|
Christian Schesaeus
Christian Schesaus (1535 – July 30, 1585) was a Transylvanian Saxon humanist, poet, and a Lutheran pastor. He was born in Mediaș, studied first in Brașov, and then from 1556 to 1558 at the University of Wittenberg. ''Ruinae Pannonnicae'', his best known work, was written in Latin and composed in dactylic hexameter on the model of Virgil's '' Aeneid''. The subject of the poem deals with the events in Transylvania, Hungary, Wallachia and Moldavia over the 31-year period of 1540 to 1571. Schesaus insists on the Roman origin and heritage of Romanians, backed by evidence he presents (together with proof of Dacian contributions). The work was first printed in Wittenberg (1571), and it ensured that Schesaus was awarded the title of Poet Laureate by Prince Stephen Bathory. Around 1580, Christian Schesaus was living in Biertan; he died of the plague Plague or The Plague may refer to: Agriculture, fauna, and medicine *Plague (disease), a disease caused b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transylvanian Saxon
The Transylvanian Saxons (german: Siebenbürger Sachsen; Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjer Såksen''; ro, Sași ardeleni, sași transilvăneni/transilvani; hu, Erdélyi szászok) are a people of German ethnicity who settled in Transylvania (german: Siebenbürgen) in waves starting from the mid- 12th century until the mid 19th century. The legal foundation of the settlement was laid down in the Diploma Andreanum issued by King Andrew II of Hungary that is known for providing the first territorial autonomy hitherto in the history. The Transylvanian "Saxons" originally came from Flanders, Hainaut, Brabant, Liège, Zeeland, Moselle, Lorraine, and Luxembourg, then situated in the north-western territories of the Holy Roman Empire around the 1140s. After 1918 and the dissolution of Austria-Hungary, in the wake of the Treaty of Trianon, Transylvania united with the Kingdom of Romania. Consequently, the Transylvanian Saxons, together with other ethnic German sub-groups in newl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
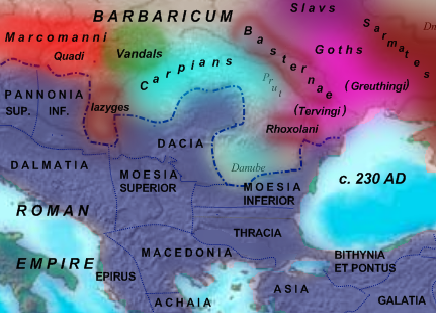
Origin Of The Romanians
Several theories address the issue of the origin of the Romanians. The Romanian language descends from the Vulgar Latin dialects spoken in the Roman provinces north of the "Jireček Line" (a proposed notional line separating the predominantly Latin-speaking territories from the Greek-speaking lands in Southeastern Europe) in Late Antiquity. The theory of Daco-Roman continuity argues that the Romanians are mainly descended from the Daco-Romans, a people developing through the cohabitation of the native Dacians and the Roman colonists in the province of Dacia Traiana (primarily in present-day Romania) north of the river Danube. The competing immigrationist theory states that the Romanians' ethnogenesis commenced in the provinces south of the river with Romanized local populations (known as Vlachs in the Middle Ages) spreading through mountain refuges, both south to Greece and north through the Carpathian Mountains. Other theories state that the Romanized local populations were p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infectious Disease Deaths In Romania
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable disease, is an illness resulting from an infection. Infections can be caused by a wide range of pathogens, most prominently bacteria and viruses. Hosts can fight infections using their immune system. Mammalian hosts react to infections with an innate response, often involving inflammation, followed by an adaptive response. Specific medications used to treat infections include antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, antiprotozoals, and antihelminthics. Infectious diseases resulted in 9.2 million deaths in 2013 (about 17% of all deaths). The branch of medicine that focuses on infections is referred to as infectious disease. Types Infections are caused by infectious agents (pathogens) including: * Bacteria (e.g. ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'', ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1585 Deaths
Events January–June * January – The Netherlands adopts the Gregorian calendar. * February – The Spanish seize Brussels. * April 24 – Pope Sixtus V succeeds Pope Gregory XIII, as the 227th pope. * May 19 – Spain seizes English ships in Spanish ports, precipitating the Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604). * June 11 – The magnitude 9.3 1585 Aleutian Islands earthquake unleashes a tsunami in the Pacific Ocean, killing many people in Hawaii and reportedly striking Japan. July–December * July 7 – The Treaty of Nemours forces King Henry III of France to capitulate to the demands of the Catholic League, triggering the Eighth War of Religion (also known as the War of the Three Henrys) in France. * August 8 – English explorer John Davis enters Cumberland Sound in Baffin Island, in his quest for the Northwest Passage. * August 14 – Queen Elizabeth I of England agrees to establish a protectorate over the Netherland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1535 Births
__NOTOC__ Year 1535 ( MDXXXV) was a common year starting on Friday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. Events January–June * January 18 – Lima, Peru, is founded by Francisco Pizarro, as '' Ciudad de los Reyes''. * February 27 – George Joye publishes his ''Apologye'' in Antwerp, to clear his name from the accusations of William Tyndale. * March – English forces under William Skeffington storm Maynooth Castle in Ireland, the stronghold of Thomas FitzGerald, 10th Earl of Kildare. * March 10 – Fray Tomás de Berlanga discovers the Galápagos Islands, when blown off course ''en route'' to Peru. * May 4 – The first of the English Carthusian Martyrs is executed. * May 10 – Amsterdam: A small troop of Anabaptists, led by the minister Jacob van Geel, attacks the city hall, in an attempted coup to seize the city. In the counter-attack by the city's militia, the burgemeester, Pieter Colijns, is killed by the rebels. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
16th-century Deaths From Plague (disease)
The 16th century begins with the Julian year 1501 ( MDI) and ends with either the Julian or the Gregorian year 1600 ( MDC) (depending on the reckoning used; the Gregorian calendar introduced a lapse of 10 days in October 1582). The 16th century is regarded by historians as the century which saw the rise of Western civilization and the Islamic gunpowder empires. The Renaissance in Italy and Europe saw the emergence of important artists, authors and scientists, and led to the foundation of important subjects which include accounting and political science. Copernicus proposed the heliocentric universe, which was met with strong resistance, and Tycho Brahe refuted the theory of celestial spheres through observational measurement of the 1572 appearance of a Milky Way supernova. These events directly challenged the long-held notion of an immutable universe supported by Ptolemy and Aristotle, and led to major revolutions in astronomy and science. Galileo Galilei became a champion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transylvanian Saxon People
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Apuseni Mountains. Broader definitions of Transylvania also include the western and northwestern Romanian regions of Crișana and Maramureș, and occasionally Banat. Transylvania is known for the scenery of its Carpathian landscape and its rich history. It also contains Romania's second-largest city, Cluj-Napoca, and other iconic cities and towns such as Brașov, Sibiu, Târgu Mureș, Alba Iulia and Sighișoara. It is also the home of some of Romania's UNESCO World Heritage Sites such as the Villages with fortified churches, the Historic Centre of Sighișoara, the Dacian Fortresses of the Orăștie Mountains and the Roșia Montană Mining Cultural Landscape. It was under the rule of the Agathyrsi, part of the Dacian Kingdom (168 BC–10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
16th-century German Lutheran Clergy
The 16th century begins with the Julian year 1501 ( MDI) and ends with either the Julian or the Gregorian year 1600 ( MDC) (depending on the reckoning used; the Gregorian calendar introduced a lapse of 10 days in October 1582). The 16th century is regarded by historians as the century which saw the rise of Western civilization and the Islamic gunpowder empires. The Renaissance in Italy and Europe saw the emergence of important artists, authors and scientists, and led to the foundation of important subjects which include accounting and political science. Copernicus proposed the heliocentric universe, which was met with strong resistance, and Tycho Brahe refuted the theory of celestial spheres through observational measurement of the 1572 appearance of a Milky Way supernova. These events directly challenged the long-held notion of an immutable universe supported by Ptolemy and Aristotle, and led to major revolutions in astronomy and science. Galileo Galilei became a champion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bubonic Plague
Bubonic plague is one of three types of plague caused by the plague bacterium (''Yersinia pestis''). One to seven days after exposure to the bacteria, flu-like symptoms develop. These symptoms include fever, headaches, and vomiting, as well as swollen and painful lymph nodes occurring in the area closest to where the bacteria entered the skin. Acral necrosis, the dark discoloration of skin, is another symptom. Occasionally, swollen lymph nodes, known as "buboes," may break open. The three types of plague are the result of the route of infection: bubonic plague, septicemic plague, and pneumonic plague. Bubonic plague is mainly spread by infected fleas from small animals. It may also result from exposure to the body fluids from a dead plague-infected animal. Mammals such as rabbits, hares, and some cat species are susceptible to bubonic plague, and typically die upon contraction. In the bubonic form of plague, the bacteria enter through the skin through a flea bite and travel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biertan
Biertan (german: Birthälm; hu, Berethalom) is a Communes of Romania, commune in Transylvania, Romania, in the north of the Sibiu County, 80 km north of Sibiu and 29 km east of Mediaș. Biertan is one of the most important Saxon villages with fortified churches in Transylvania, having been on the list of UNESCO World Heritage Sites since 1993. The Biertan fortified church was the seat of the Lutheran Evangelical Bishop in Transylvania between 1572 and 1867. The commune is composed of three villages: Biertan, Copșa Mare (''Gross-Kopisch''; ''Nagykapus''), and Richiș (''Reichesdorf''; ''Riomfalva''), each of which has a fortified church. History The first documentary testimony about the village dates from 1283 in a document about the taxes paid by the inhabitants of 7 villages and so it is believed to have been founded sometime between 1224 and 1283 by Transylvanian Saxons. The village settlement quickly developed into an important market town and by 1510 Biertan s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen Bathory, King Of Poland
Stephen or Steven is a common English first name. It is particularly significant to Christians, as it belonged to Saint Stephen ( grc-gre, Στέφανος ), an early disciple and deacon who, according to the Book of Acts, was stoned to death; he is widely regarded as the first martyr (or "protomartyr") of the Christian Church. In English, Stephen is most commonly pronounced as ' (). The name, in both the forms Stephen and Steven, is often shortened to Steve or Stevie. The spelling as Stephen can also be pronounced which is from the Greek original version, Stephanos. In English, the female version of the name is Stephanie. Many surnames are derived from the first name, including Stephens, Stevens, Stephenson, and Stevenson, all of which mean "Stephen's (son)". In modern times the name has sometimes been given with intentionally non-standard spelling, such as Stevan or Stevon. A common variant of the name used in English is Stephan ; related names that have found some c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Transylvanian Rulers
List of rulers of Transylvania, from the 10th century, until 1867. Overview Before 1556, the administration of the eastern parts of the Hungarian Kingdom, referred as ''Partes Transsylvana'' (Latin for "parts beyond the forests"), was in the hands of a voivode ( hu, vajda) appointed by the king. The word voivod or voievod first appeared in historical documents in 1193. Prior to that, the term ispán was used for the chief official of the County of Fehér. The whole territory of Transylvania came under the jurisdiction of the voievod after 1263, when the functions of Count of Szolnok (Doboka) and Count of Fehér were terminated. The Voivode of Transylvania (''woyuoda Transsiluanus'') was one of the barons of the kingdom. The voivode was, in effect, a territorial governor or viceroy appointed by the Hungarian crown. He was also the chief magistrate and military commander of Transylvania's seven counties. His jurisdiction, however, was limited, because the Transylvanian Saxons an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |