|
Christiaan Freeling
Christian Freeling (born 1 February 1947, in Enschede, Netherlands) is a Dutch game designer and inventor of abstract strategy games, notably Dameo, Grand Chess, Havannah, and Hexdame. Freeling's designs cover a range of game types. Several of his games are endeavors to improve on established games that he concluded are flawed or limited in some way, while some introduce familiar game mechanics into uncommon settings. He also regularly translates rules for orthogonal board games to the hexagonal grid, resulting in new versions with altered properties – usually enhanced strategy and tactics options, and fewer draws. "Christian's games often embody a desire to get to the heart of the concepts used in abstract games. This is most clearly displayed by his minimalist chess variant, Chad, and his version of column checkers, Emergo." Among all his games, Freeling considers Dameo, Emergo, Grand Chess, Storisende, Sygo, and Symple to be his most important, with Emergo as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enschede
Enschede (; known as in the local Twents dialect) is a municipality and city in the eastern Netherlands in the province of Overijssel and in the Twente region. The eastern parts of the urban area reaches the border of the German city of Gronau. The municipality of Enschede consisted of the city of Enschede until 1935, when the rural municipality of Lonneker, which surrounded the city, was annexed after the rapid industrial expansion of Enschede which began in the 1860s and involved the building of railways and the digging of the Twentekanaal. The proposal for consolidation began in 1872, per the Tubantia newspaper article on 22 June 1872 that referenced a committee of 5 to oversee a study. They were: J. Mosman (Johannes Theodorus Mosman), H. Fikkert, H. G. Blijdenstein J. Bz., C. C. Schleucker, and G. J. van Heek. In sports and culture, Enschede is known for being home to football club FC Twente, one-time Dutch champions, and the University of Twente. The municipality of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symple (game)
Symple is a two-player abstract strategy game created in 2010 by Christian Freeling and Benedikt Rosenau.Ploog, David.The Movement Protocol of Symple. ''Abstract Games... for the competitive thinker Issue 19'', 2020, pp. 8-13Archivedfrom original 27 August, 2021. Accessed 2 Sept. 2020. The goal of Symple is to end the game with the highest score, with score being determined via points for controlling territory on the board less a penalty for each separate group of stones. Like Go, Symple is played on a 19x19 grid of lines; unlike Go, there are no mechanics allowing capture of stones once placed. Symple is a drawless finite perfect information game. Rules Movement Each player has one of two color stones, one darker and one lighter, often black and white. The game set up starts with an empty board. Each turn a player must either: # Grow all of their groups of stones. # Put a stone on a vacant cell unconnected to any other friendly group. A group is defined as any one or mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capablanca Chess
Capablanca chess (or Capablanca's chess) is a chess variant invented in the 1920s by World Chess Champion José Raúl Capablanca. It incorporates two new pieces and is played on a 10×8 board. Capablanca believed that chess would be played out in a few decades (meaning games between grandmasters would always end in draws). This threat of "draw death" for chess was his main motivation for creating a more complex version of the game. * The archbishop combines powers of a bishop and a knight. * The chancellor combines powers of a rook and a knight. The new pieces allow new strategies and possibilities that change the game. For example, the archbishop by itself can checkmate a lone king in the corner (when placed diagonally with one square in between). Setup and rules Capablanca proposed two opening setups for Capablanca chess. His final revision placed the archbishop between the and ; the chancellor between the and . The king moves three squares when castling instead of mov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop (chess)
The bishop (♗, ♝) is a piece in the game of chess. It moves and captures along without jumping over intervening pieces. Each player begins the game with two bishops. One starts between the and the king, the other between the and the queen. The starting squares are c1 and f1 for White's bishops, and c8 and f8 for Black's bishops. Placement and movement The king's bishop is placed between the king and the king's knight, f1 for White and f8 for Black; the queen's bishop is placed between the queen and the queen's knight, c1 for White and c8 for Black. The bishop has no restrictions in distance for each move but is limited to diagonal movement. It cannot jump over other pieces. A bishop captures by occupying the square on which an enemy piece stands. As a consequence of its diagonal movement, each bishop always remains on one square color. Due to this, it is common to refer to a bishop as a light-squared or dark-squared bishop. Comparison – other pieces Versus rook A r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princess (chess)
The princess is a fairy chess piece that can move like a bishop or a knight. It cannot jump over other pieces when moving as a bishop but may do so when moving as a knight. The piece has acquired many names and is frequently called archbishop or cardinal; it may also simply be called the bishop+knight compound. Chess moves in this article use ''A'' as notation for the princess. Movement The princess can move as a bishop or a knight. History and nomenclature The princess is one of the most simply described fairy chess pieces and as such has a long history and has gone by many names. It was first used in Turkish Great Chess, a large medieval variant of chess, where it was called the ''vizir'' (not to be confused with the piece more commonly referred to as the wazir today, which is the (1,0) leaper). It was introduced in the West with Carrera's chess, a chess variant from 1617, where it was called a ''centaur'', and has been used in many chess variants since then. The n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knight (chess)
The knight (♘, ♞) is a piece in the game of chess, represented by a horse's head and neck. It moves two squares vertically and one square horizontally, or two squares horizontally and one square vertically, jumping over other pieces. Each player starts the game with two knights on the b- and g-, each located between a rook and a bishop. Movement Compared to other chess pieces, the knight's movement is unique: it moves two squares vertically and one square horizontally, or two squares horizontally and one square vertically (with both forming the shape of a capital L). When moving, the knight can jump over pieces to reach its destination. Knights capture in the same way, replacing the enemy piece on the square and removing it from the board. A knight can have up to eight available moves at once. Knights and pawns are the only pieces that can be moved in the chess starting position. Value Knights and bishops, also known as , have a value of about three pawns. Bishops utili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rook (chess)
The rook (; ♖, ♜) is a piece in the game of chess. It may move any number of squares horizontally or vertically without jumping, and it may an enemy piece on its path; additionally, it may participate in castling. Each player starts the game with two rooks, one in each corner on their own side of the board. Formerly, the rook (from Persian رخ ''rokh''/''rukh'', meaning "chariot") was alternatively called the tower, marquess, rector, and comes (count or earl). The term "castle" is considered to be informal, incorrect, or old-fashioned. Placement and movement The white rooks start on squares a1 and h1, while the black rooks start on a8 and h8. The rook moves horizontally or vertically, through any number of unoccupied squares (see diagram). The rook cannot jump over pieces. The rook may capture an enemy piece by moving to the square on which the enemy piece stands, removing it from play. The rook also participates with the king in a special move called castling, wherein i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empress (chess)
The empress is a fairy chess piece that can move like a rook or a knight. It cannot jump over other pieces when moving as a rook but may do so when moving as a knight. The piece has acquired many names and is frequently called chancellor or marshal. Chess moves in this article use ''C'' as notation for the empress. Movement The empress can move as a rook or a knight. History and nomenclature The empress is one of the most simply described fairy chess pieces and as such has a long history and has gone by many names. It was first used in Turkish Great Chess, a large medieval variant of chess, where it was called the ''war machine'' (dabbabah; not to be confused with the piece more commonly referred to as the dabbaba today, which is the (2,0) leaper). It was introduced in the West with Carrera's chess from 1617, where it was called a ''champion'', and has been used in many chess variants since then. The name ''chancellor'' was introduced by Ben Foster in his large varian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairy Chess Piece
A fairy chess piece, variant chess piece, unorthodox chess piece, or heterodox chess piece is a chess piece not used in conventional chess but incorporated into certain chess variants and some chess problems. Compared to conventional pieces, fairy pieces vary mostly in the way they move, but they may also follow special rules for capturing, promotions, etc. Because of the distributed and uncoordinated nature of unorthodox chess development, the same piece can have different names, and different pieces can have the same name in various contexts. Most are symbolised as inverted or rotated icons of the standard pieces in diagrams, and the meanings of these "wildcards" must be defined in each context separately. Pieces invented for use in chess variants rather than problems sometimes instead have special icons designed for them, but with some exceptions (the princess, empress, and occasionally amazon), many of these are not used beyond the individual games for which they were invented ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
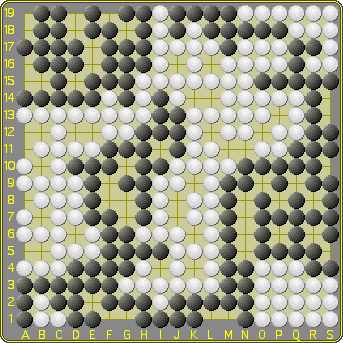
Grand Chess Init Config
Grand may refer to: People with the name * Grand (surname) * Grand L. Bush (born 1955), American actor * Grand Mixer DXT, American turntablist * Grand Puba (born 1966), American rapper Places * Grand, Oklahoma * Grand, Vosges, village and commune in France with Gallo-Roman amphitheatre * Grand Concourse (other), several places * Grand County (other), several places * Grand Geyser, Upper Geyser Basin of Yellowstone * Grand Rounds National Scenic Byway, a parkway system in Minneapolis, Minnesota, United States * Le Grand, California, census-designated place * Grand Staircase, a place in the US. Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Grand'' (Erin McKeown album), 2003 * ''Grand'' (Matt and Kim album), 2009 * ''Grand'' (magazine), a lifestyle magazine related to related to grandparents * ''Grand'' (TV series), American sitcom, 1990 * Grand piano, musical instrument * Grand Production, Serbian record label company * The Grand Tour, a new British automobile show ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epaminondas (game)
Epaminondas is a strategy board game invented by Robert Abbott in 1975. The game is named after the Theban general Epaminondas, known for the use of phalanx strategy in combat. The concept of the phalanx is integral to the game. Epaminondas was originally introduced in Sid Sackson's ''A Gamut of Games'' as '' Crossings''. While the original version used an 8×8 checkerboard, the current game uses a 12×14 board and different rules for capture. When published, it claimed to be one of the first modern games to acknowledge the name of its inventor in its rules. Phalanx In the game, a ''phalanx'' is a horizontal, vertical, or diagonal line of two or more stones of the same color, with no empty spaces or enemy stones between them. A stone may belong to more than one phalanx, depending on the direction considered. Rules Moves White moves first; then turns alternate. * A player can move a single piece one space in any direction (the same as a king in chess Chess is a board game ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkish Draughts
Turkish draughts (Turkish: Dama)(Armenian: շաշկի)(Arabic: دامە)(Kurmanji: دامە) is a variant of draughts (checkers) played in Turkey, Greece, Egypt, Kuwait, Lebanon, Syria, Jordan and several other locations around the Mediterranean Sea and Middle East. Rules On an 8×8 board, 16 ' are lined up on each side, in two rows. The back rows are vacant. A traditional Turkish draughts is mono-coloured. White moves first. Men move orthogonally forwards or sideways one square, capturing by means of a jump; they cannot move or capture backwards or diagonally. When a man reaches the back row, it promotes to a ''king''. Kings can move any number of empty squares orthogonally forwards, backwards or sideways. A king captures by jumping over a single piece any number of empty squares away, landing on any open square beyond the captured piece along a straight line. If a jump is available it must be taken. If there is more than one way to jump, the one capturing the most number of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.png)