|
Christie D. Rowe
Christie D. Rowe (born 1978) is a Professor of Geology at McGill University. She holds a Canada Research Chair in Earthquake Geology and was awarded the 2017 Geological Association of Canada W. W. Hutchison Medal. Early life and education Rowe is from Strawberry, Tuolumne County, California, Strawberry, Tuolumne County, California, Tuolumne County, Northern California. Rowe eventually studied geology at Smith College, where she worked on metamorphic rocks including blueschists and eclogites. She was taught by John Brady and H. Robert (Bob) Burger. In 2007, Rowe received her Doctor_of_Philosophy, PhD from the University of California, Santa Cruz. Rowe's doctoral work with J. Casey Moore attempted to reconstruct the earthquake cycles in Kodiak Island. Rowe moved to South Africa in 2007 where she taught structural geology and plate tectonics at the University of Cape Town. Research and career In 2009 Rowe was appointed an National Science Foundation-MARGINS postdoctoral scholar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smith College
Smith College is a Private university, private Liberal arts colleges in the United States, liberal arts Women's colleges in the United States, women's college in Northampton, Massachusetts. It was chartered in 1871 by Sophia Smith (Smith College), Sophia Smith and opened in 1875. It is the largest member of the historic Seven Sisters (colleges), Seven Sisters colleges, a group of elite women's colleges in the Northeastern United States. Smith is also a member of the Five College Consortium, along with four other nearby institutions in the Pioneer Valley: Mount Holyoke College, Amherst College, Hampshire College, and the University of Massachusetts Amherst; students of each college are allowed to attend classes at any other member institution. On campus are Smith's Smith College Museum of Art, Museum of Art and The Botanic Garden of Smith College, Botanic Garden, the latter designed by Frederick Law Olmsted. Smith has 41 academic departments and programs and is structured around a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudotachylite
Pseudotachylyte (sometimes written as pseudotachylite) is an extremely fine-grained to glassy, dark, cohesive rock occurring as veinsTrouw, R.A.J., C.W. Passchier, and D.J. Wiersma (2010) ''Atlas of Mylonites- and related microstructures.'' Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Germany. 322 pp. that form through frictional melting and subsequent quenching during earthquakes, large-scale landslides, and impacts events. Chemical composition of pseudotachylyte generally reflects the local bulk chemistry, though may skew to slightly more mafic compositions due to the preferential incorporation of hydrous and ferro-magnesian minerals (mica and amphibole, respectively) into the melt phase. Pseudotachylyte was first documented by Shand in the Vredefort Impact Structure and was named due to its close resemblance to tachylyte, a basaltic glass. Though pseudotachylyte is reported to have a glassy appearance, they are extremely susceptible to alteration and are thus rarely found to be entirely composed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franciscan Complex
The Franciscan Complex or Franciscan Assemblage is a geologic term for a late Mesozoic terrane of heterogeneous rocks found throughout the California Coast Ranges, and particularly on the San Francisco Peninsula. It was named by geologist Andrew Lawson, who also named the San Andreas fault that defines the western extent of the assemblage. The Franciscan Complex is dominated by greywacke sandstones, shales and conglomerates which have experienced low-grade metamorphism. Other important lithologies include chert, basalt, limestone, serpentinite, and high-pressure, low-temperature metabasites (blueschists and eclogites) and meta-limestones. Fossils like radiolaria are found in chert beds of the Franciscan Complex. These fossils have been used to provide age constraints on the different terranes that constitute the Franciscan. The mining opportunities within the Franciscan are restricted to deposits of cinnabar and limestone. The outcrops of the formation have a very large range ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
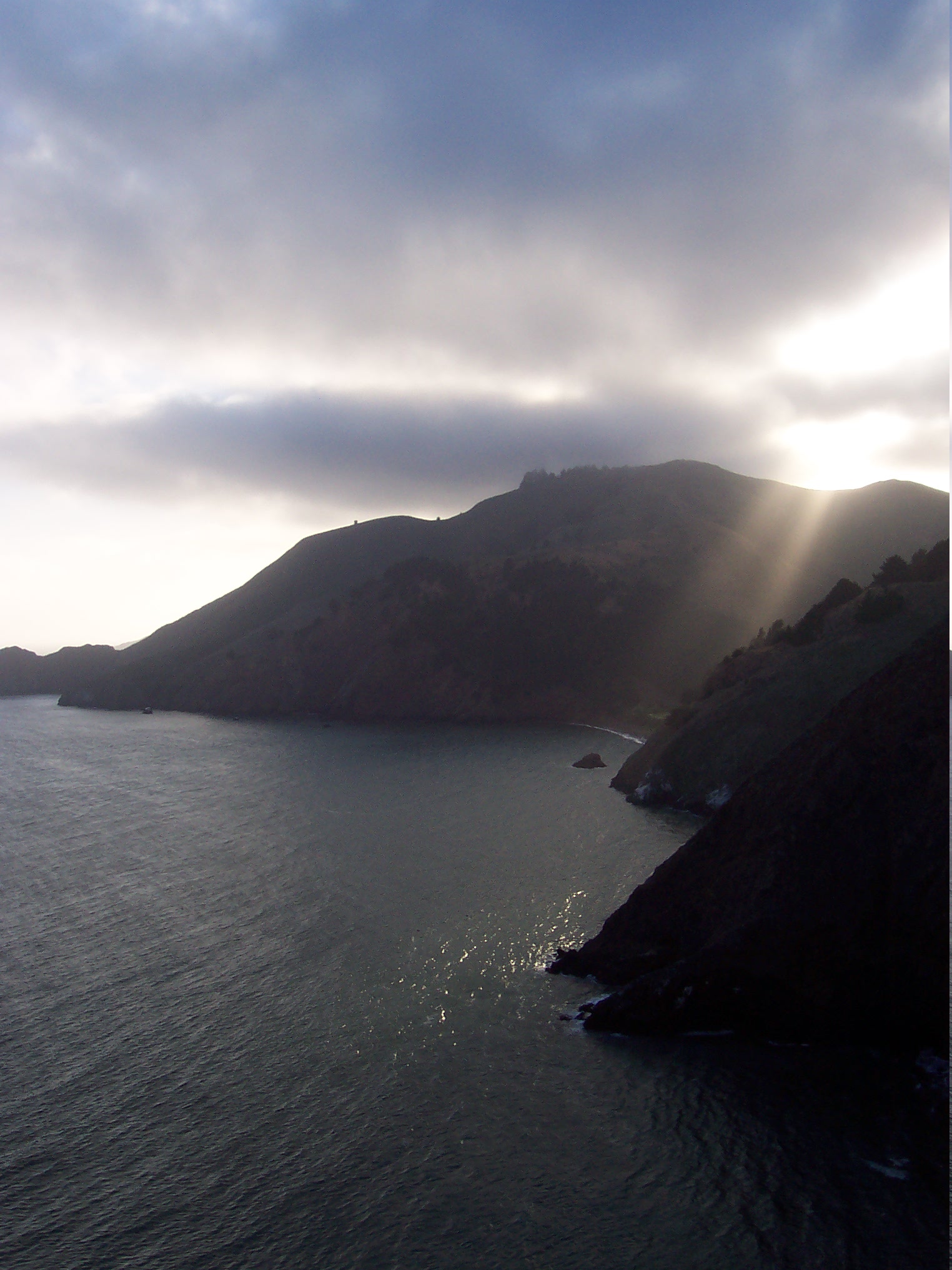
Marin Headlands
The Marin Headlands is a hilly peninsula at the southernmost end of Marin County, California, United States, located just north of San Francisco across the Golden Gate Bridge, which connects the two counties and peninsulas. The entire area is part of the Golden Gate National Recreation Area. The Headlands are famous for their views of the Bay Area, especially of the Golden Gate Bridge. Climate The Headlands sometimes create their own clouds when moist, warm Pacific Ocean breezes are pushed into higher, colder air, causing condensation, fog, fog drip and perhaps rain. The hills also get more precipitation than at sea level, for the same reason. However, despite being relatively wet, strong gusty Pacific winds prevent dense forests from forming. The many gaps, ridges, and valleys in the hills increase the wind speed and periodically, during powerful winter storms, these winds can reach hurricane force. In summer, breezes can still be very gusty, when the oceanic air and fog cross ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern California Earthquake Center
The Southern California Earthquake Center (SCEC) is a collaboration of more than 1,000 scientists across 100 research institutions with a mission to: conduct research on earthquakes in Southern California and elsewhere by gathering data, conducting theoretical studies, and performing computer simulations; integrate information into a comprehensive, physics-based understanding of earthquake phenomena; and communicate that understanding to end-users and society at large as useful knowledge for reducing earthquake risk and improving community resilience.. SCEC headquarters are at the University of Southern California. SCEC partners with many other research and education/outreach organizations in many disciplines. Primary funding for SCEC activities is provided by the National Science Foundation and the United States Geological Survey. The current director of SCEC is Yehuda Ben-Zion. The Southern California Earthquake Center (SCEC) was founded as a Science & Technology Center on Febru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2011 Tōhoku Earthquake
Eleven or 11 may refer to: *11 (number), the natural number following 10 and preceding 12 * one of the years 11 BC, AD 11, 1911, 2011, or any year ending in 11 Literature * ''Eleven'' (novel), a 2006 novel by British author David Llewellyn *''Eleven'', a 1970 collection of short stories by Patricia Highsmith *''Eleven'', a 2004 children's novel in The Winnie Years by Lauren Myracle *''Eleven'', a 2008 children's novel by Patricia Reilly Giff *''Eleven'', a short story by Sandra Cisneros Music *Eleven (band), an American rock band * Eleven: A Music Company, an Australian record label *Up to eleven, an idiom from popular culture, coined in the movie ''This Is Spinal Tap'' Albums * ''11'' (The Smithereens album), 1989 * ''11'' (Ua album), 1996 * ''11'' (Bryan Adams album), 2008 * ''11'' (Sault album), 2022 * ''Eleven'' (Harry Connick, Jr. album), 1992 * ''Eleven'' (22-Pistepirkko album), 1998 * ''Eleven'' (Sugarcult album), 1999 * ''Eleven'' (B'z album), 2000 * ''Eleven'' (Reamonn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
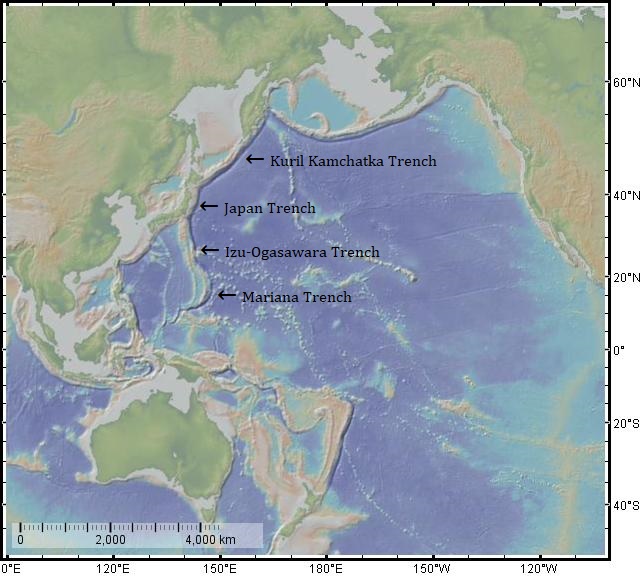
Japan Trench
The Japan Trench is an oceanic trench part of the Pacific Ring of Fire off northeast Japan. It extends from the Kuril Islands to the northern end of the Izu Islands, and is at its deepest. It links the Kuril–Kamchatka Trench to the north and the Izu–Ogasawara Trench to its south with a length of . This trench is created as the oceanic Pacific plate subducts beneath the continental Okhotsk Plate (a microplate formerly a part of the North American Plate). The subduction process causes bending of the down going plate, creating a deep trench. Continuing movement on the subduction zone associated with the Japan Trench is one of the main causes of tsunamis and earthquakes in northern Japan, including the megathrust Tōhoku earthquake and resulting tsunami that occurred on 11 March 2011. The rate of subduction associated with the Japan Trench has been recorded at about /yr. Tectonic history During the late Neogene period (23.03-2.58 million years ago), the Japan Trench underwent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
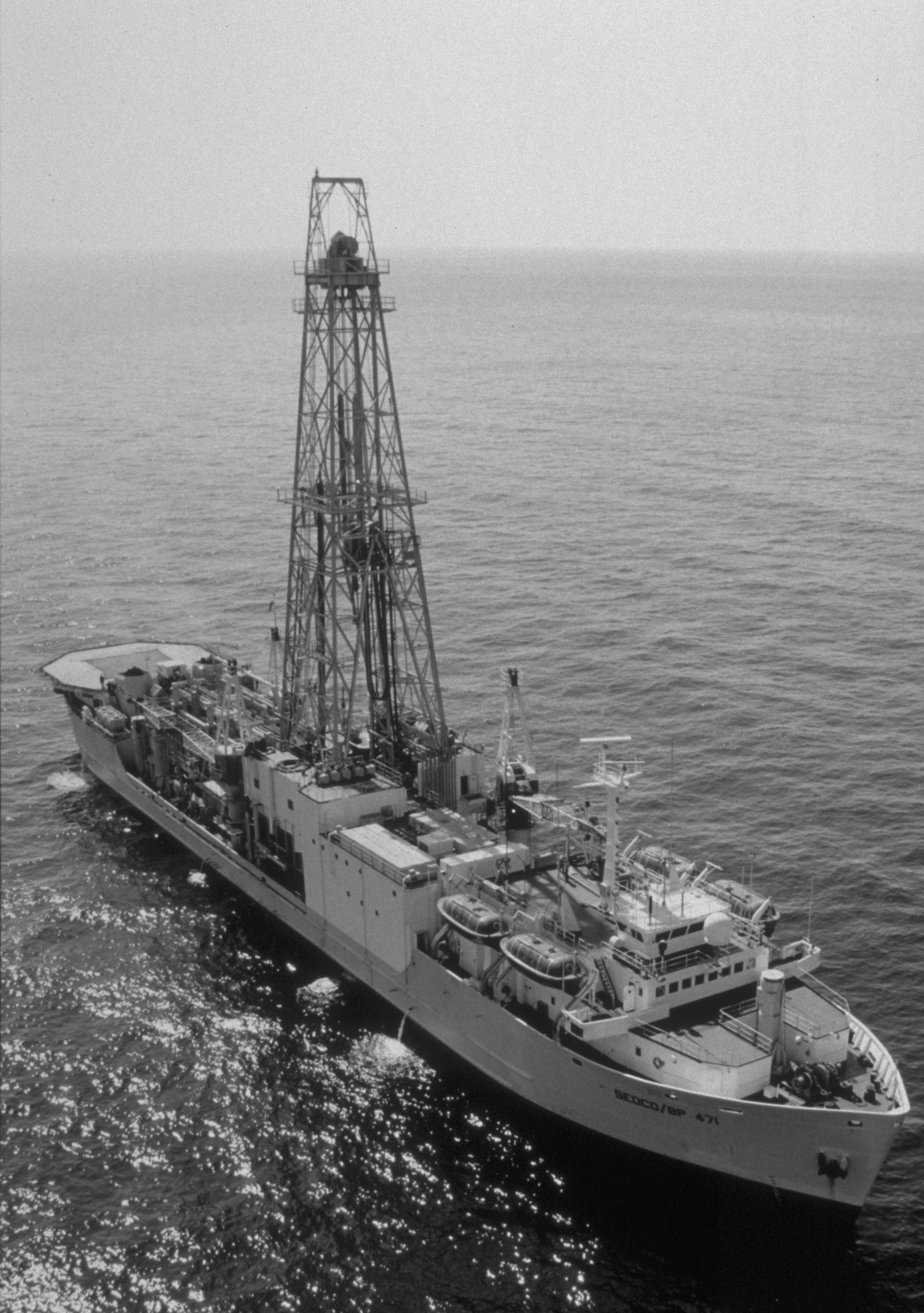
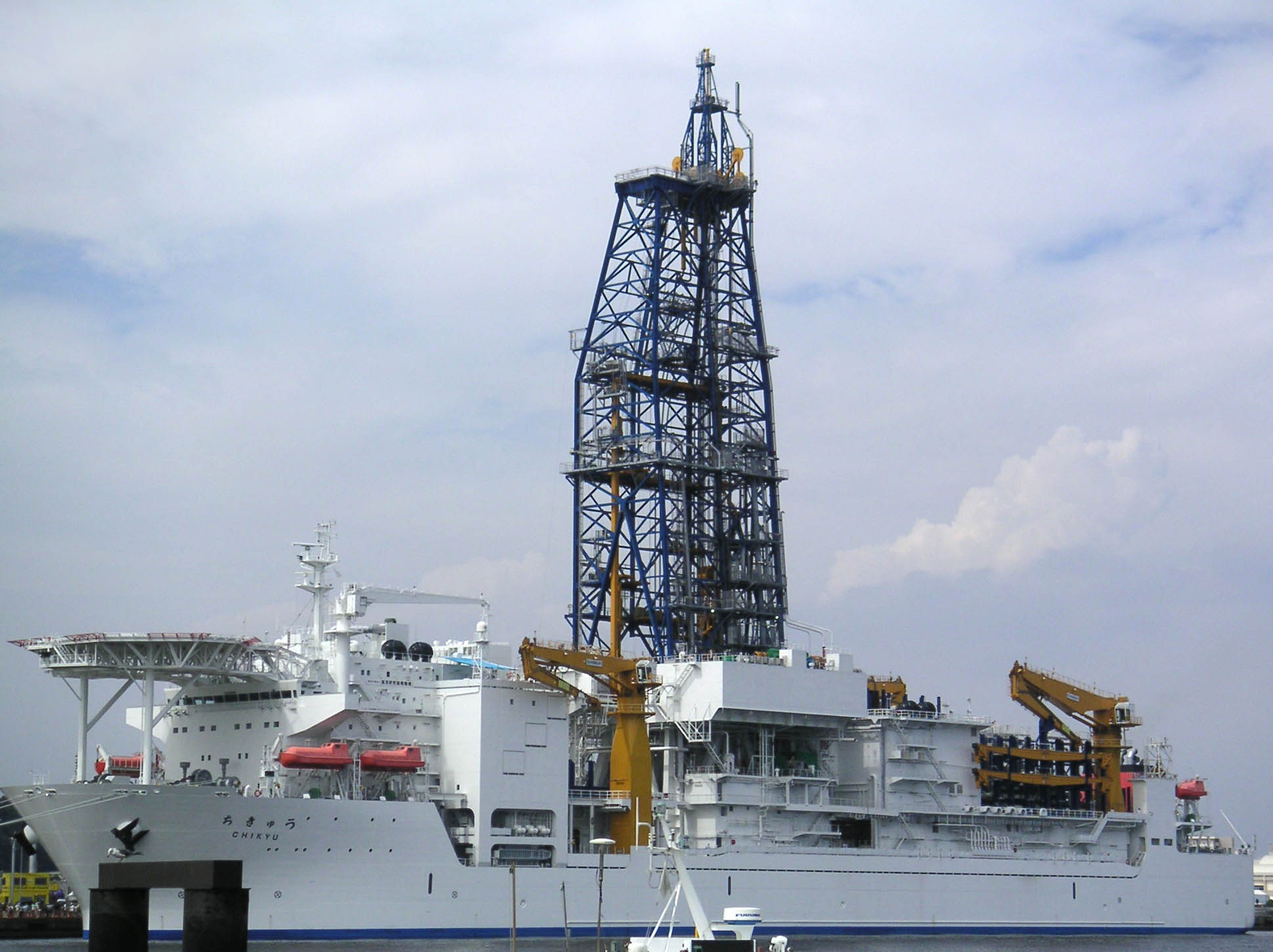
Chikyū
is a Japanese scientific drilling ship built for the Integrated Ocean Drilling Program (IODP). The vessel is designed to ultimately drill beneath the seabed, where the Earth's crust is much thinner, and into the Earth's mantle, deeper than any other hole drilled in the ocean thus far. While the planned depth of the hole is significantly less than the Russian Kola Superdeep Borehole (which reached depth on land), the scientific results are expected to be much more interesting since the regions targeted by ''Chikyū'' include some of the most seismically-active regions of the world. Other deep holes have been drilled by the drill ship JOIDES Resolution during the Deep Sea Drilling Project and the Ocean Drilling Program. Operation The Japanese part of the IODP program is called , Japanese for "Earth Discovery". ''Chikyū'' is operated by the Centre for Deep Earth Research (CDEX), a subdivision of the Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology (JAMSTEC). JAMSTEC also ope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Ocean Drilling Program
The Integrated Ocean Drilling Program (IODP) was an international marine research program. The program used heavy drilling equipment mounted aboard ships to monitor and sample sub-seafloor environments. With this research, the IODP documented environmental change, Earth processes and effects, the biosphere, solid earth cycles, and geodynamics. The program began a new 10-year phase with the International Ocean Discovery Program, from the end of 2013. Navigating the route to discovery Scientific ocean drilling represented the longest running and most successful international collaboration among the Earth sciences. Scientific ocean drilling began in 1961 with the first sample of oceanic crust recovered aboard the ''CUSS 1'', a modified U.S. Navy barge. American author John Steinbeck, also an amateur oceanographer, documented Project Mohole for LIFE Magazine. Legacy programs The Deep Sea Drilling Project (DSDP), established in June 1966, operated the ''Glomar Challenger'' i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2011 Tōhoku Earthquake And Tsunami
The occurred at 14:46 JST (05:46 UTC) on 11 March. The magnitude 9.0–9.1 (M) undersea megathrust earthquake had an epicenter in the Pacific Ocean, east of the Oshika Peninsula of the Tōhoku region, and lasted approximately six minutes, causing a tsunami. It is sometimes known in Japan as the , among other names. The disaster is often referred to in both Japanese and English as simply 3.11 (read in Japanese). It was the most powerful earthquake ever recorded in Japan, and the fourth most powerful earthquake in the world since modern record-keeping began in 1900. The earthquake triggered powerful tsunami waves that may have reached heights of up to in Miyako in Tōhoku's Iwate Prefecture,Yomiuri Shimbun evening edition 2-11-04-15 page 15, nearby Aneyoshi fishery port (姉吉漁港)(Google map E39 31 57.8, N 142 3 7.6) 2011-04-15大震災の津波、宮古で38.9 m…明治三陸上回るby okayasu Akio (岡安 章夫) and which, in the Sendai area, traveled at a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mineralogy
Mineralogy is a subject of geology specializing in the scientific study of the chemistry, crystal structure, and physical (including optical) properties of minerals and mineralized artifacts. Specific studies within mineralogy include the processes of mineral origin and formation, classification of minerals, their geographical distribution, as well as their utilization. History Early writing on mineralogy, especially on gemstones, comes from ancient Babylonia, the ancient Greco-Roman world, ancient and medieval China, and Sanskrit texts from ancient India and the ancient Islamic world. Books on the subject included the ''Naturalis Historia'' of Pliny the Elder, which not only described many different minerals but also explained many of their properties, and Kitab al Jawahir (Book of Precious Stones) by Persian scientist Al-Biruni. The German Renaissance specialist Georgius Agricola wrote works such as '' De re metallica'' (''On Metals'', 1556) and ''De Natura Fossilium'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)