|
Cholinergics
Cholinergic agents are compounds which mimic the action of acetylcholine and/or butyrylcholine. In general, the word "choline" describes the various quaternary ammonium salts containing the ''N'',''N'',''N''-trimethylethanolammonium cation. Found in most animal tissues, choline is a primary component of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine and functions with inositol as a basic constituent of lecithin. Choline also prevents fat deposits in the liver and facilitates the movement of fats into cells. The parasympathetic nervous system, which uses acetylcholine almost exclusively to send its messages, is said to be almost entirely cholinergic. Neuromuscular junctions, preganglionic neurons of the sympathetic nervous system, the basal forebrain, and brain stem complexes are also cholinergic, as are the receptor for the merocrine sweat glands. In neuroscience and related fields, the term cholinergic is used in these related contexts: * A substance (or ligand) is cholinergic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
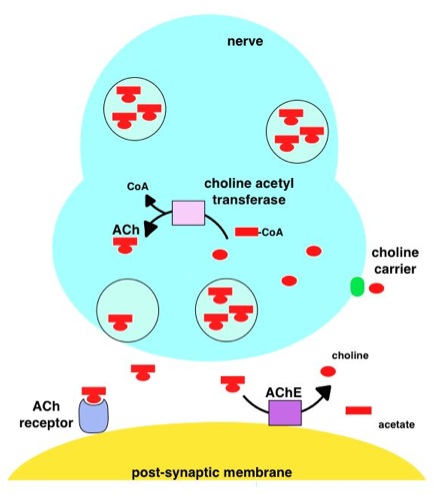
Acetylcholinesterase
Acetylcholinesterase (HGNC symbol ACHE; EC 3.1.1.7; systematic name acetylcholine acetylhydrolase), also known as AChE, AChase or acetylhydrolase, is the primary cholinesterase in the body. It is an enzyme Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ... that catalysis, catalyzes the breakdown of acetylcholine and some other choline esters that function as neurotransmitters: : acetylcholine + H2O = choline + acetate It is found at mainly neuromuscular junctions and in chemical synapses of the cholinergic type, where its activity serves to terminate neurotransmission, synaptic transmission. It belongs to the carboxylesterase family of enzymes. It is the primary target of inhibition by organophosphorus compounds such as nerve agents and pesticides. Enzyme structure and mechani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasympathomimetic Drug
A parasympathomimetic drug, sometimes called a cholinomimetic drug or cholinergic receptor stimulating agent, is a substance that stimulates the parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS). These chemicals are also called cholinergic drugs because acetylcholine (ACh) is the neurotransmitter used by the PSNS. Chemicals in this family can act either directly by stimulating the nicotinic or muscarinic receptors (thus mimicking acetylcholine), or indirectly by inhibiting cholinesterase, promoting acetylcholine release, or other mechanisms. Common uses of parasympathomimetics include glaucoma, sjögren syndrome and underactive bladder. Some chemical weapons such as sarin or VX, non-lethal riot control agents such as tear gas, and insecticides such as diazinon fall into this category. Structure activity relationships for parasympathomimetic drugs For a cholinergic agent, the following criteria describe the structure activity relationship: # Ing's Rule of 5: there should be no more than five ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetylcholine
Acetylcholine (ACh) is an organic chemical that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals (including humans) as a neurotransmitter. Its name is derived from its chemical structure: it is an ester of acetic acid and choline. Parts in the body that use or are affected by acetylcholine are referred to as cholinergic. Substances that increase or decrease the overall activity of the cholinergic system are called cholinergics and anticholinergics, respectively. Acetylcholine is the neurotransmitter used at the neuromuscular junction—in other words, it is the chemical that motor neurons of the nervous system release in order to activate muscles. This property means that drugs that affect cholinergic systems can have very dangerous effects ranging from paralysis to convulsions. Acetylcholine is also a neurotransmitter in the autonomic nervous system, both as an internal transmitter for the sympathetic nervous system and as the final product released by the parasymp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butyrylcholine Receptor
Butyrylcholine is a choline-based ester that can function as a neurotransmitter. It is similar to acetylcholine, with activation of some of the same receptors as acetylcholine. Butyrylcholine is a synthetic compound and does not occur in the body naturally. It is used as a clinical laboratory tool to distinguish between the cholinesterases; acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase Butyrylcholinesterase ( HGNC symbol BCHE; EC 3.1.1.8), also known as BChE, BuChE, BuChase, pseudocholinesterase, or plasma (cholin)esterase, is a nonspecific cholinesterase enzyme that hydrolyses many different choline-based esters. In humans, it ... preferentially lyse acetylcholine and butyrylcholine, respectively. It is also known as pseudocholinesterase. References Quaternary ammonium compounds Butyrate esters {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choline
Choline is an essential nutrient for humans and many other animals. Choline occurs as a cation that forms various salts (X− in the depicted formula is an undefined counteranion). Humans are capable of some ''de novo synthesis'' of choline but require additional choline in the diet to maintain health. Dietary requirements can be met by choline per se or in the form of choline phospholipids, such as phosphatidylcholine. Choline is not formally classified as a vitamin despite being an essential nutrient with an amino acid–like structure and metabolism. In most animals, choline phospholipids are necessary components in cell membranes, in the membranes of cell organelles, and in very low-density lipoproteins. Choline is required to produce acetylcholine – a neurotransmitter – and ''S''-adenosylmethionine (SAM), a universal methyl donor. Upon methylation SAM is transformed into homocysteine. Symptomatic choline deficiency causes non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and muscle dama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butyrylcholine
Butyrylcholine is a choline-based ester that can function as a neurotransmitter. It is similar to acetylcholine, with activation of some of the same receptors as acetylcholine. Butyrylcholine is a synthetic compound and does not occur in the body naturally. It is used as a clinical laboratory tool to distinguish between the cholinesterases; acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase Butyrylcholinesterase ( HGNC symbol BCHE; EC 3.1.1.8), also known as BChE, BuChE, BuChase, pseudocholinesterase, or plasma (cholin)esterase, is a nonspecific cholinesterase enzyme that hydrolyses many different choline-based esters. In humans, it ... preferentially lyse acetylcholine and butyrylcholine, respectively. It is also known as pseudocholinesterase. References Quaternary ammonium compounds Butyrate esters {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetylcholine
Acetylcholine (ACh) is an organic chemical that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals (including humans) as a neurotransmitter. Its name is derived from its chemical structure: it is an ester of acetic acid and choline. Parts in the body that use or are affected by acetylcholine are referred to as cholinergic. Substances that increase or decrease the overall activity of the cholinergic system are called cholinergics and anticholinergics, respectively. Acetylcholine is the neurotransmitter used at the neuromuscular junction—in other words, it is the chemical that motor neurons of the nervous system release in order to activate muscles. This property means that drugs that affect cholinergic systems can have very dangerous effects ranging from paralysis to convulsions. Acetylcholine is also a neurotransmitter in the autonomic nervous system, both as an internal transmitter for the sympathetic nervous system and as the final product released by the parasymp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lecithin
Lecithin (, from the Greek ''lekithos'' "yolk") is a generic term to designate any group of yellow-brownish fatty substances occurring in animal and plant tissues which are amphiphilic – they attract both water and fatty substances (and so are both hydrophilic and lipophilic), and are used for smoothing food textures, emulsifying, homogenizing liquid mixtures, and repelling sticking materials. Lecithins are mixtures of glycerophospholipids including phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylinositol, phosphatidylserine, and phosphatidic acid. Lecithin was first isolated in 1845 by the French chemist and pharmacist Théodore Gobley. In 1850, he named the phosphatidylcholine ''lécithine''. Gobley originally isolated lecithin from egg yolk – λέκιθος ''(lekithos)'' is "egg yolk" in Ancient Greek – and established the complete chemical formula of phosphatidylcholine in 1874; in between, he demonstrated the presence of lecithin in a variety of biologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rivastigmine
Rivastigmine (sold under the trade name Exelon among others) is a cholinesterase inhibitor used for the treatment of mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease. The drug can be administered orally or via a transdermal patch; the latter form reduces the prevalence of side effects, which typically include nausea and vomiting. The drug is eliminated through the urine, and appears to have relatively few drug-drug interactions. It was patented in 1985 and came into medical use in 1997. Medical uses Rivastigmine capsules, liquid solution and patches are used for the treatment of mild to moderate dementia of the Alzheimer's type. Rivastigmine has demonstrated treatment effects on the cognitive (thinking and memory), functional (activities of daily living) and behavioural problems commonly associated with Alzheimer's. Efficacy In people with either type of dementia, rivastigmine has been shown to provide meaningful symptomatic effects that may allow patients to remain independent and ‘b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donepezil
Donepezil, sold under the brand name Aricept among others, is a medication used to treat dementia of the Alzheimer's disease, Alzheimer's type. It appears to result in a small benefit in mental function and ability to function. Use, however, has not been shown to change the progression of the disease. Treatment should be stopped if no benefit is seen. It is taken Oral administration, by mouth or via a transdermal patch. Common side effects include nausea, trouble sleeping, aggression, diarrhea, feeling tired, and muscle cramps. Serious side effects may include arrhythmia, abnormal heart rhythms, urinary incontinence, and seizures. Donepezil is a central nervous system, centrally acting reversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitor and structurally unrelated to other anticholinesterase, anticholinesterase agents. Donepezil was approved for medical use in the United States in 1996. It is available as a generic medication. In 2020, it was the 112th most commonly prescribed medicatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs) also often called cholinesterase inhibitors, inhibit the enzyme acetylcholinesterase from breaking down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine into choline and acetate, thereby increasing both the level and duration of action of acetylcholine in the central nervous system, autonomic ganglia and neuromuscular junctions, which are rich in acetylcholine receptors. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are one of two types of cholinesterase inhibitors; the other being butyryl-cholinesterase inhibitors. Acetylcholinesterase is the primary member of the cholinesterase enzyme family. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are classified as reversible, irreversible, or quasi-irreversible (also called pseudo-irreversible). Mechanism of action Organophosphates Organophosphates like TEPP and sarin inhibit cholinesterases, enzymes that hydrolyze the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. The active centre of cholinesterases feature two important sites, namely th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyoscine Hydrobromide
Scopolamine, also known as hyoscine, or Devil's Breath, is a natural or synthetically produced tropane alkaloid and anticholinergic drug that is formally used as a medication for treating motion sickness and postoperative nausea and vomiting. It is also sometimes used before surgery to decrease saliva. When used by injection, effects begin after about 20 minutes and last for up to 8 hours. It may also be used orally and as a transdermal patch since it has been long known to have transdermal bioavailability Scopolamine is in the antimuscarinic family of drugs and works by blocking some of the effects of acetylcholine within the nervous system. Scopolamine was first written about in 1881 and started to be used for anesthesia around 1900. Scopolamine is also the main active component produced by certain plants of the nightshade family, which historically have been used as psychoactive drugs (known as ''deliriants'') due to their antimuscarinic-induced hallucinogenic ef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |