick" (or "Watson–Crick–Franklin") base pairs (guanine–cytosine and adenine–thymine) allow the DNA helix to maintain a regular helical structure that is subtly dependent on its nucleotide sequence. The Complementarity (molecular biology), complementary nature of this based-paired structure provides a Redundancy (information theory), redundant copy of the genetic information encoded within each strand of DNA. The regular structure and data redundancy provided by the DNA double helix make DNA well suited to the storage of genetic information, while base-pairing between DNA and incoming nucleotides provides the mechanism through which DNA polymerase replicates DNA and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histone
In biology, histones are highly basic proteins abundant in lysine and arginine residues that are found in eukaryotic cell nuclei and in most Archaeal phyla. They act as spools around which DNA winds to create structural units called nucleosomes. Nucleosomes in turn are wrapped into 30- nanometer fibers that form tightly packed chromatin. Histones prevent DNA from becoming tangled and protect it from DNA damage. In addition, histones play important roles in gene regulation and DNA replication. Without histones, unwound DNA in chromosomes would be very long. For example, each human cell has about 1.8 meters of DNA if completely stretched out; however, when wound about histones, this length is reduced to about 9 micrometers (0.09 mm) of 30 nm diameter chromatin fibers. There are five families of histones, which are designated H1/H5 (linker histones), H2, H3, and H4 (core histones). The nucleosome core is formed of two H2A-H2B dimers and a H3-H4 tetramer. The tight wr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linker Histone H1 Variants
In molecular biology, the linker histone H1 is a protein family forming a critical component of eukaryotic chromatin. H1 histones bind to the linker DNA exiting from the nucleosome core particle, while the core histones ( H2A, H2B, H3 and H4) form the octamer core of the nucleosome around which the DNA is wrapped. H1 forms a complex family of related proteins with distinct specificity for tissues, developmental stages, and organisms in which they are expressed. Individual H1 proteins are often referred to as ''isoforms'' or ''variants''. The discovery of H1 variants in calf thymus preceded the discovery of core histone variants. Human linker histone variants In human and mouse cells 11 H1 variants have been described and are encoded by single genes. Six of the variants are mainly expressed during the S phase and hence replication-dependent. They are encoded by genes within histone cluster 1 located in human cells on chromosome 6. The five further variants are expressed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linker DNA
In molecular biology, linker DNA is double-stranded DNA (38-53 base pairs long) in between two nucleosome cores that, in association with histone H1, holds the cores together. Linker DNA is seen as the string in the "beads and string model", which is made by using an ionic solution on the chromatin. Linker DNA connects to histone H1 and histone H1 sits on the nucleosome core. Nucleosome is technically the consolidation of a nucleosome core and one adjacent linker DNA; however, the term nucleosome is used freely for solely the core. Linker DNA may be degraded by endonucleases.Molecular Biology of The Cell, Fifth Edition, Alberts et al., Garland Science, 2008 The linkers are short double stranded DNA segments which are formed of oligonucleotides. These contain target sites for the action of one or more restriction enzyme A restriction enzyme, restriction endonuclease, REase, ENase or'' restrictase '' is an enzyme that cleaves DNA into fragments at or near specific recognition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |