|
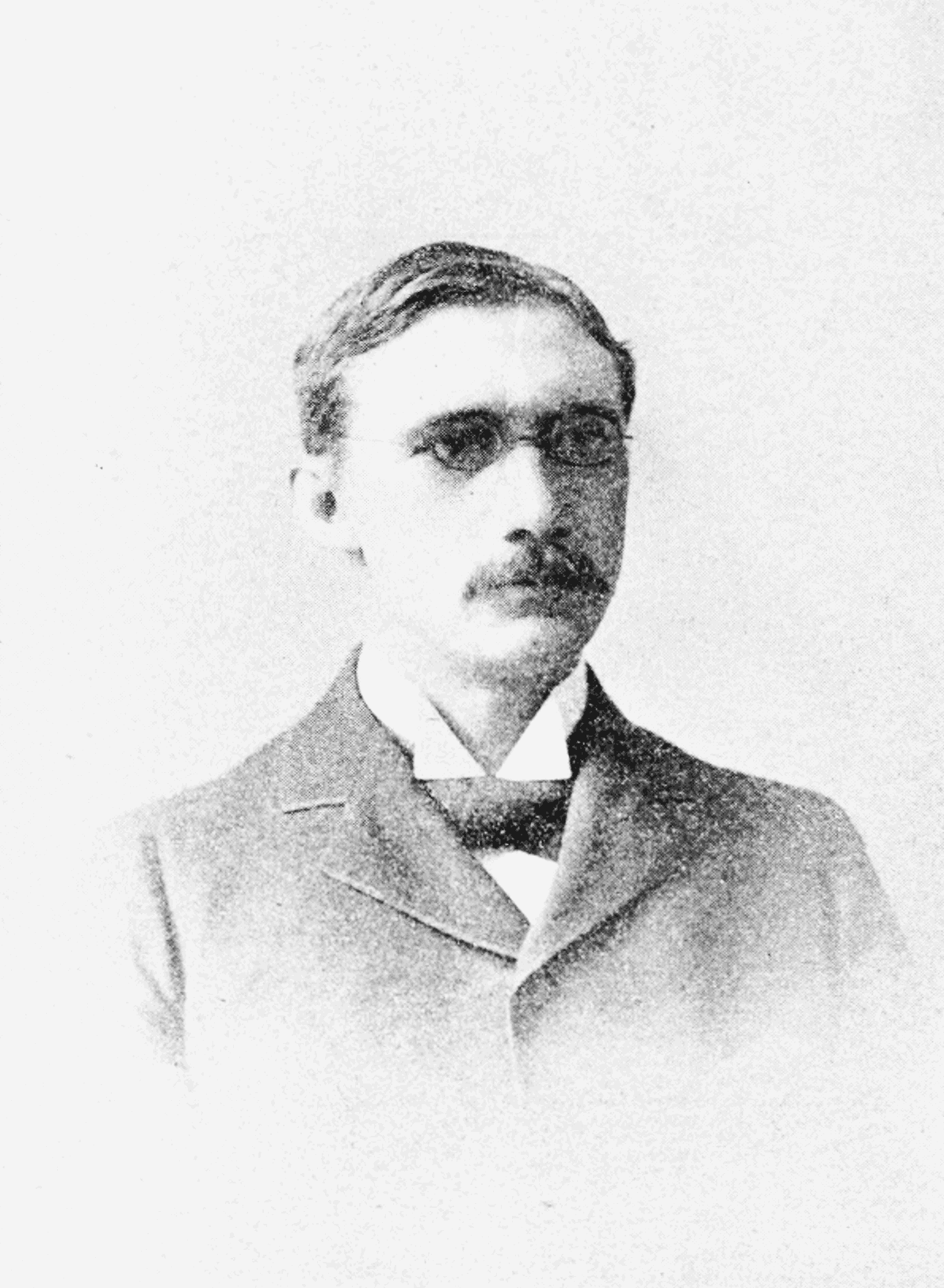
Christian Christiansen (physicist)
Christian Christiansen (9 October 1843 in Lønborg, Denmark – 28 November 1917 Frederiksberg) was a Danish physicist. Christiansen first taught at the local polytechnical school. In 1886, he was appointed to a chair for physics at the University of Copenhagen. He mainly studied radiant heat and optical dispersion, discovering the Christiansen effect (Christiansen filter). Around 1917, he discovered the anomalous dispersion of numerous dyes, including aniline red (fuchsine), by recording absorption spectra. In 1884, he confirmed the Stefan–Boltzmann law. Christiansen was elected a member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences in 1902. He was doctoral advisor to Niels Bohr. In 1912, he retired and Martin Knudsen Martin Hans Christian Knudsen (February 15, 1871 in Hasmark on Funen – May 27, 1949 in Copenhagen) was a Danish physicist who taught and conducted research at the Technical University of Denmark. He is primarily known for his study of molecu ... became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christiansen Effect
The Christiansen effect is named after the Danish physicist Christian Christiansen and describes the reduced scattering of multi-phase microstructures at wavelengths where their refractive indices match. A Christiansen filter is a narrow bandpass or monochromatic optical filter which consists of an optical cell which is stuffed with a crushed substance (e.g. glass) and a (mostly organic) liquid. The liquid is chosen according to the substance, so that the dispersion curves coincide at one wavelength. For this wavelength the filled optical cell behaves like a plane-parallel, homogeneous disk and allows transmission. All other wavelength ranges of the spectrum are reflected, scattered as well as refracted at the many interfaces between substance and liquid. A change of the transmission behavior of this dispersion filter can be achieved by variation of the liquid, the temperature or variation of the pressure. The fundamental consequence is the change of the refractive index of the liq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Swedish Academy Of Sciences
The Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences ( sv, Kungliga Vetenskapsakademien) is one of the Swedish Royal Academies, royal academies of Sweden. Founded on 2 June 1739, it is an independent, non-governmental scientific organization that takes special responsibility for promoting natural sciences and mathematics and strengthening their influence in society, whilst endeavouring to promote the exchange of ideas between various disciplines. The goals of the academy are: * to be a forum where researchers meet across subject boundaries, * to offer a unique environment for research, * to provide support to younger researchers, * to reward outstanding research efforts, * to communicate internationally among scientists, * to advance the case for science within society and to influence research policy priorities * to stimulate interest in mathematics and science in school, and * to disseminate and popularize scientific information in various forms. Every year, the academy awards the Nobel Priz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1917 Deaths
Events Below, the events of World War I have the "WWI" prefix. January * January 9 – WWI – Battle of Rafa: The last substantial Ottoman Army garrison on the Sinai Peninsula is captured by the Egyptian Expeditionary Force's Desert Column. * January 10 – Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition: Seven survivors of the Ross Sea party were rescued after being stranded for several months. * January 11 – Unknown saboteurs set off the Kingsland Explosion at Kingsland (modern-day Lyndhurst, New Jersey), one of the events leading to United States involvement in WWI. * January 16 – The Danish West Indies is sold to the United States for $25 million. * January 22 – WWI: United States President Woodrow Wilson calls for "peace without victory" in Germany. * January 25 ** WWI: British armed merchantman is sunk by mines off Lough Swilly (Ireland), with the loss of 354 of the 475 aboard. ** An anti-prostitution drive in San Francisco occurs, and police ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1843 Births
Events January–March * January ** Serial publication of Charles Dickens's novel ''Martin Chuzzlewit'' begins in London; in the July chapters, he lands his hero in the United States. ** Edgar Allan Poe's short story "The Tell-Tale Heart" is published in a Boston magazine. ** The Quaker magazine '' The Friend'' is first published in London. * January 3 – The ''Illustrated Treatise on the Maritime Kingdoms'' (海國圖志, ''Hǎiguó Túzhì'') compiled by Wei Yuan and others, the first significant Chinese work on the West, is published in China. * January 6 – Antarctic explorer James Clark Ross discovers Snow Hill Island. * January 20 – Honório Hermeto Carneiro Leão, Marquis of Paraná, becomes ''de facto'' first prime minister of the Empire of Brazil. * February – Shaikh Ali bin Khalifa Al-Khalifa captures the fort and town of Riffa after the rival branch of the family fails to gain control of the Riffa Fort and flees to Manama. Shaikh Mohamed bin Ahmed is kille ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Physicists
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Because light is an electromagnetic wave, other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties. Most optical phenomena can be accounted for by using the classical electromagnetic description of light. Complete electromagnetic descriptions of light are, however, often difficult to apply in practice. Practical optics is usually done using simplified models. The most common of these, geometric optics, treats light as a collection of rays that travel in straight lines and bend when they pass through or reflect from surfaces. Physical optics is a more comprehensive model of light, which includes wave effects such as diffraction and interference that cannot be acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danish Physicists
Danish may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to the country of Denmark People * A national or citizen of Denmark, also called a "Dane," see Demographics of Denmark * Culture of Denmark * Danish people or Danes, people with a Danish ancestral or ethnic identity * A member of the Danes, a Germanic tribe * Danish (name), a male given name and surname Language * Danish language, a North Germanic language used mostly in Denmark and Northern Germany * Danish tongue or Old Norse, the parent language of all North Germanic languages Food * Danish cuisine * Danish pastry, often simply called a "Danish" See also * Dane (other) * * Gdańsk * List of Danes * Languages of Denmark The Kingdom of Denmark has only one official language, Danish, the national language of the Danish people, but there are several minority languages spoken, namely Faroese, German, and Greenlandic. A large majority (about 86%) of Danes also s ... {{disambiguation Language and nation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Francis Magie
William Francis Magie (1858–1943) was an American physicist, a founder of the American Physical Society (president from 1910–12) and the first professor of physics at Princeton University, where he had graduated (class valedictorian, 1879) and where he served for two decades as dean of the faculty. His papers on the contact angle of liquids and solids and on the specific heat of solutions were notable, as was his text ''Principles of Physics''. Personal views Magie served as the president of the Men's Anti-Suffrage League of New Jersey. In this capacity, he argued that women's suffrage would ruin the family structure, destroy gender roles, and "undermine civilization." Selected works *Magie, William Francis, editor, translator. (1899). : Memoirs by Carnot, Clausius and Thomson Thomson may refer to: Names * Thomson (surname), a list of people with this name and a description of its origin * Thomson baronets, four baronetcies created for persons with the surname Thomson ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martin Knudsen
Martin Hans Christian Knudsen (February 15, 1871 in Hasmark on Funen – May 27, 1949 in Copenhagen) was a Danish physicist who taught and conducted research at the Technical University of Denmark. He is primarily known for his study of molecular gas flow and the development of the Knudsen cell, which is a primary component of molecular beam epitaxy systems. Knudsen received the University's gold medal in 1895 and earned his master's degree in physics the following year. He became lecturer in physics at the University in 1901 and professor in 1912, when Christian Christiansen (1843–1917) retired. He held this post until his own retirement in 1941. Knudsen was renowned for his work on kinetic-molecular theory and low-pressure phenomena in gases. His name is associated with the Knudsen flow, Knudsen diffusion, Knudsen number, Knudsen layer and Knudsen gases. Also there is the Knudsen equation; two instruments, the Knudsen absolute manometer and Knudsen gauge; and one g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niels Bohr
Niels Henrik David Bohr (; 7 October 1885 – 18 November 1962) was a Danish physicist who made foundational contributions to understanding atomic structure and quantum theory, for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1922. Bohr was also a philosopher and a promoter of scientific research. Bohr developed the Bohr model of the atom, in which he proposed that energy levels of electrons are discrete and that the electrons revolve in stable orbits around the atomic nucleus but can jump from one energy level (or orbit) to another. Although the Bohr model has been supplanted by other models, its underlying principles remain valid. He conceived the principle of complementarity: that items could be separately analysed in terms of contradictory properties, like behaving as a wave or a stream of particles. The notion of complementarity dominated Bohr's thinking in both science and philosophy. Bohr founded the Institute of Theoretical Physics at the University of Cope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stefan–Boltzmann Law
The Stefan–Boltzmann law describes the power radiated from a black body in terms of its temperature. Specifically, the Stefan–Boltzmann law states that the total energy radiated per unit surface area of a black body across all wavelengths per unit time j^ (also known as the black-body ''radiant emittance'') is directly proportional to the fourth power of the black body's thermodynamic temperature ''T'': : j^ = \sigma T^. The constant of proportionality ''σ'', called the Stefan–Boltzmann constant, is derived from other known physical constants. Since 2019, the value of the constant is : \sigma=\frac = 5.670374419\times 10^\, \mathrm, where ''k'' is the Boltzmann constant, ''h'' is Planck's constant, and ''c'' is the speed of light in a vacuum. The radiance from a specified angle of view (watts per square metre per steradian) is given by : L = \frac\pi = \frac\sigma\pi T^. A body that does not absorb all incident radiation (sometimes known as a grey body) emits ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absorption Spectrum
Absorption spectroscopy refers to spectroscopic techniques that measure the absorption of radiation, as a function of frequency or wavelength, due to its interaction with a sample. The sample absorbs energy, i.e., photons, from the radiating field. The intensity of the absorption varies as a function of frequency, and this variation is the absorption spectrum. Absorption spectroscopy is performed across the electromagnetic spectrum. Absorption spectroscopy is employed as an analytical chemistry tool to determine the presence of a particular substance in a sample and, in many cases, to quantify the amount of the substance present. Infrared and ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy are particularly common in analytical applications. Absorption spectroscopy is also employed in studies of molecular and atomic physics, astronomical spectroscopy and remote sensing. There is a wide range of experimental approaches for measuring absorption spectra. The most common arrangement is to dire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |